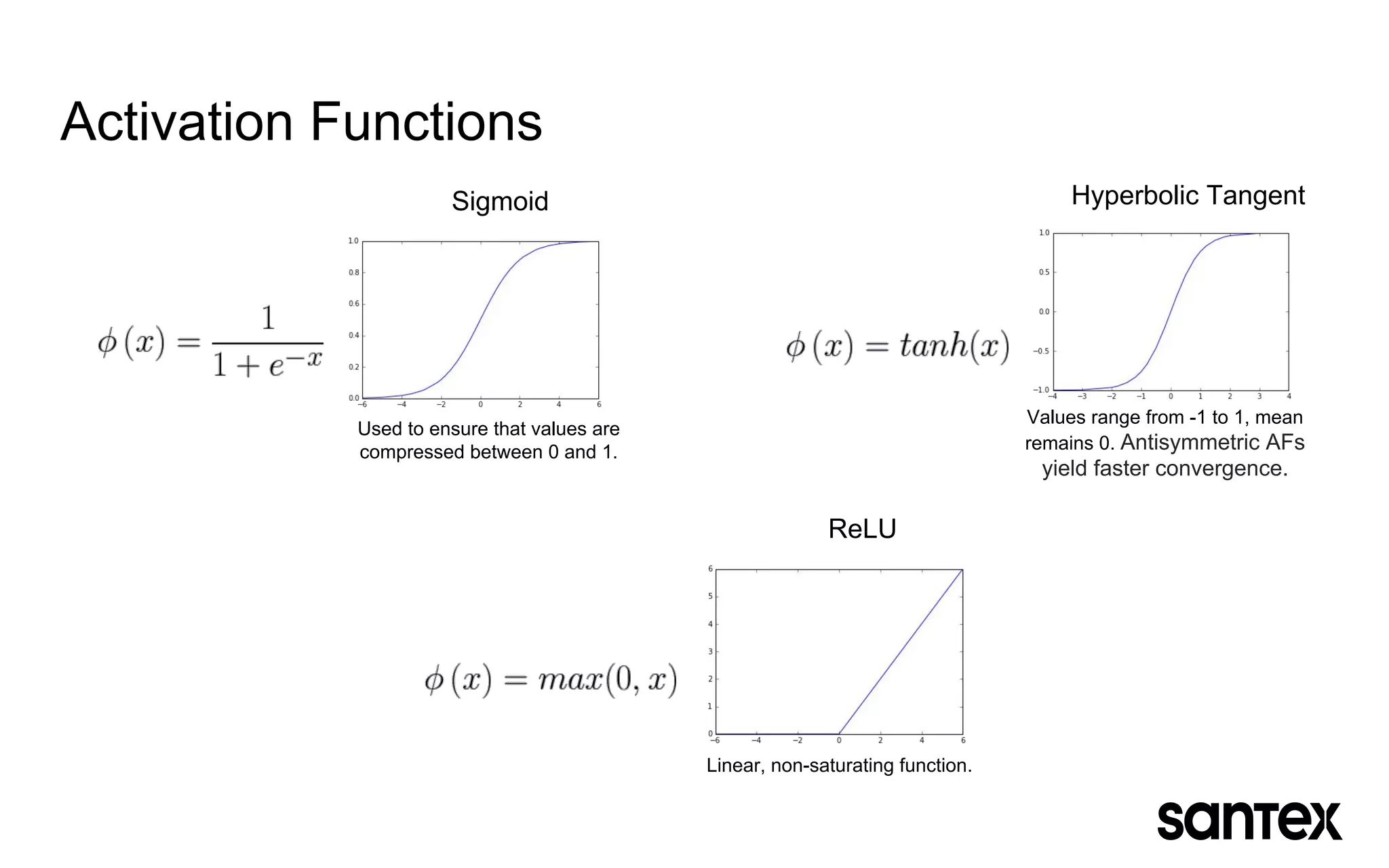
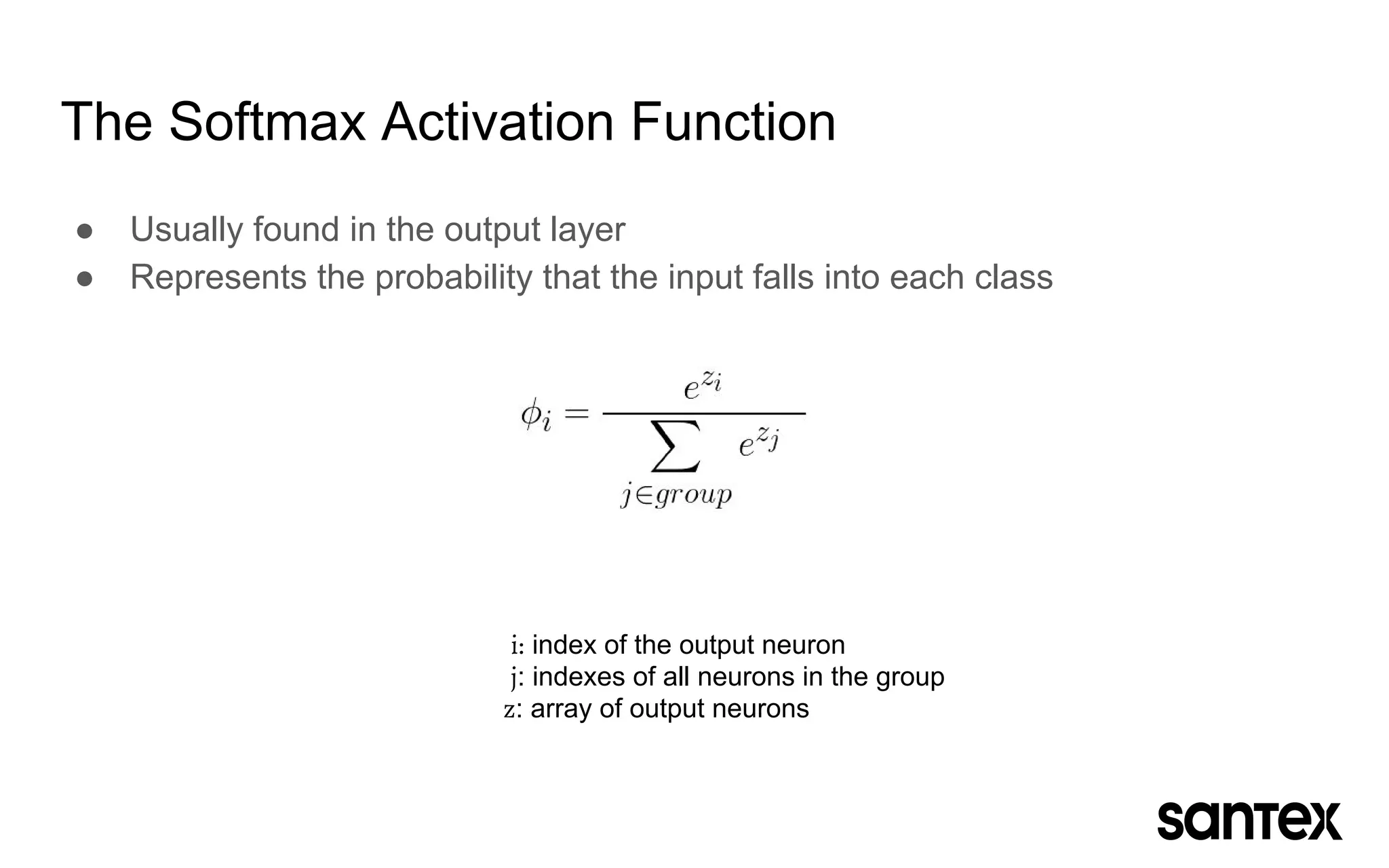
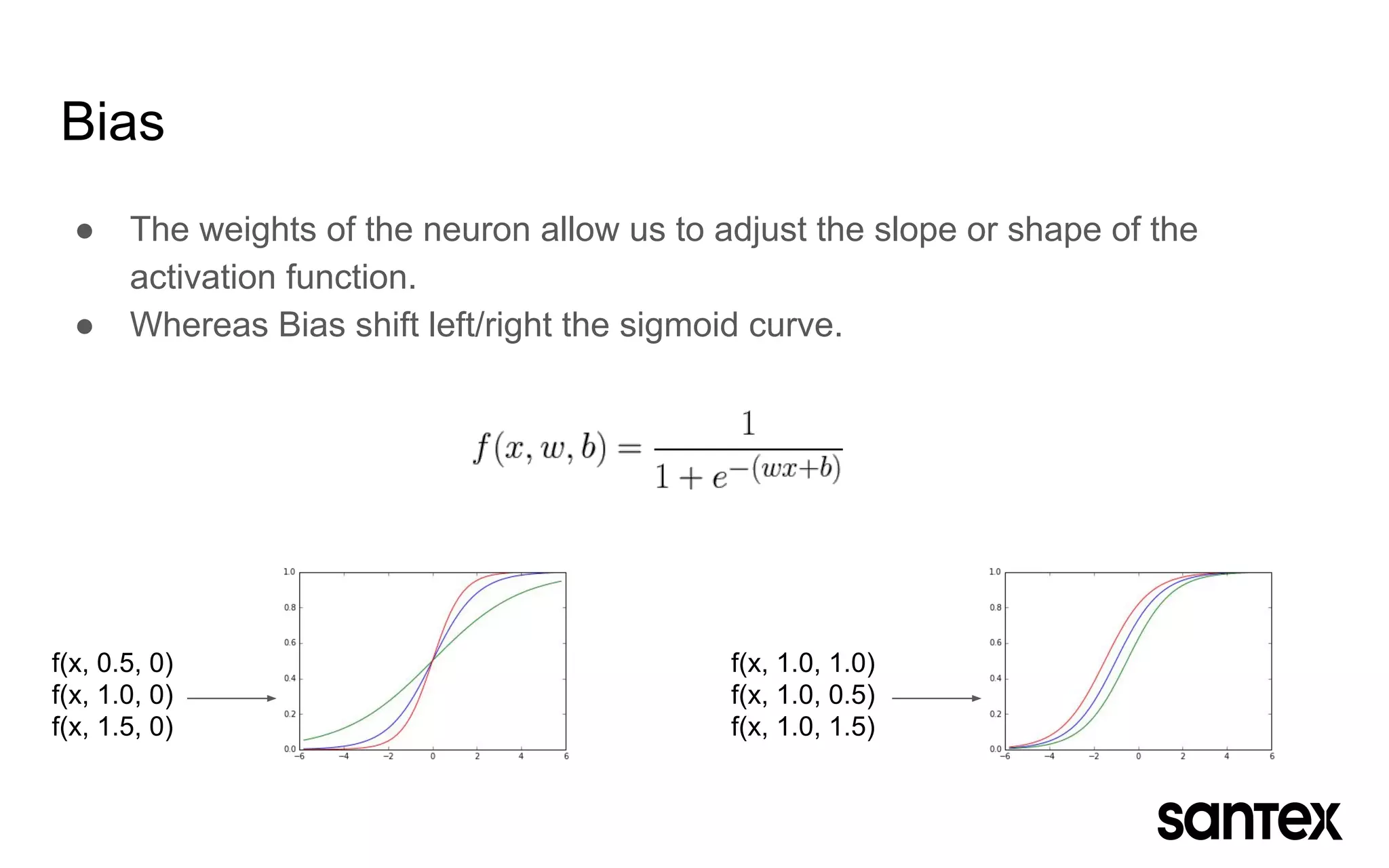
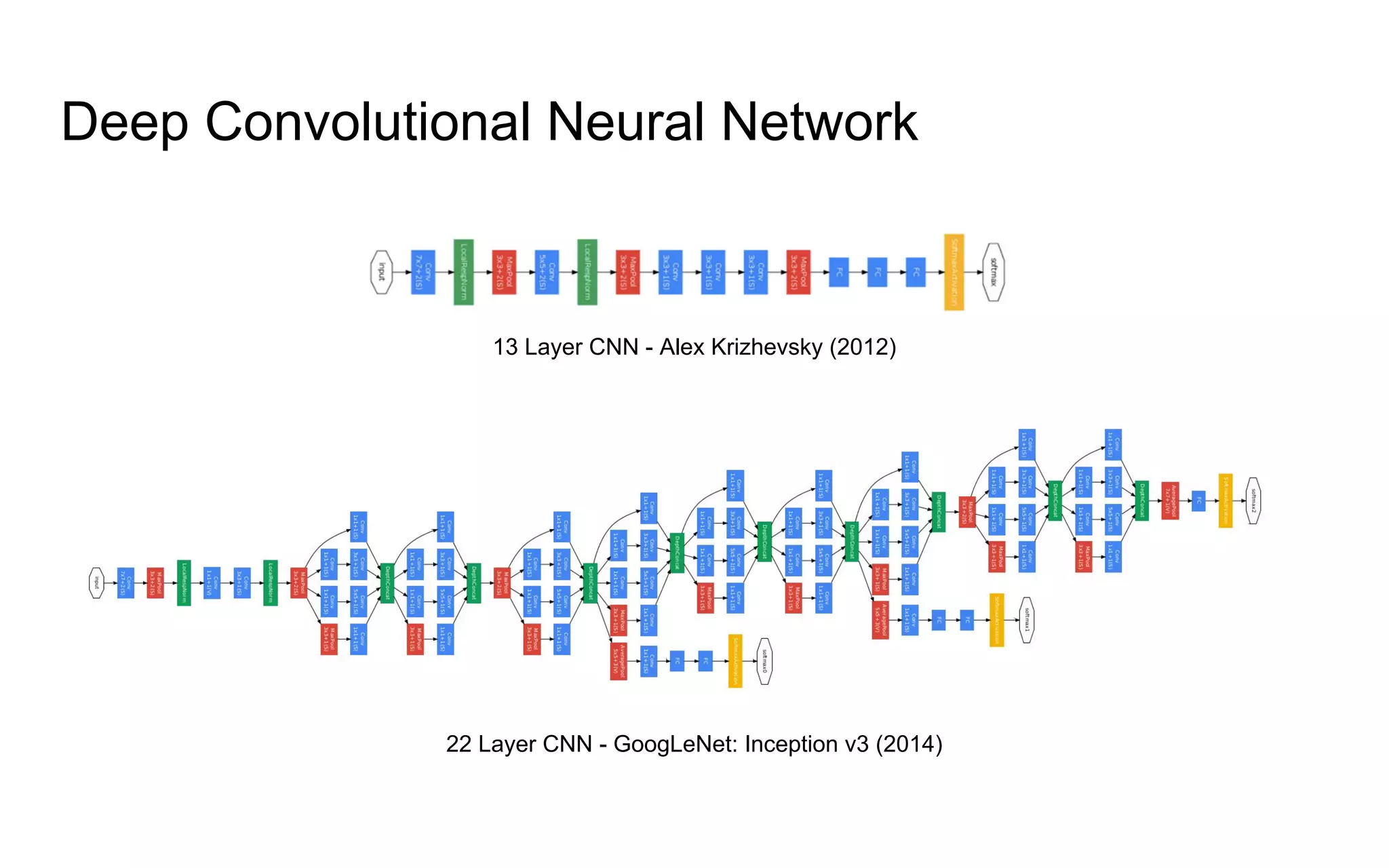
