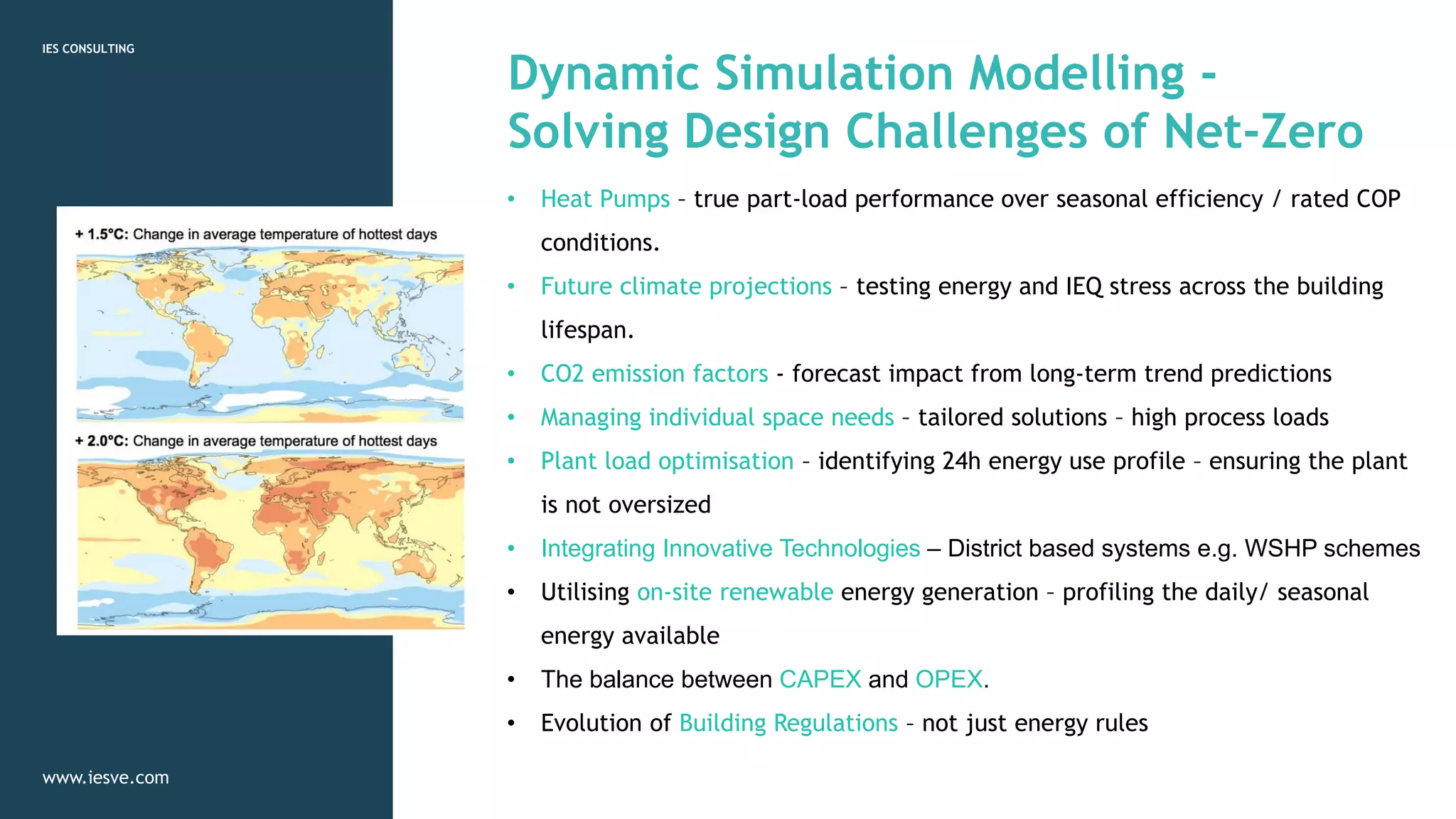
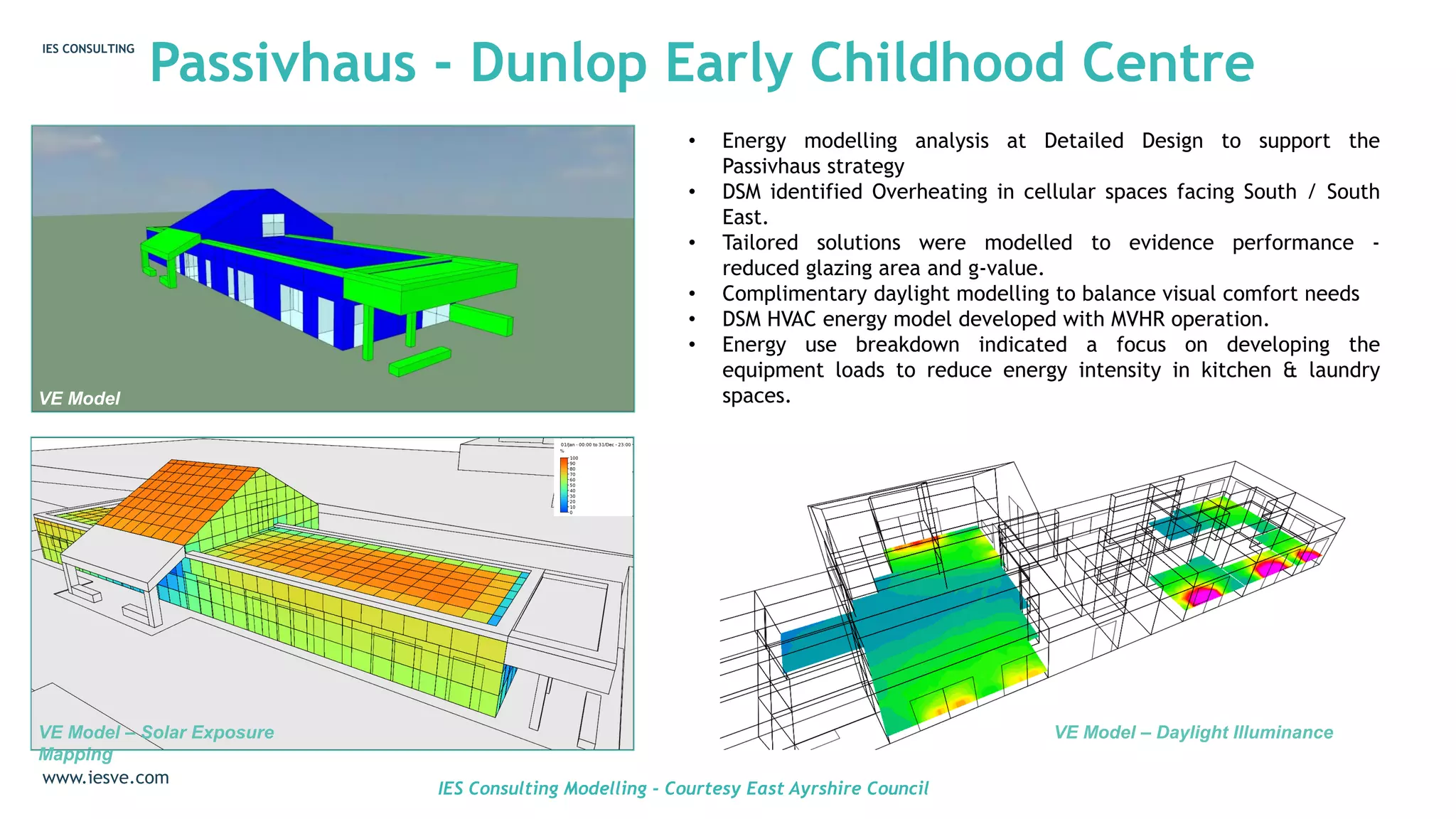
The webinar focused on the journey to net zero carbon ambitions for local authorities, highlighting the significant challenge of creating low energy solutions through dynamic simulation modelling (DSM). It emphasized supporting new and existing buildings by integrating energy modelling, passive design principles, and comprehensive stakeholder collaboration to meet operational energy targets. Case studies illustrated the application of DSM in projects like Passivhaus and Enerphit, showcasing how it aids in addressing energy demand and indoor environmental quality.