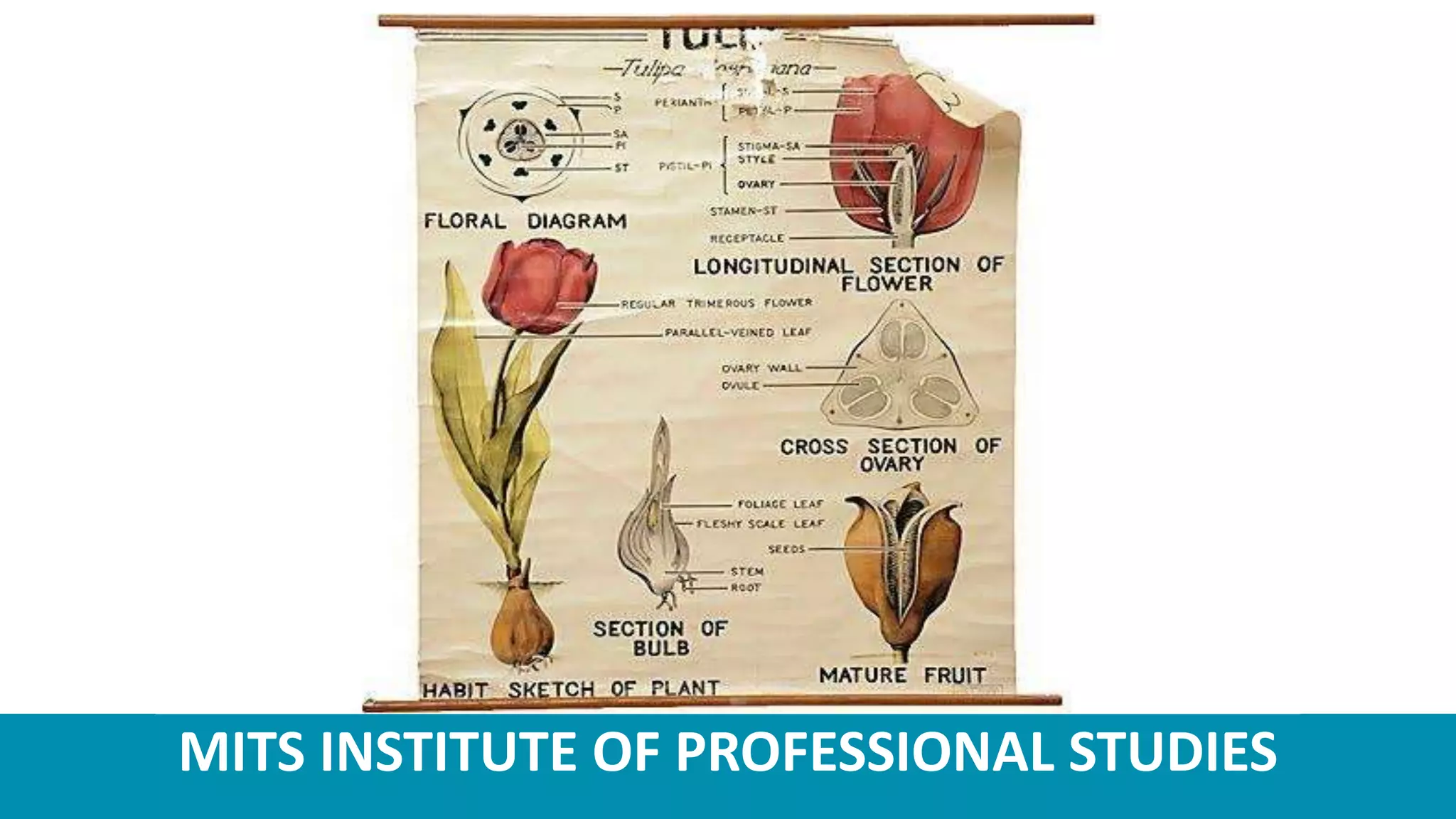
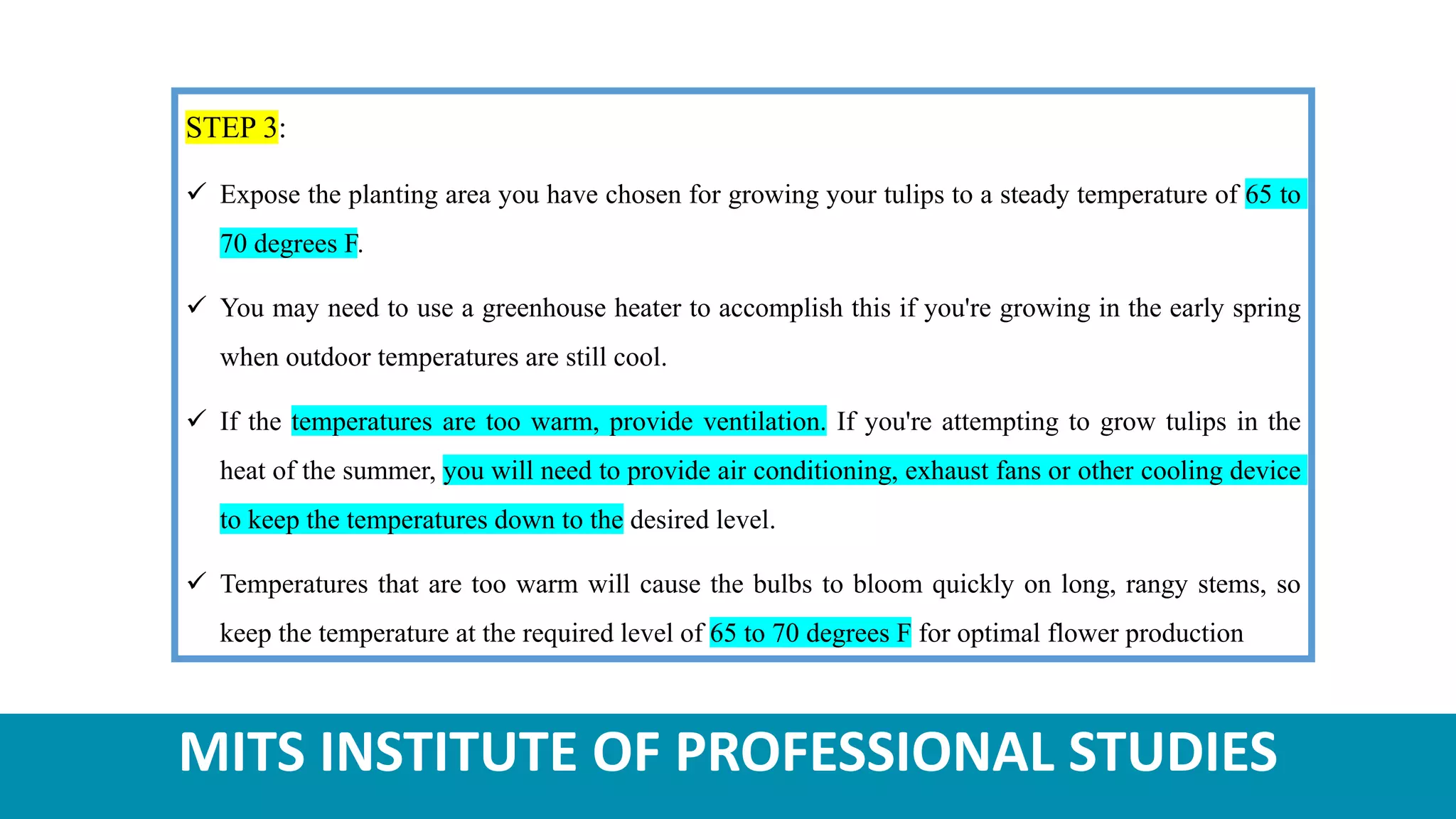
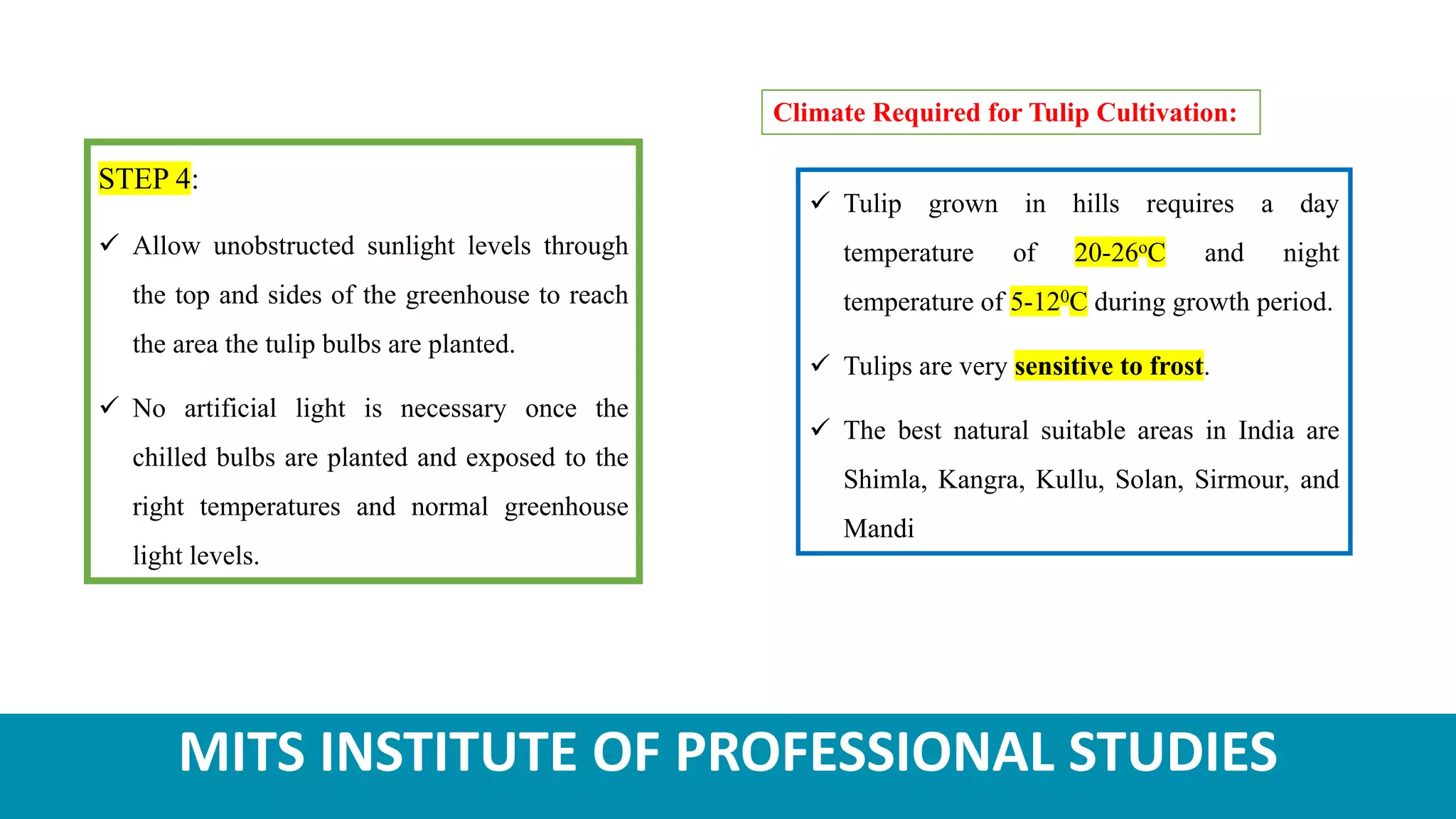
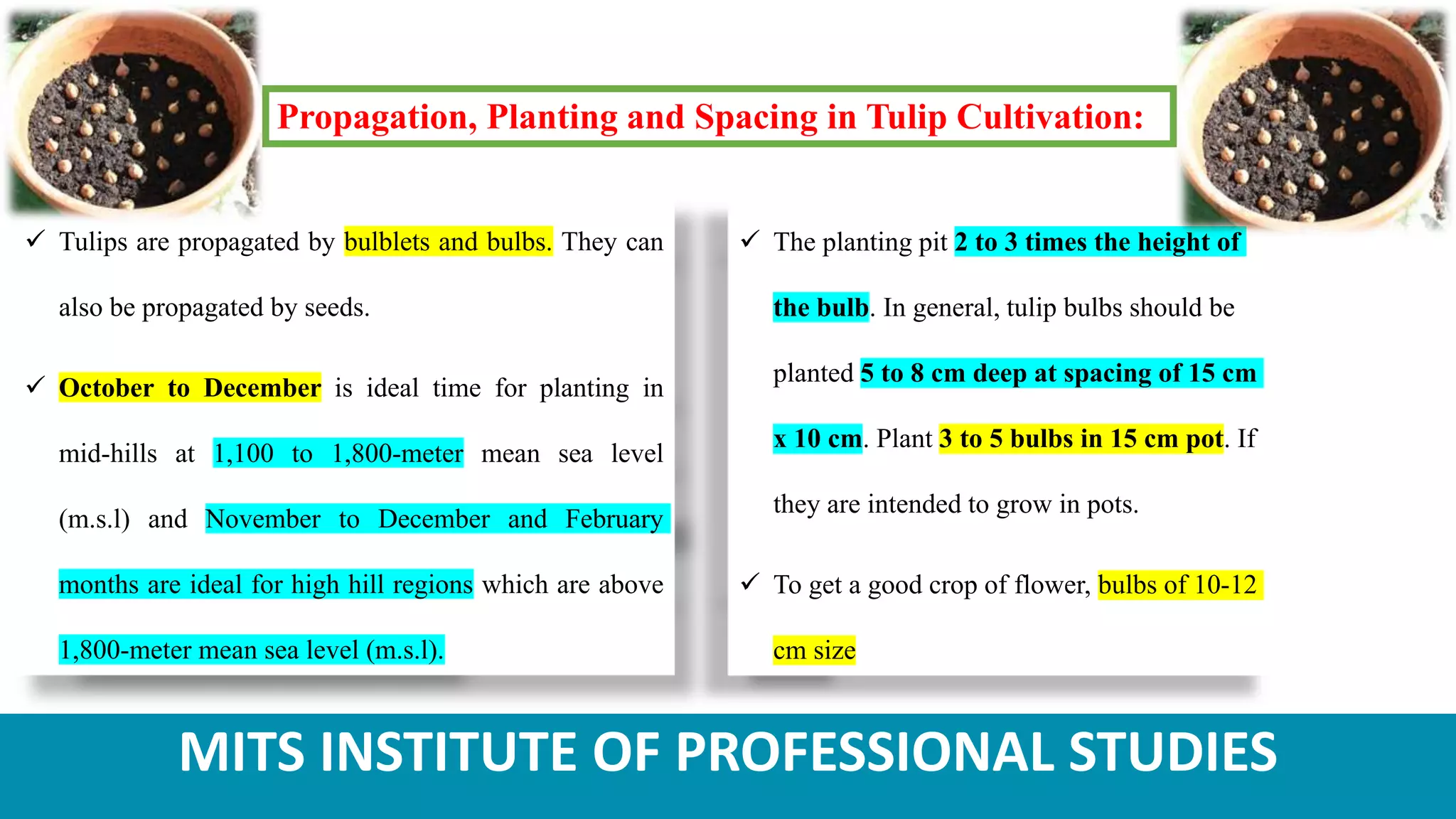
Tulips are ornamental bulbous flowers that are well-suited for cultivation in the temperate regions of India, such as Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir. Tulip cultivation requires providing the bulbs with a chilling period, planting them in well-drained soil at the appropriate spacing and depth, and maintaining optimum temperature, light, and moisture conditions for growth. Common pests that affect tulips include thrips and aphids, while diseases such as bulb rot and fusarium infection must also be controlled. Tulips are harvested when the flowers are 25-50% colored.