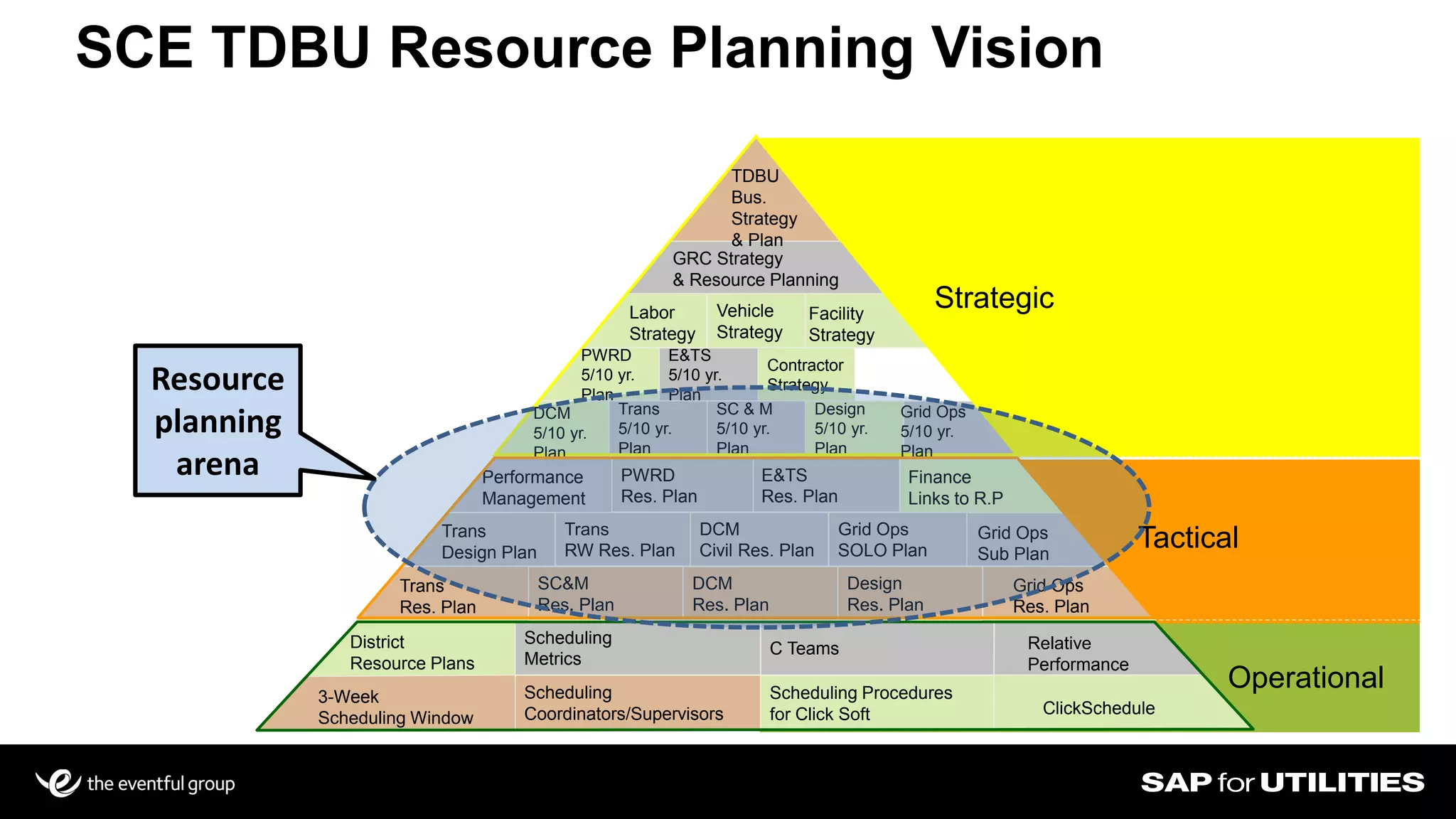
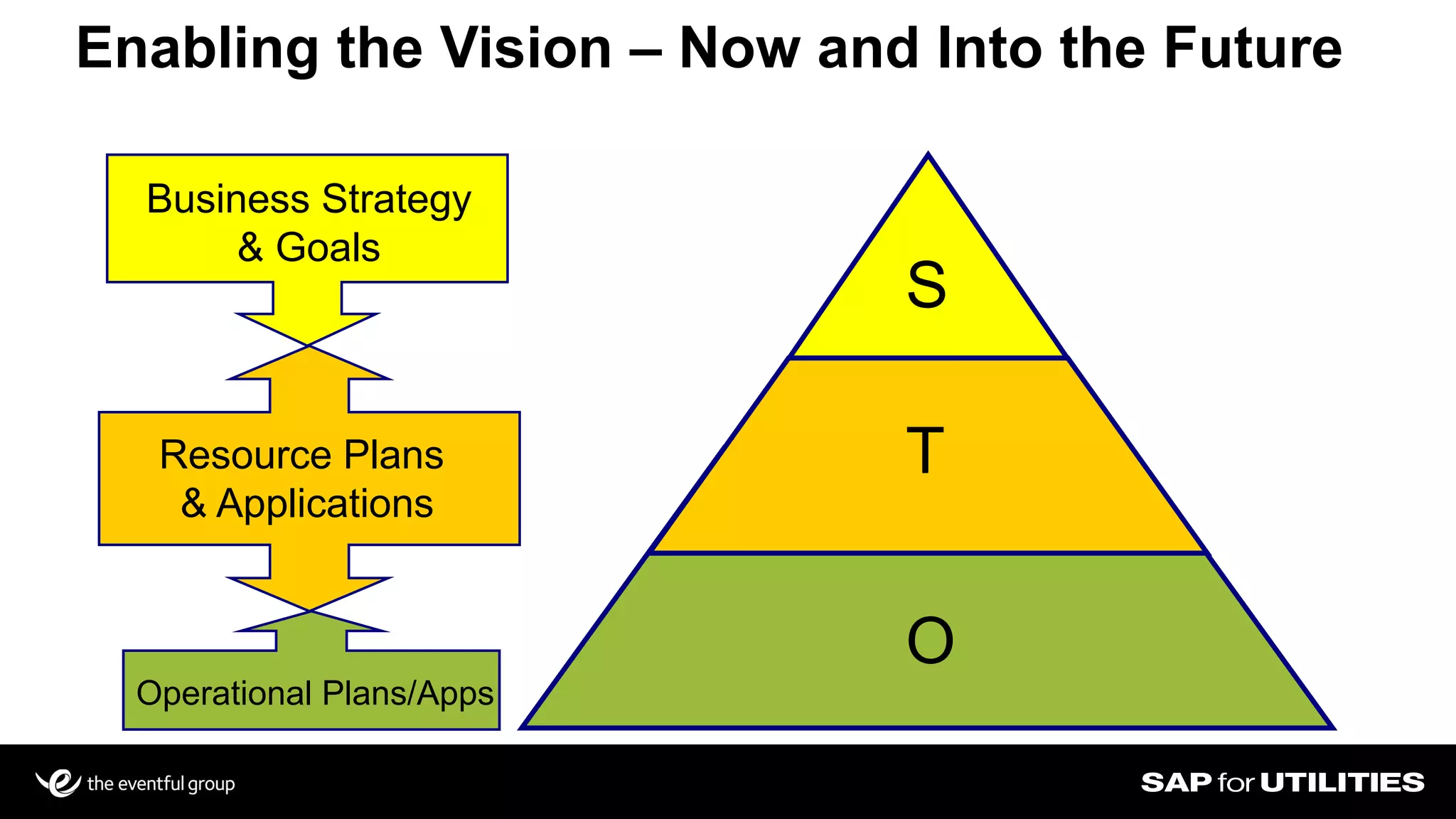
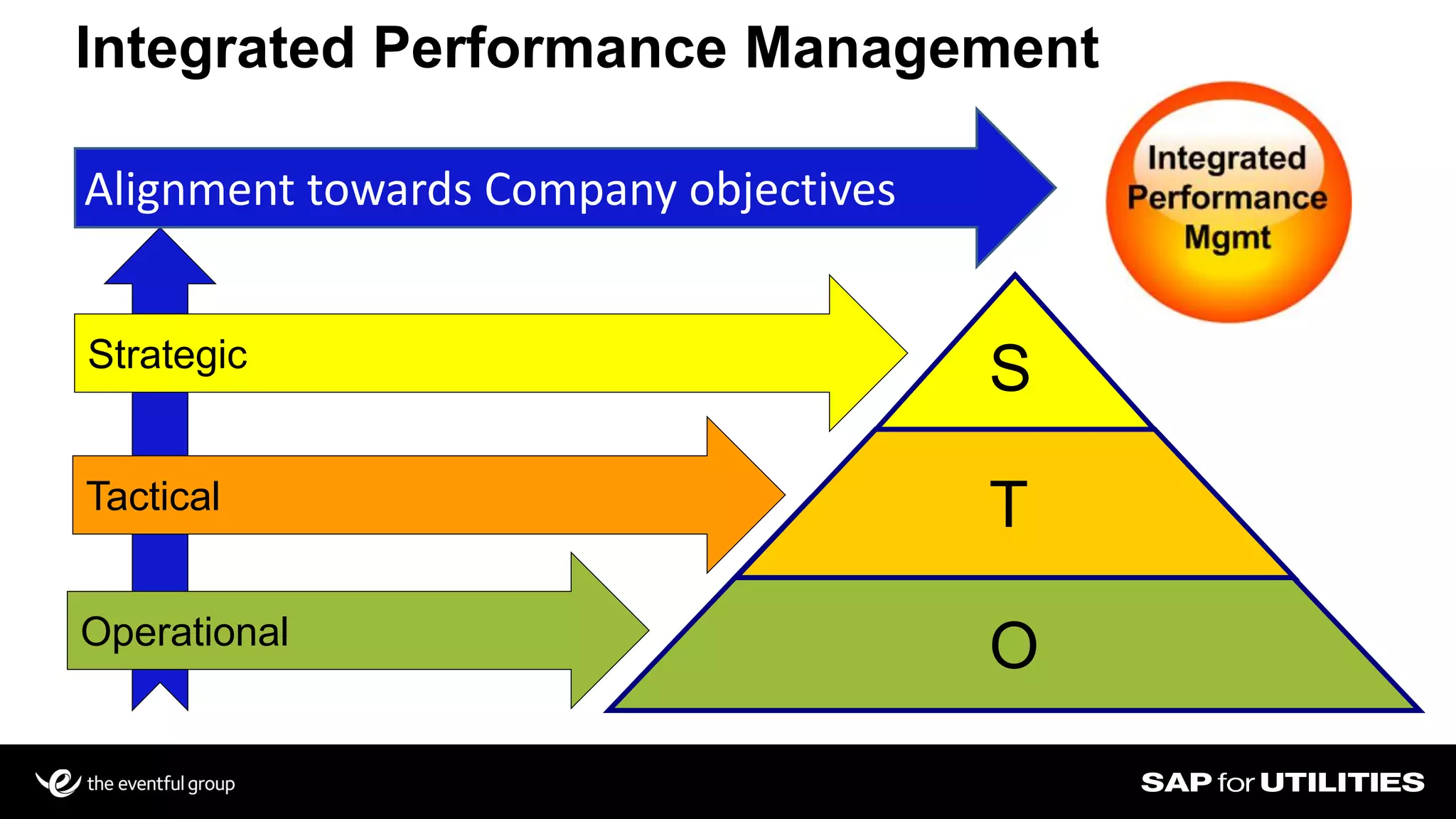
