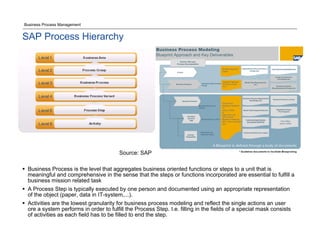
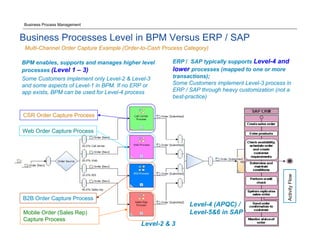
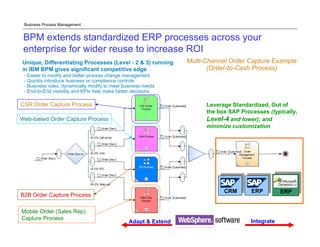
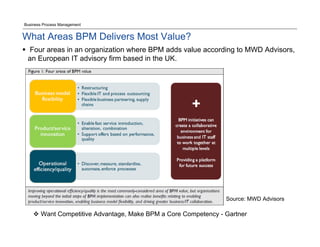
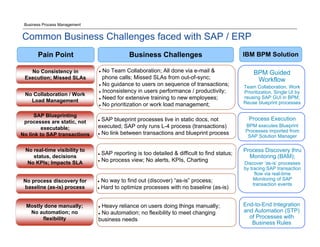
The document discusses the differences between Business Process Management (BPM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), particularly focusing on the APQC Process Classification Framework (PCF) and its levels. It emphasizes how BPM can extend standardized ERP processes to enhance flexibility, collaboration, and real-time visibility, while also outlining common challenges faced with ERP implementations. Additionally, the document notes the importance of BPM as a core competency for competitive advantage and achieving business agility.