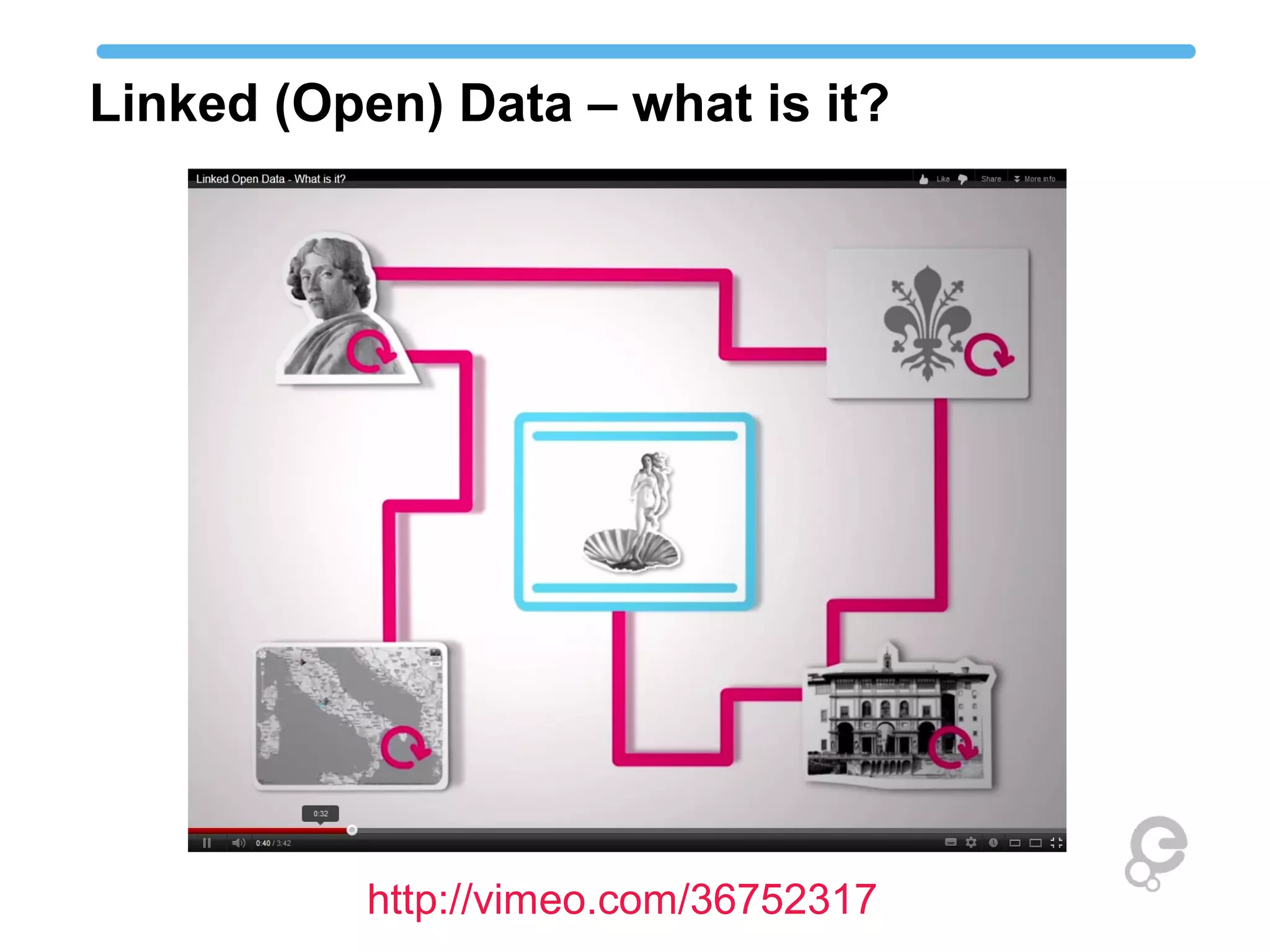
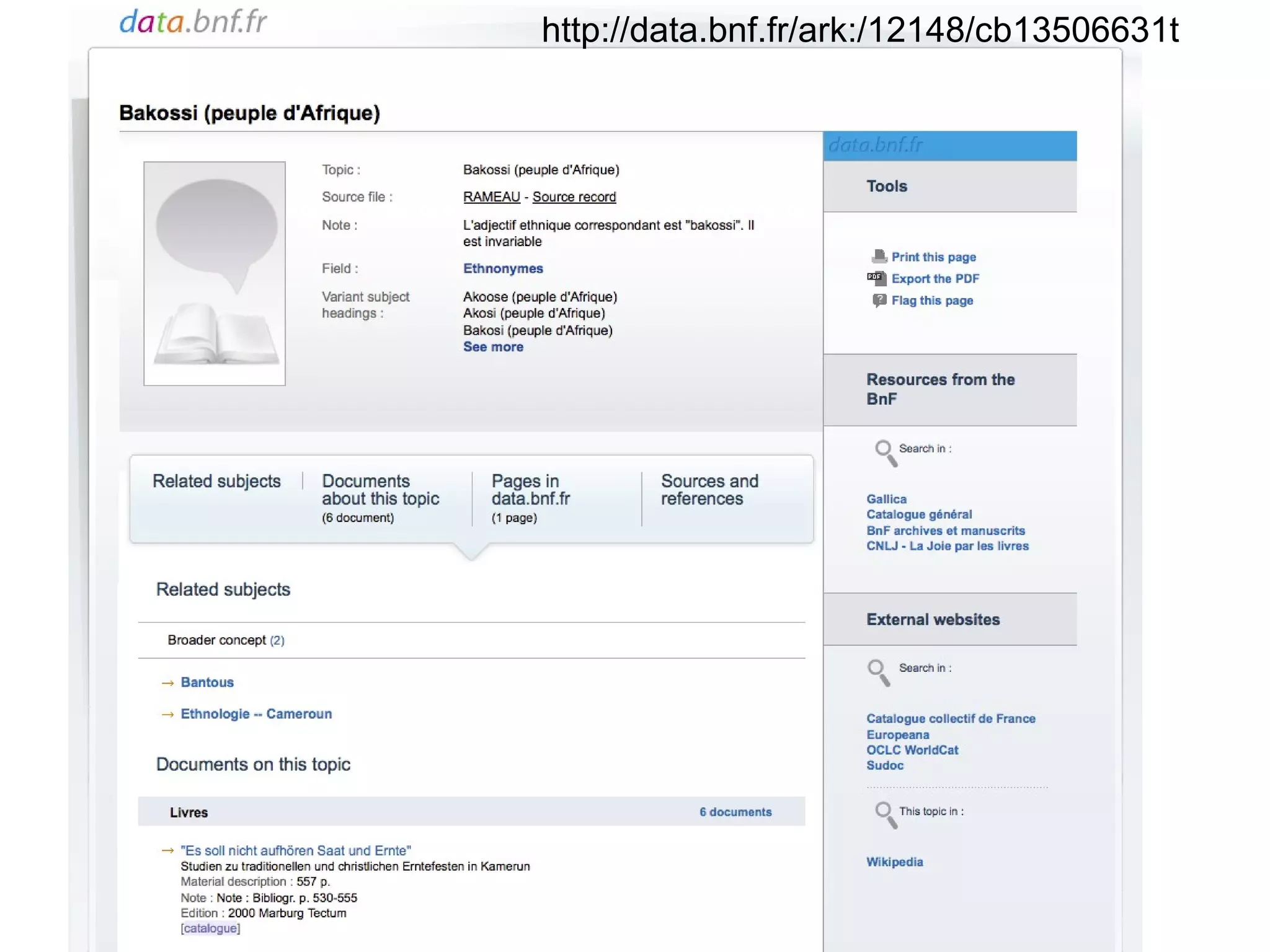
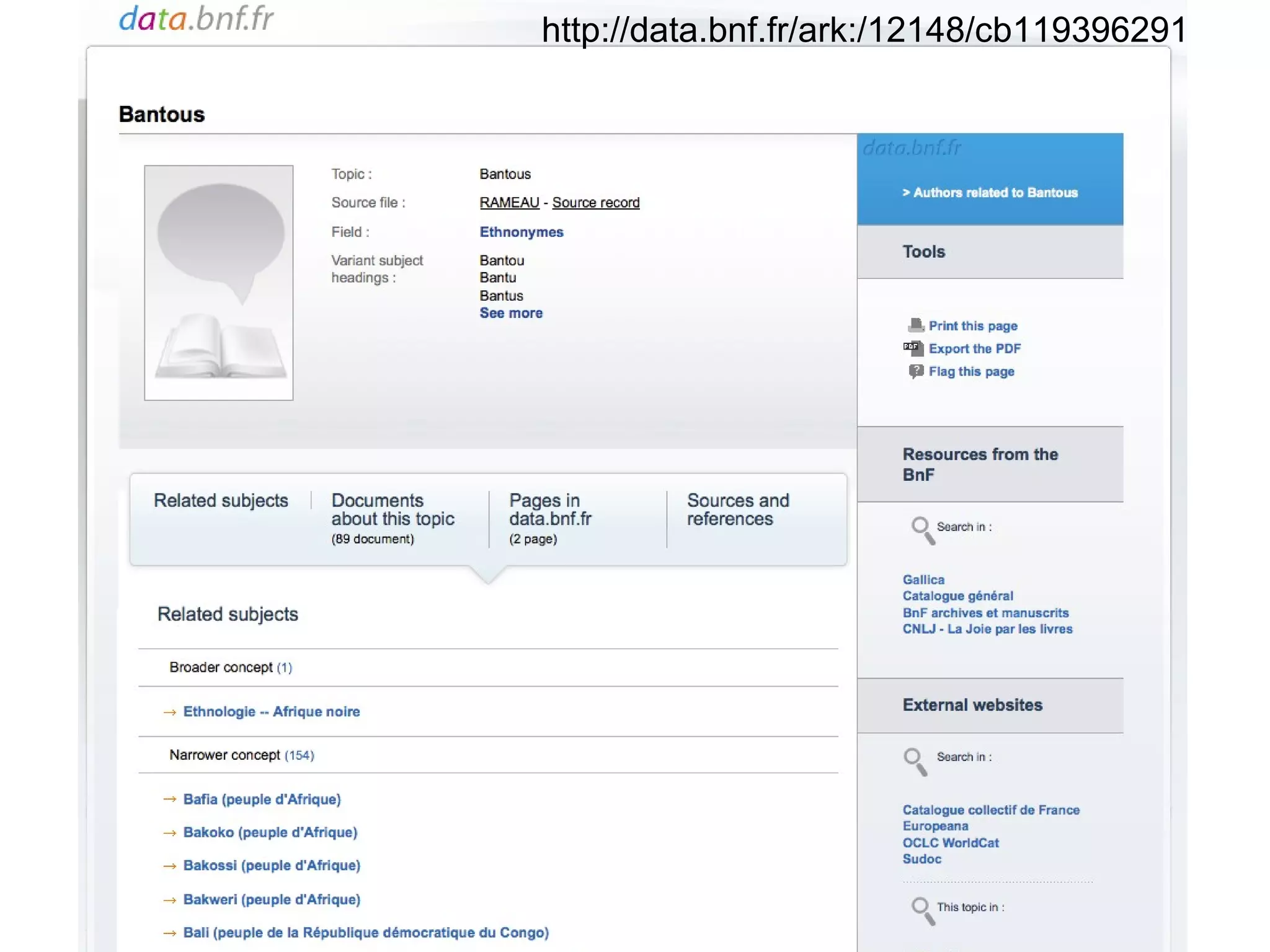