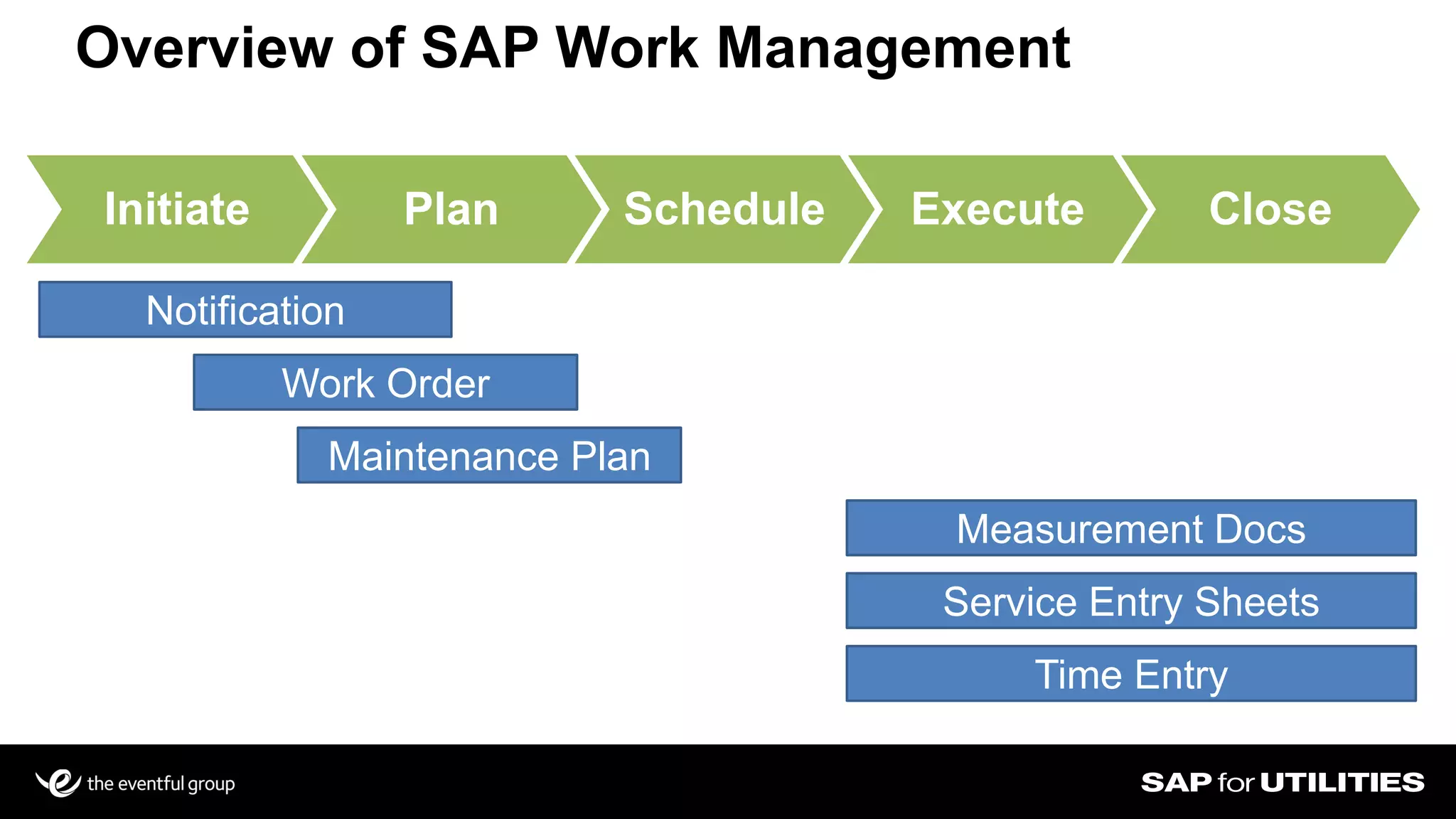
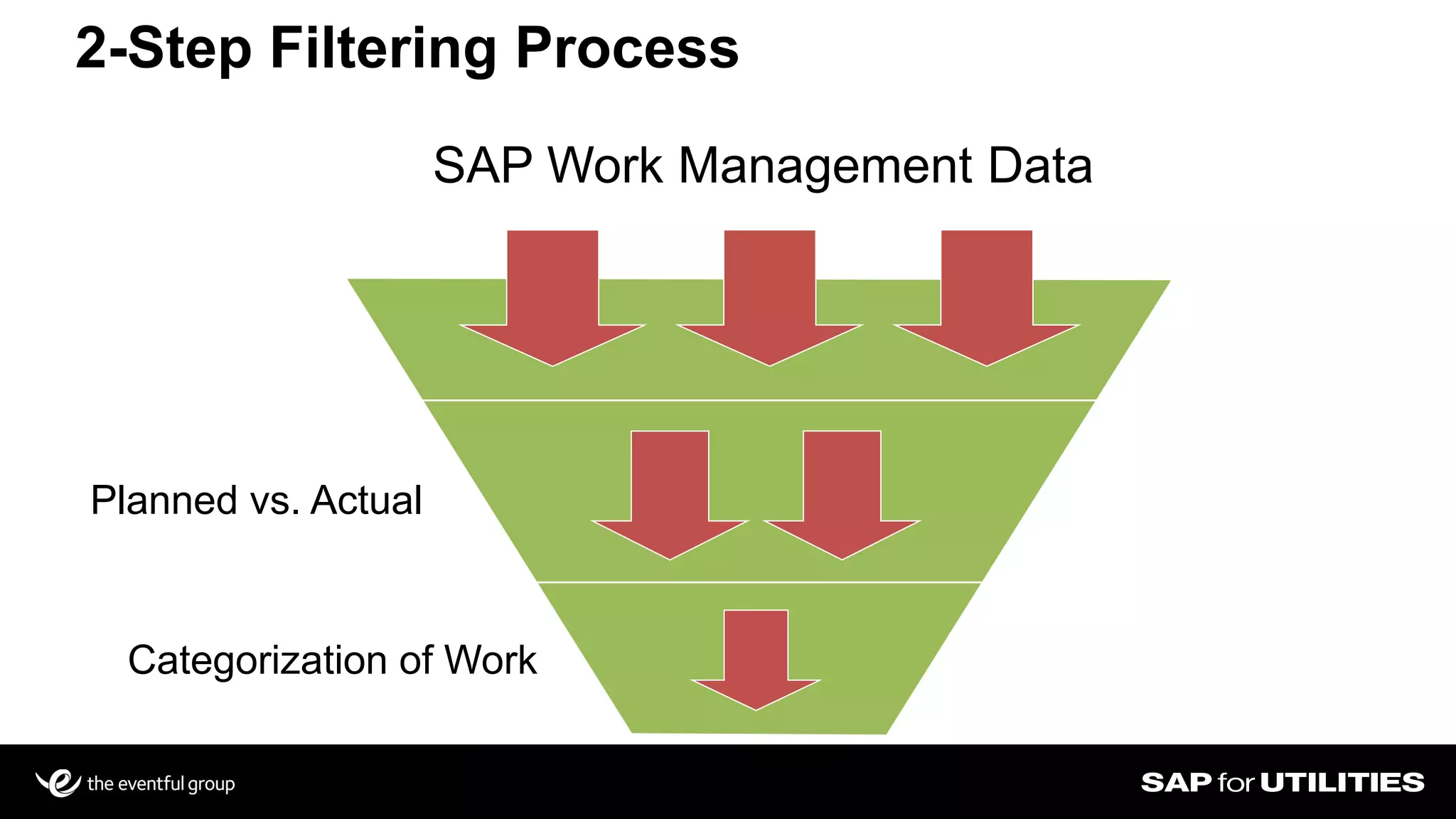
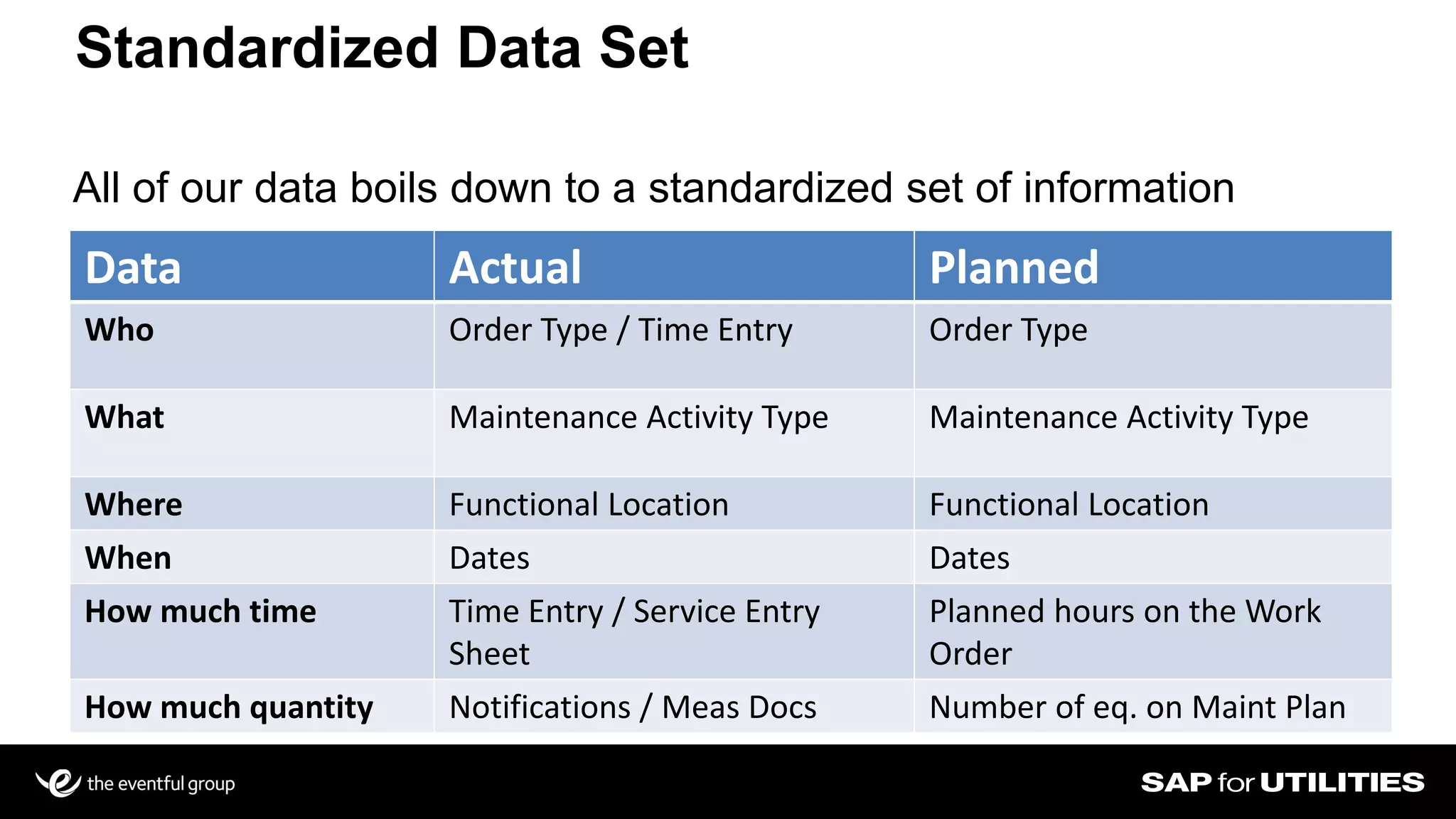
