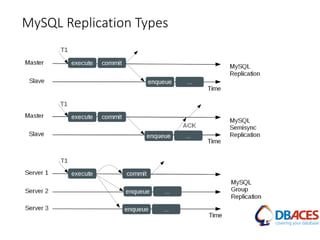
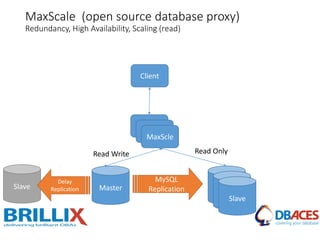
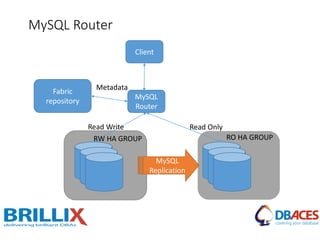
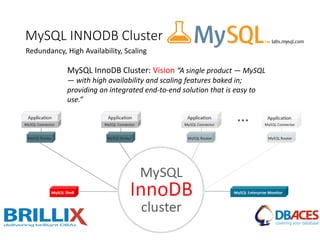
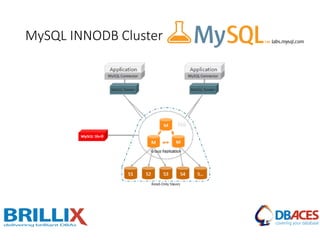
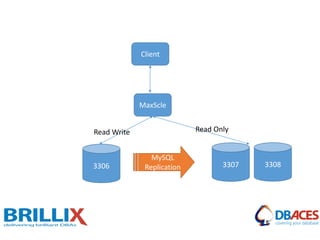
This document discusses various MySQL high availability solutions and best practices. It begins with an introduction to the presenter and their background and experience. Then it discusses the problems of redundancy, scaling, and high availability that these solutions aim to address. Several specific solutions are covered in detail, including Galera Cluster, master-slave replication, MySQL Cluster, Group Replication, MaxScale, MySQL Router, and MySQL InnoDB Cluster. Key features of each are summarized. The document concludes with an invitation for questions.













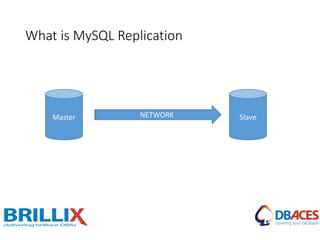
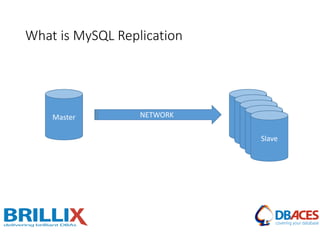

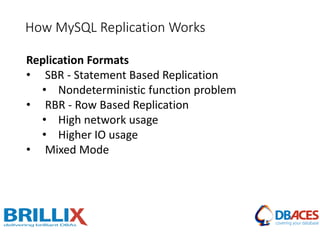




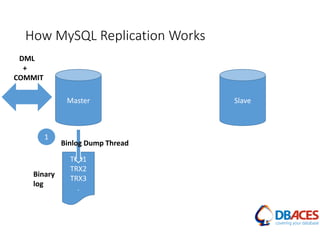
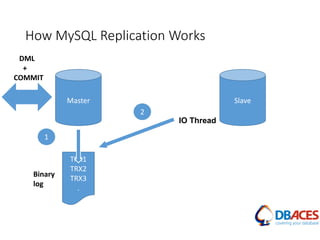








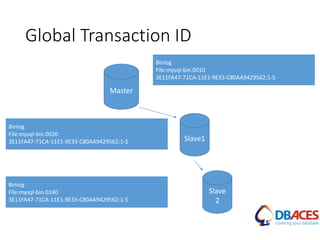

![Replication Setup
master.my.cnf
[mysqld]
...
server-id=1
report-host=blue
binlog-format=MIXED
log-bin
log-slave-updates=true
gtid-mode=on
enforce-gtid-consistency=true
master-info-repository=TABLE
relay-log-info-repository=TABLE
sync-master-info=1
binlog-checksum=CRC32
master-verify-checksum=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlha-161203083432/85/MySQL-highav-Availability-46-320.jpg)
![Replication Setup
slave.my.cnf
[mysqld]
...
server-id=2
report-host=white
binlog-format=MIXED
log-slave-updates=true
log-bin
gtid-mode=on
enforce-gtid-consistency=true
master-info-repository=TABLE
relay-log-info-repository=TABLE
sync-master-info=1
slave-parallel-workers=2
binlog-checksum=CRC32
master-verify-checksum=1
slave-sql-verify-checksum=1
binlog-rows-query-log_events=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlha-161203083432/85/MySQL-highav-Availability-47-320.jpg)