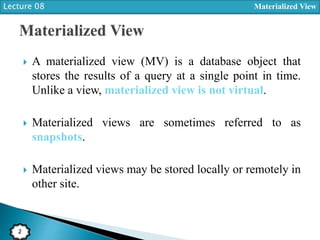
A materialized view stores the results of a query at a single point in time, unlike a view which is virtual. Materialized views can increase query performance and efficiently support remote users. They must be managed through defining, refreshing, and dropping the view. Materialized views can be read-only or updatable and use different refresh methods like complete or fast refresh.


![Lecture 08 Materialized View
5
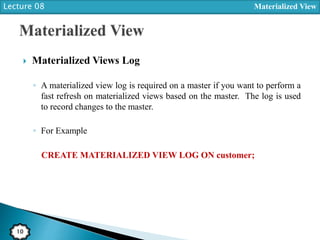
Basic Syntax
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW view-name
BUILD [IMMEDIATE | DEFERRED]
REFRESH [FAST | COMPLETE | FORCE ]
ON [COMMIT | DEMAND ]
[ON PREBUILT TABLE]
AS
SELECT ...;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect08materializedview-160204080127/85/Lect-08-materialized-view-5-320.jpg)