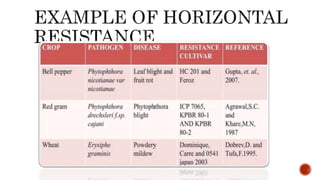
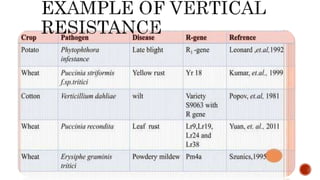
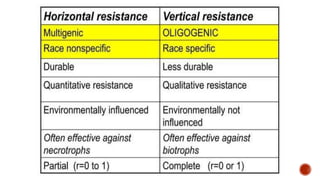
Genetic resistance in plants refers to heritable traits that suppress pathogen development. It is controlled by one or more nuclear or cytoplasmic genes. Most plants are resistant to most diseases through non-host resistance. Resistance is more common than susceptibility. Genetic resistance can be categorized as horizontal/general resistance, effective against all pathogen races, or vertical/race-specific resistance, effective against only some races. Horizontal resistance involves polygenic, quantitative traits and allows some pathogen reproduction but not epidemic growth, while vertical resistance is often controlled by single major genes and provides complete resistance or susceptibility depending on pathogen virulence.