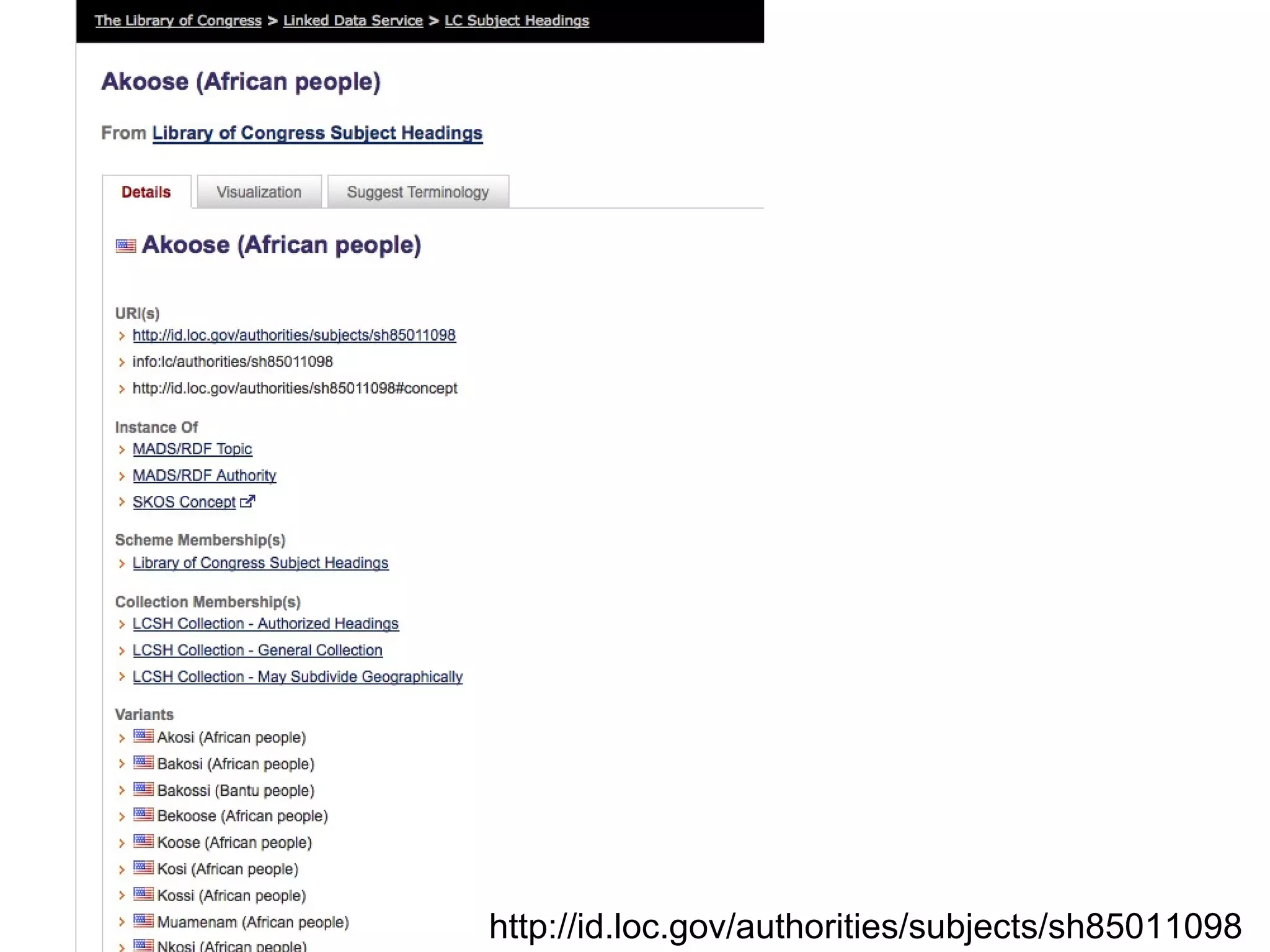
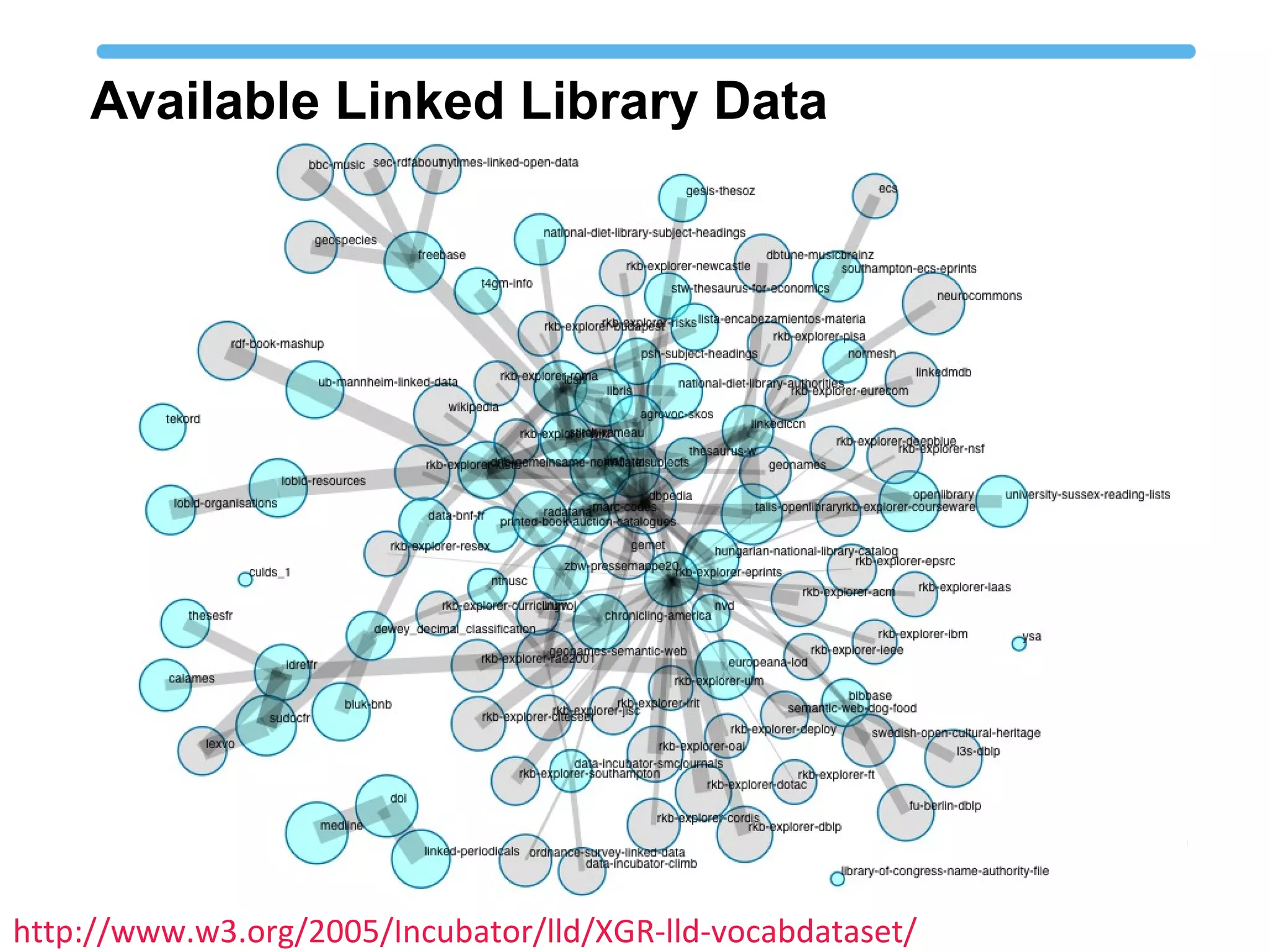
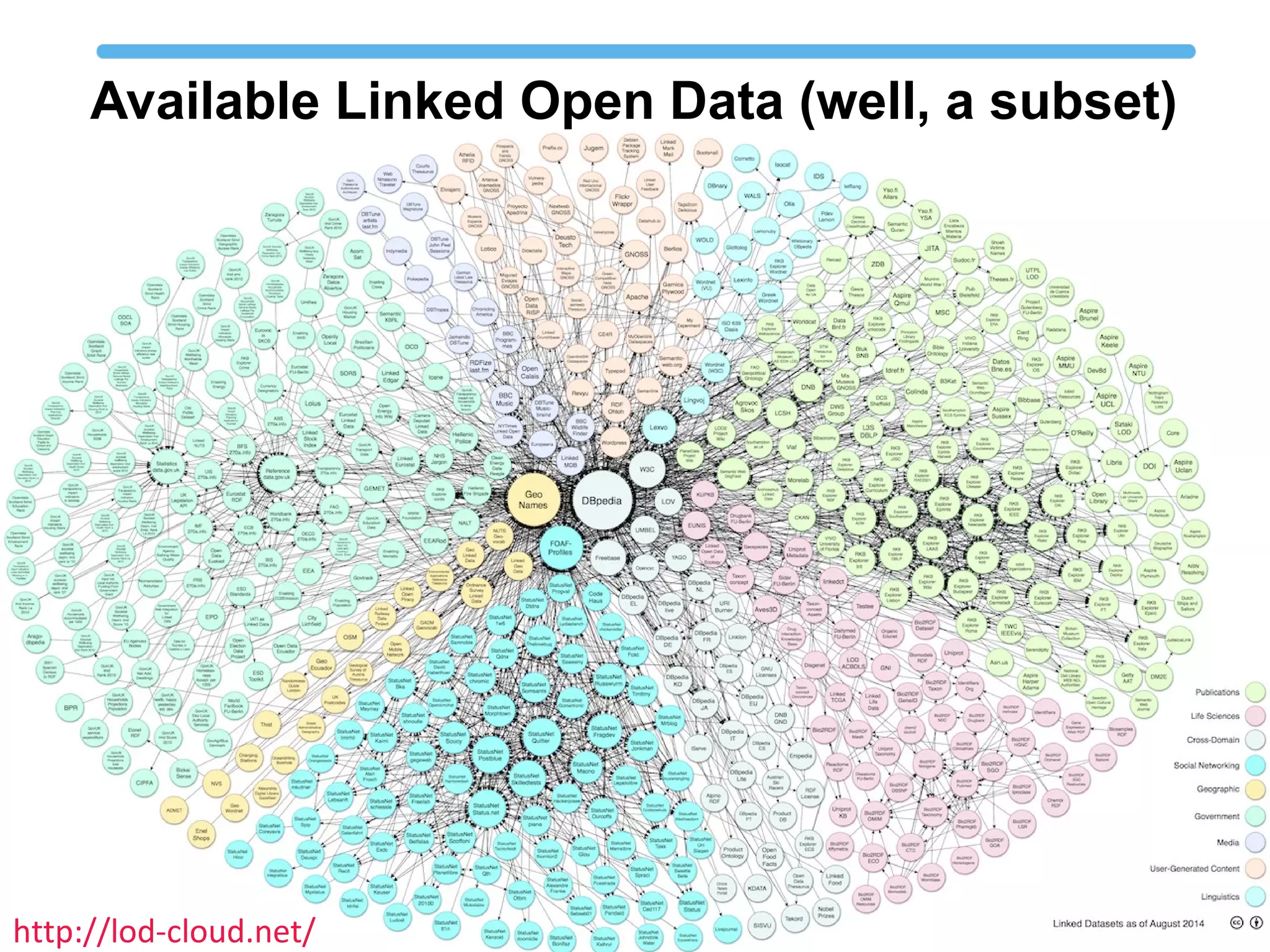
The document discusses linked open data best practices for publishing, sharing, and interlinking structured data on the web. It highlights benefits for researchers, developers, librarians, and institutions, including improved data integration, reduced duplication of efforts, and the potential for greater discovery. The document also addresses challenges and the importance of open data while emphasizing that it enhances but does not replace the role of librarians in metadata creation.