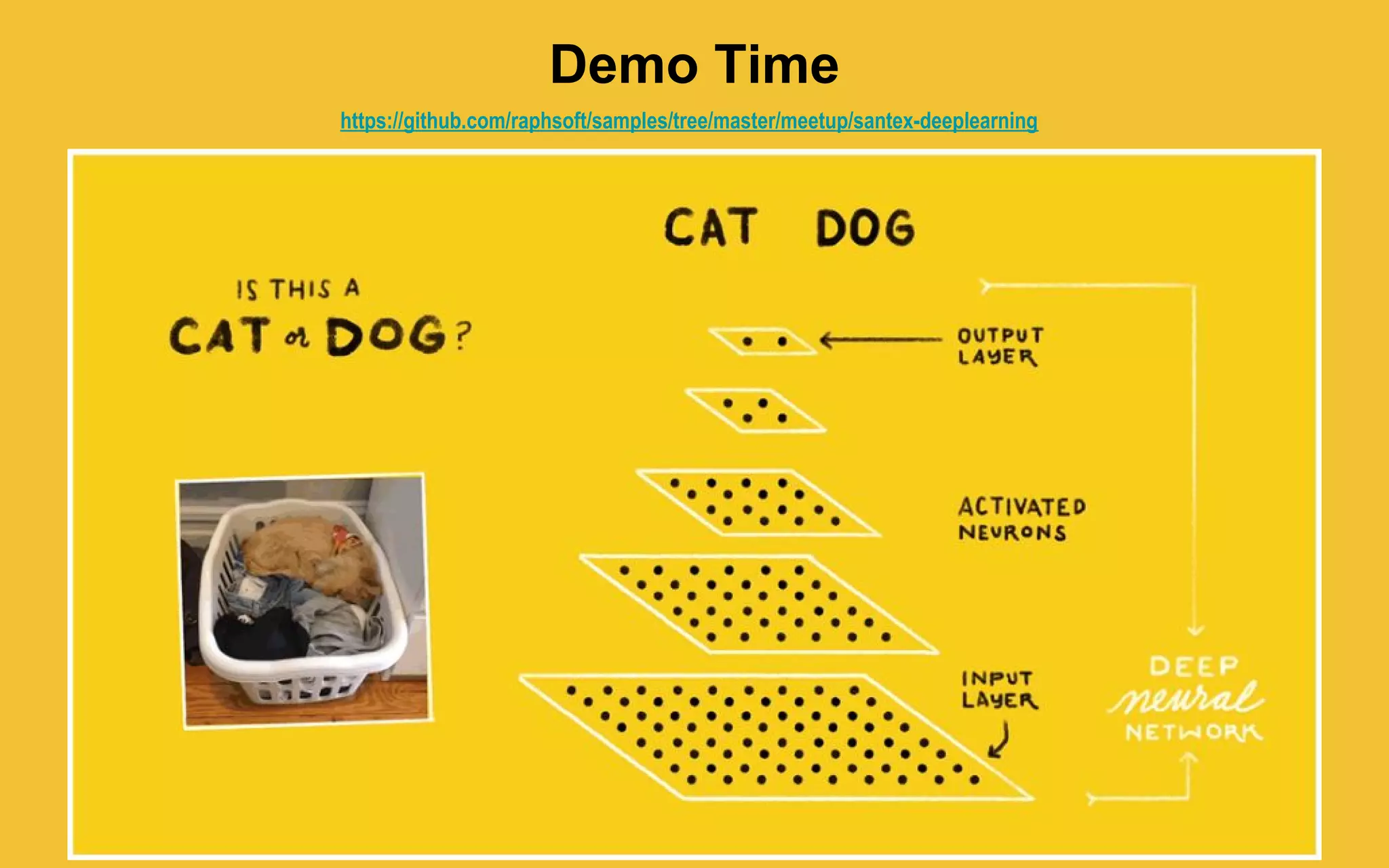
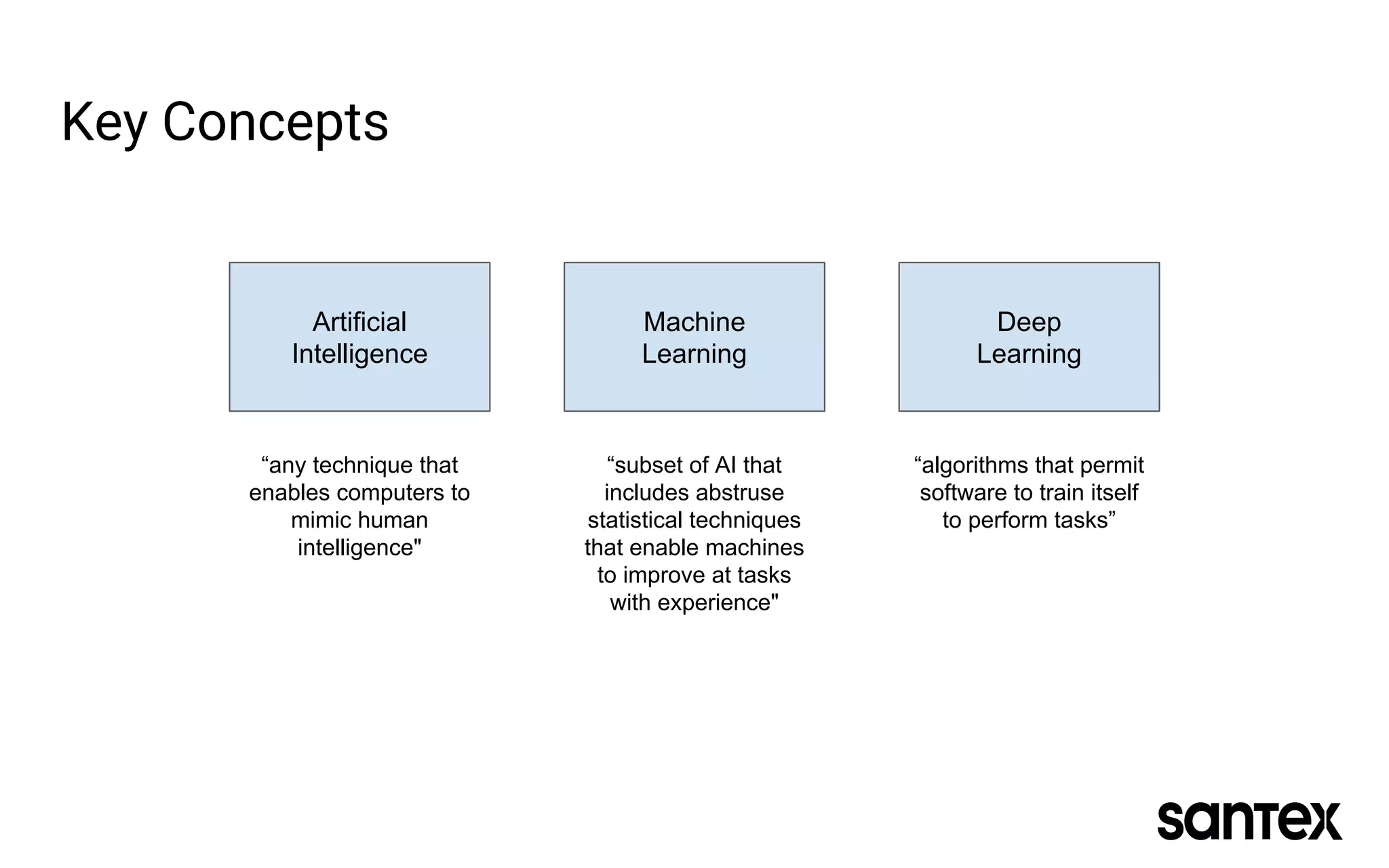
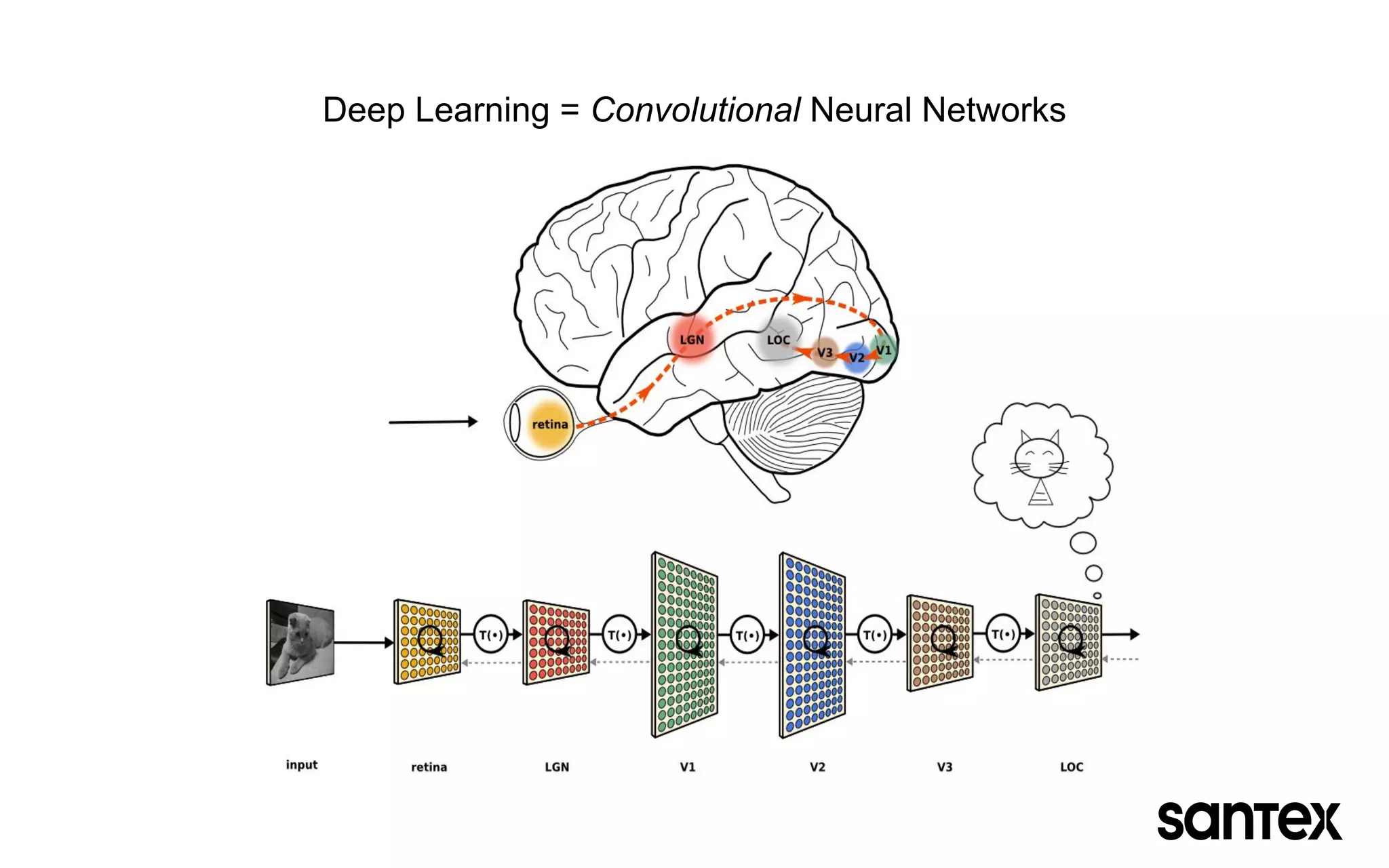
The document discusses how machine learning, and specifically deep learning using neural networks, is changing the world. It provides an overview of key concepts like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. It then discusses the history and basic concepts of neural networks like neurons, layers, activation functions, and optimization. Finally, it discusses applications of deep learning like computer vision, natural language processing, and more.





![Float Array
A Typical Neural Network
Input
Layer
Hidden Layers
(black box)
Output
Layer
[input pattern] [output pattern]
many different architectures define the
interaction between the input and the
output layer
Float Array
[ -0.025, 0.23, 0.44 ] [ 0.712, 0.471 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howmachinelearningischangingtheworld-170217040618/75/How-machine-learning-is-changing-the-world-9-2048.jpg)