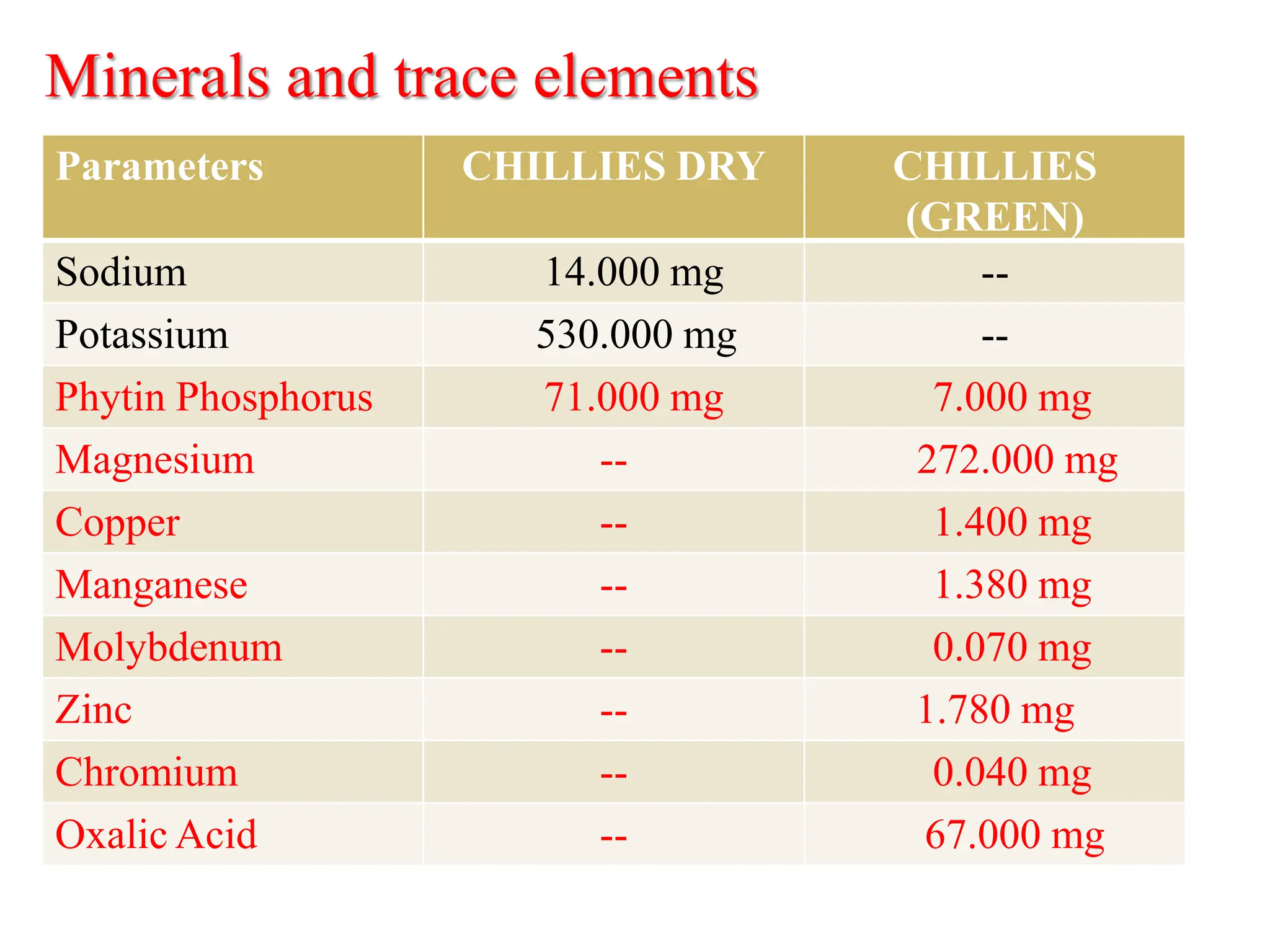
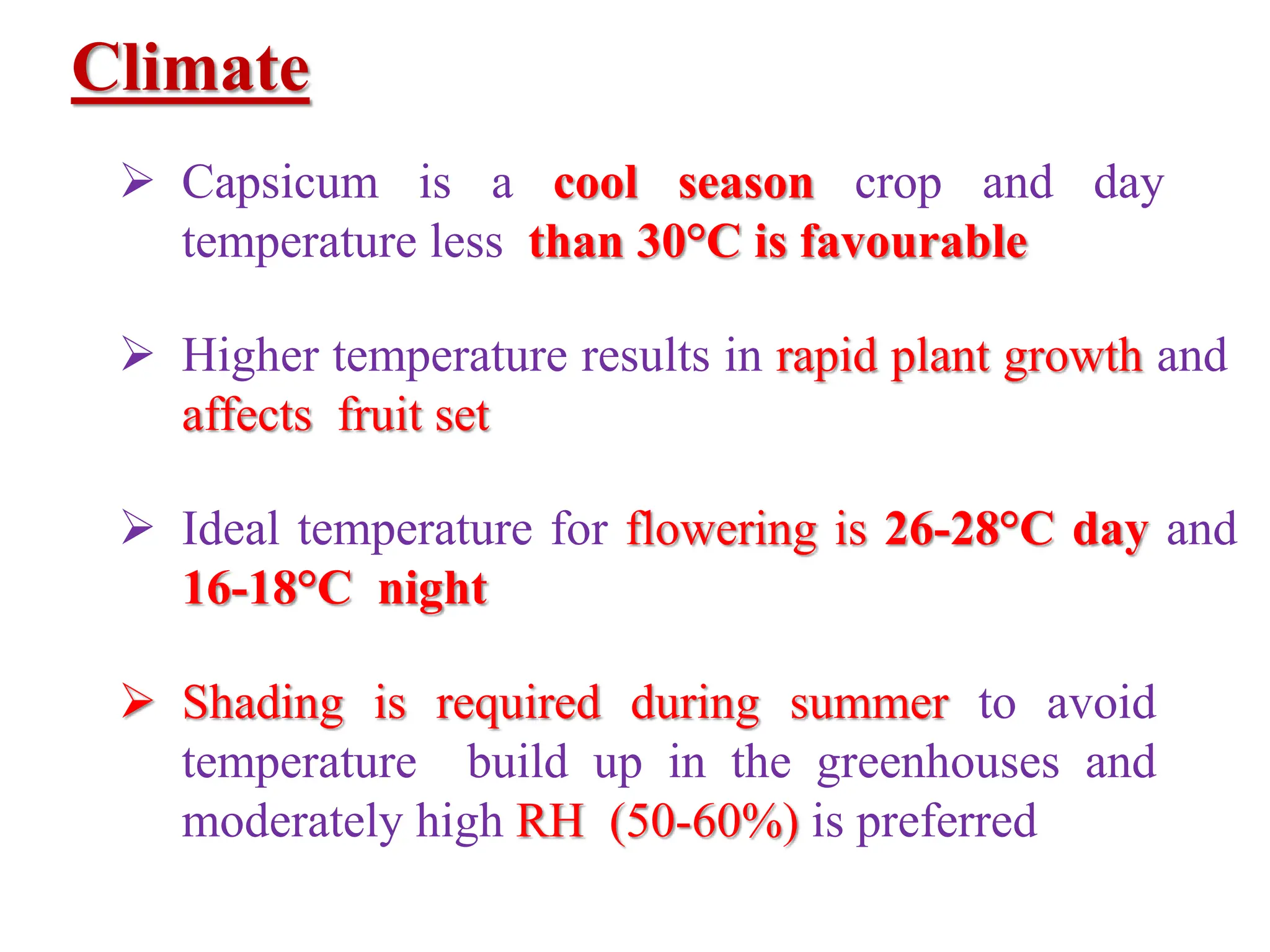
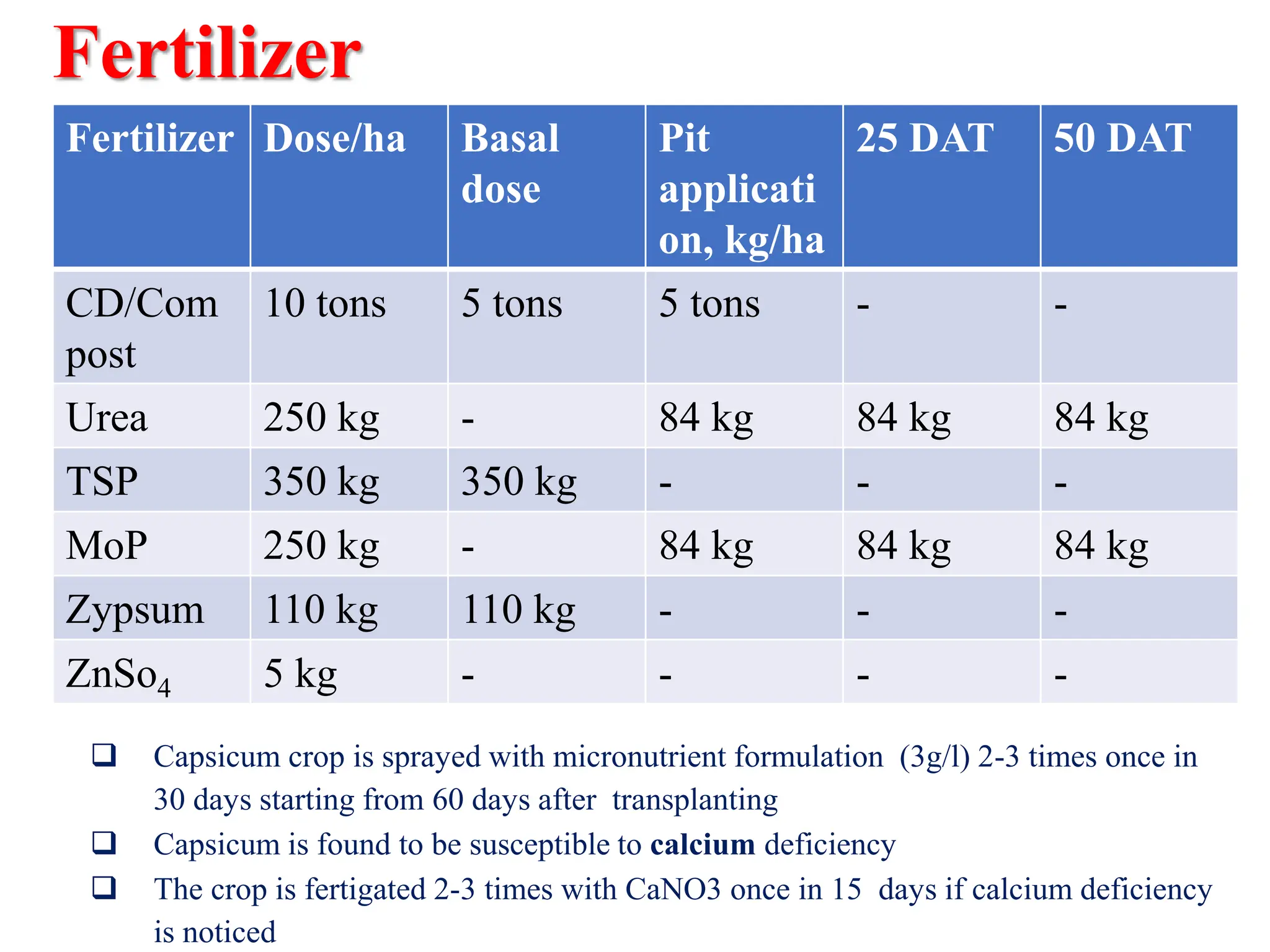
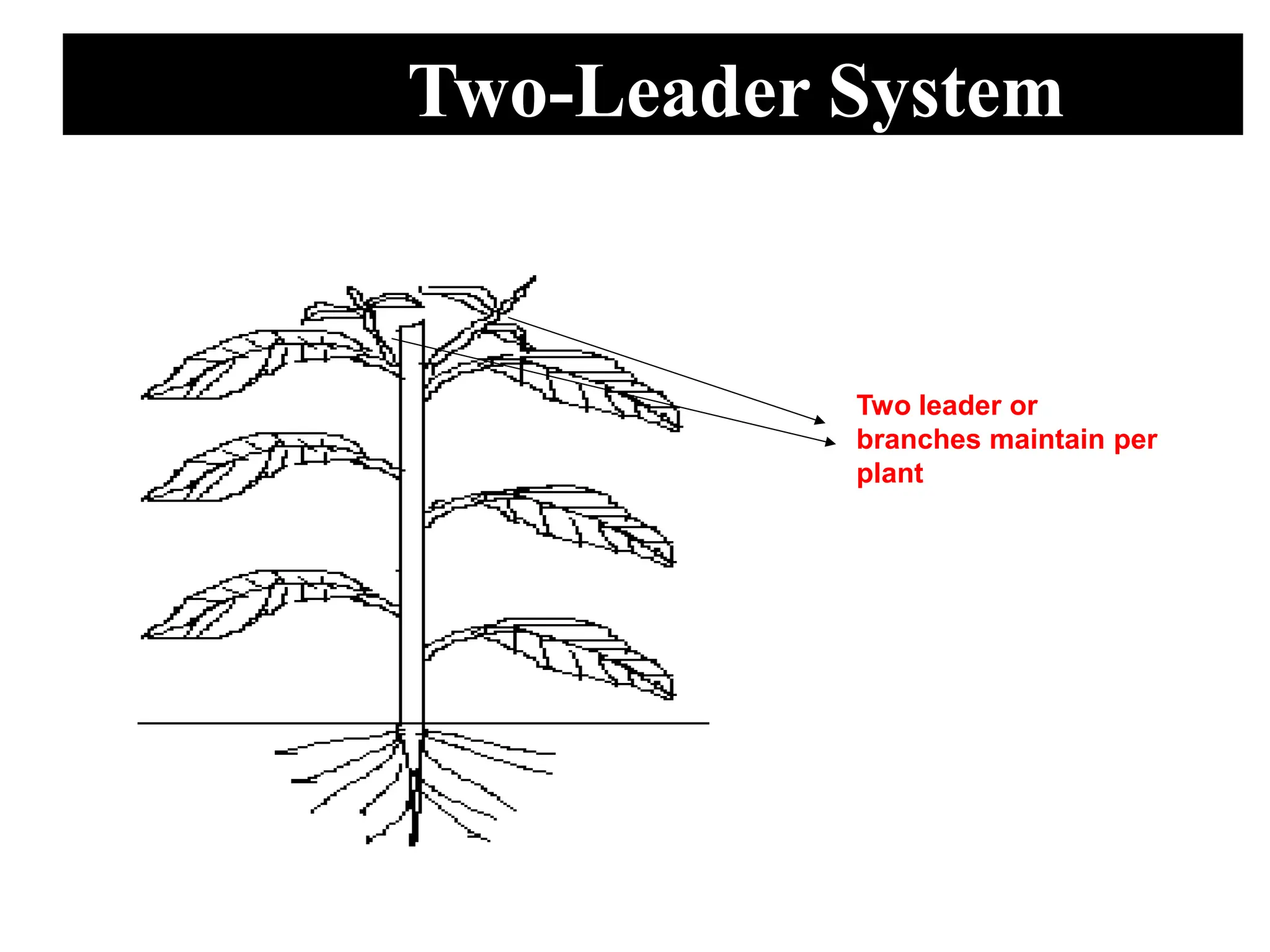
This document provides information on the cultivation of sweet pepper/capsicum. It begins with the systematic classification of capsicum, then discusses its history and origin. It describes ideal growing conditions for capsicum including climate, soil type, variety selection, nursery preparation, transplanting, training, pruning, harvesting and post-harvest handling. The document also addresses common production practices like irrigation, fertilizer management, and pest and disease control. Overall, the document is a comprehensive guide to successful capsicum cultivation.