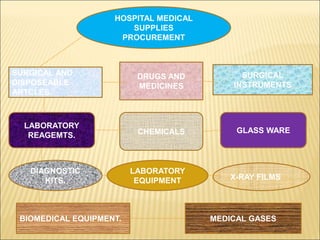
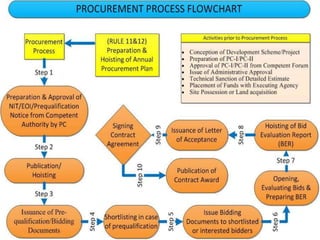
The document provides information about the procurement process for medical supplies and equipment at hospitals. It discusses the different types of supplies that must be procured, including medical equipment, disposable supplies, laboratory chemicals and diagnostics, vaccines, and medical gases. It also outlines the national hospital formulary that determines which medicines are procured according to the essential medicines list from the WHO. The document discusses the various methods used for procurement, including open competitive bidding, request for quotations, direct contracting and petty purchases, in accordance with the relevant rules and regulations.