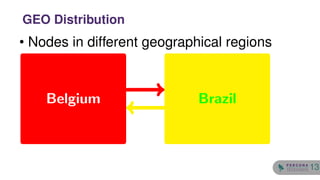
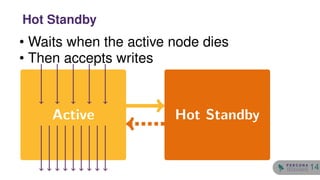
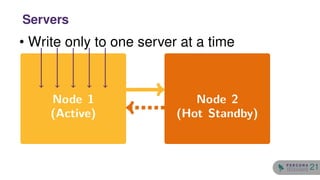
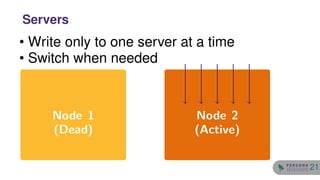
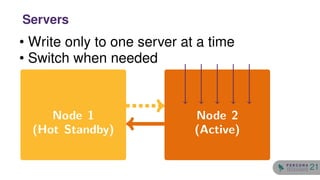
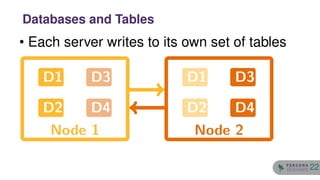
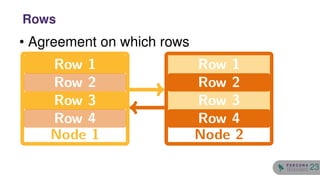
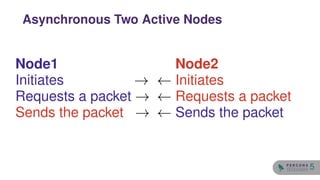
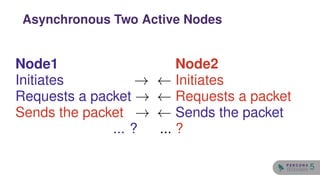
The document discusses the safety and setup of asynchronous active-active configurations in MySQL, outlining potential issues that can arise with two active nodes, such as duplicate key errors and synchronization penalties. It emphasizes the importance of writing to one server at a time to avoid conflicts and suggests methods for structuring databases and tables to maintain system integrity. Additionally, techniques for achieving geographical distribution and optimal performance in active-active setups are highlighted.





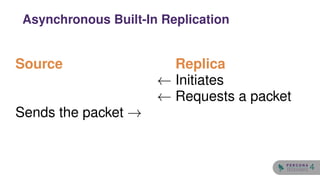

















![• Multiple machines for better scalability
Node 1 Node 2
[Read] Scale
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynctd2020-201017125746/85/How-Safe-is-Asynchronous-Master-Master-Setup-27-320.jpg)