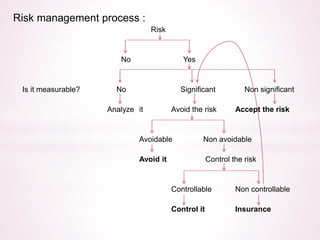
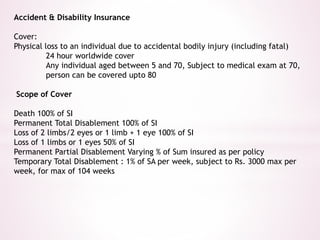
This document provides an overview of insurance planning and various insurance concepts. It discusses risk and risk management, the concept of insurance, principles of insurance including utmost good faith, insurable interest, and indemnity. It also covers types of insurance policies for life and general insurance, products, tax benefits, underwriting, and claims processes. Key terms related to insurance are defined throughout the document.