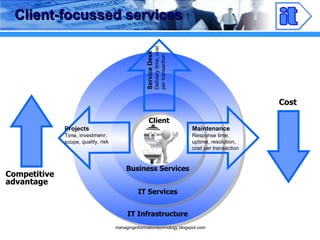
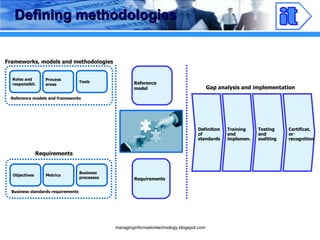
The document discusses strategies for providing effective IT services through client-focused services and standardization. It emphasizes defining standards for project management, software development, and IT infrastructure maintenance to ensure consistent service delivery, quality, and cost efficiency. Key considerations include flexibility, interoperability, and a focus on client needs.