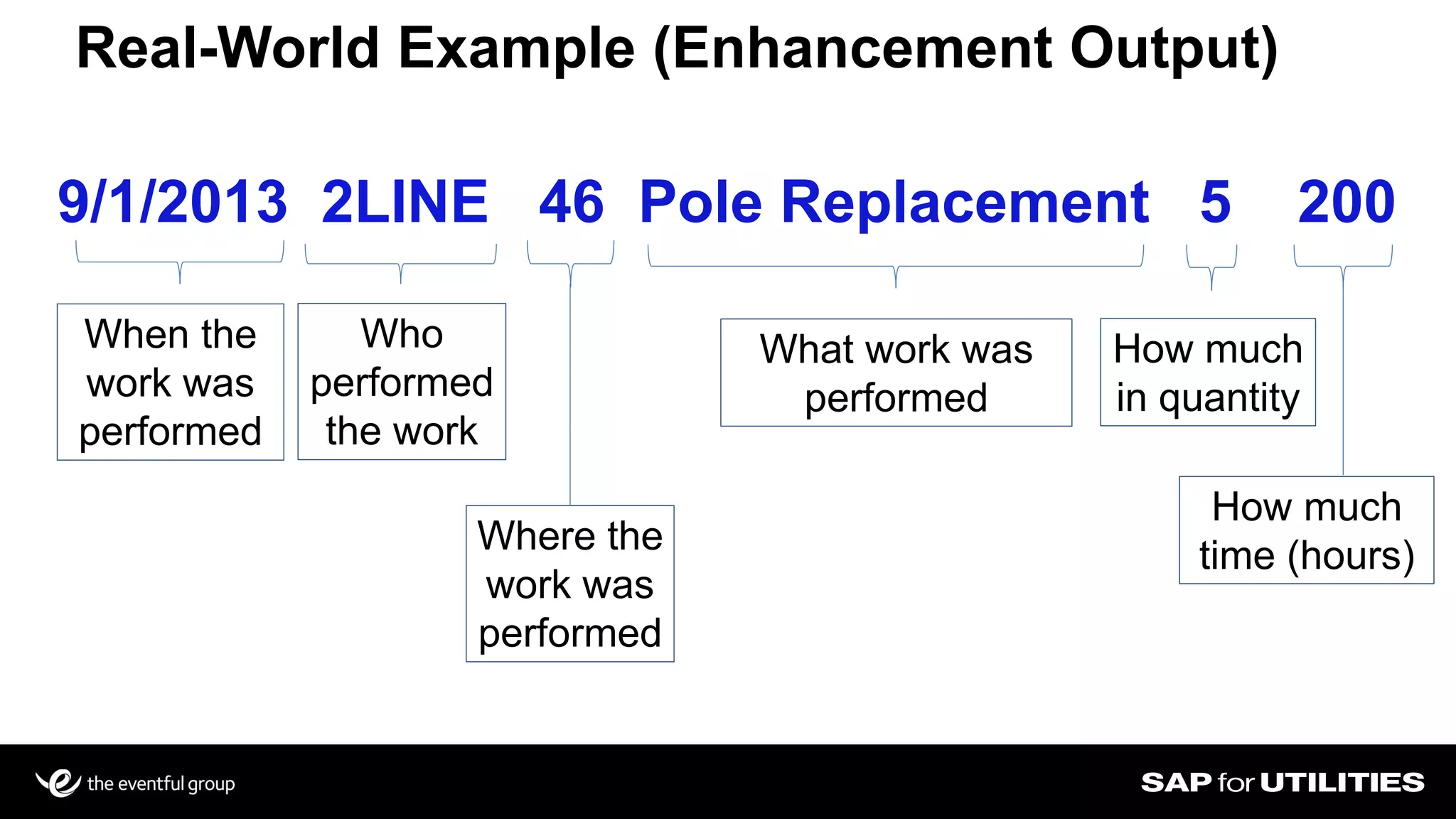
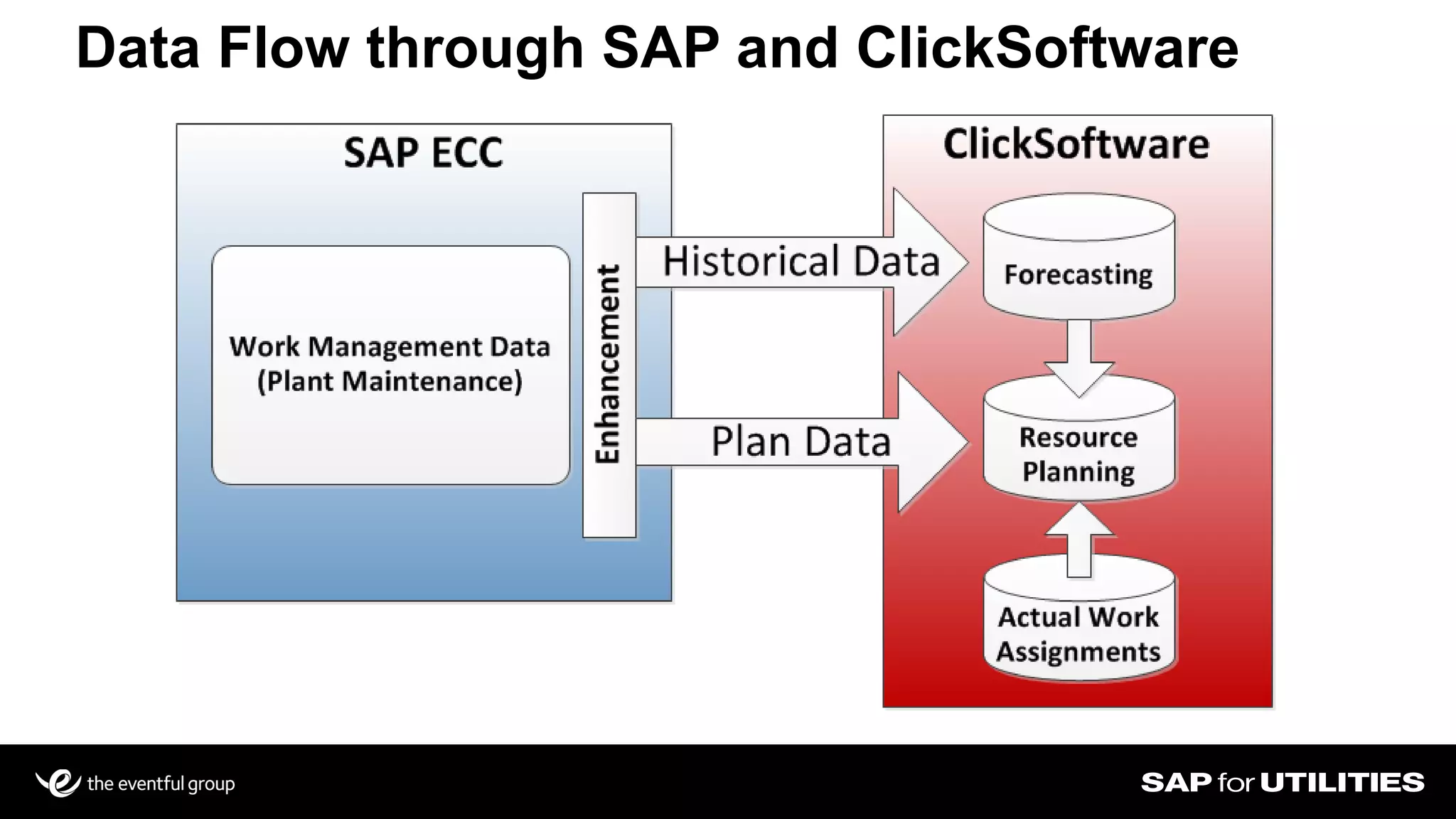
Southern California Edison analyzed its SAP work management data to optimize workforce planning and performance. It filtered data into standardized sets for actual vs planned work, categorizing by who, what, where, when and quantities. This provided visibility into workloads, resources, and performance against strategic goals. Challenges included developing flexible solutions and strong user involvement. Benefits included reduced processing time, integrated planning views, and increased precision to better manage costs, throughput and infrastructure goals. Key lessons included establishing business sponsorship, involving users, and driving change through plans rather than individuals.