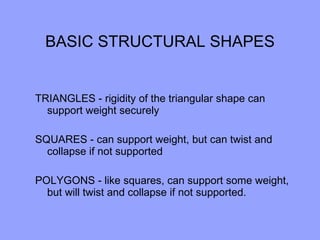
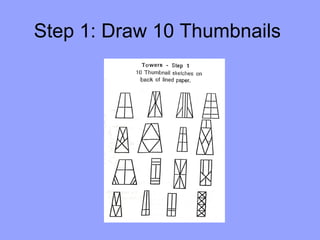
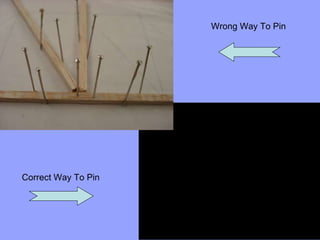
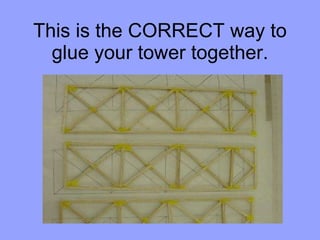
Students will build a balsa wood tower and test how much weight it can hold. They will learn basic engineering principles like tension, compression, and structural shapes. They will be provided 4800mm of balsa wood and design their tower within this limitation. Towers will be tested and awards given to the tower that holds the most weight and has the highest efficiency rating based on materials used and weight held.