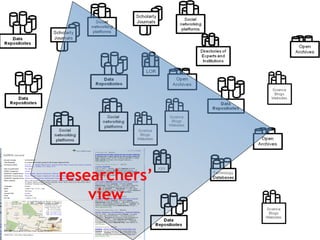
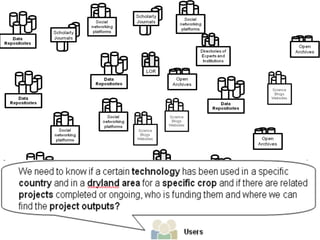
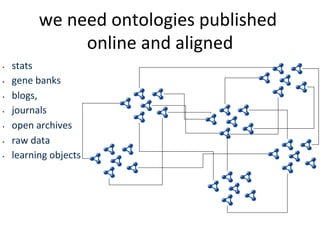
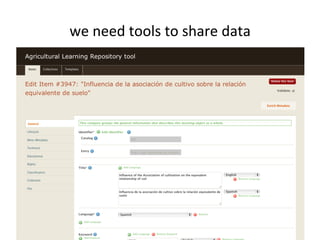
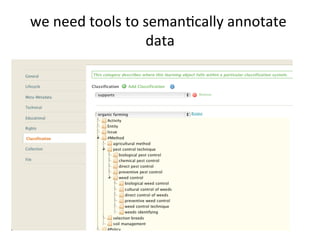
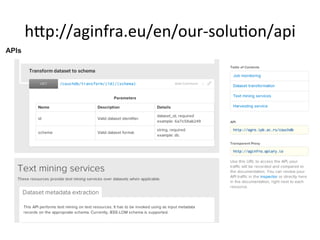
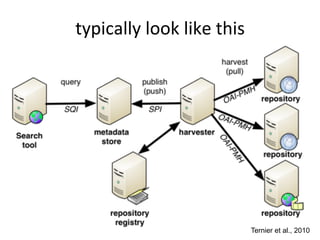
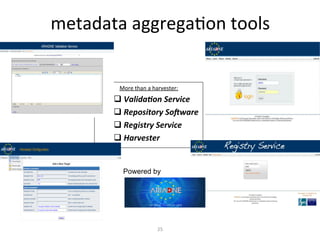
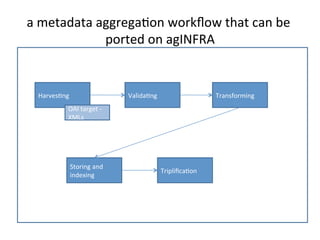
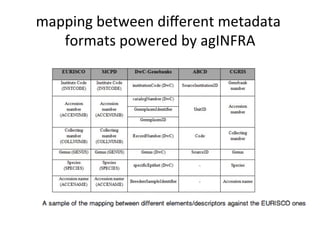
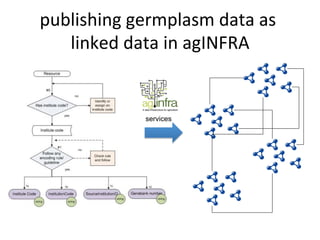
This document discusses how e-infrastructure can help link germplasm data. It describes the need for e-infrastructure to overcome issues like data silos and lack of interoperability. The agINFRA approach provides services like metadata aggregation, vocabulary publishing, and APIs that can transform and expose germplasm descriptions as linked data. This will help link germplasm databases and make the data more discoverable. Next steps include developing recommendations for publishing germplasm data and deploying transformers and APIs on the agINFRA platform.