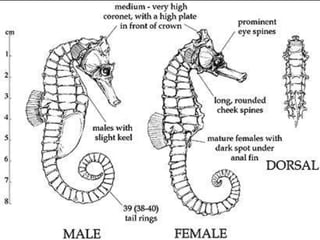
Seahorses, known for their horse-like heads, belong to the genus Hippocampus and are found in tropical and subtropical coastal waters. They have unique features such as a monkey-like tail and can change color for camouflage while feeding on small organisms. Male seahorses are responsible for pregnancy, with a unique courtship ritual that involves dancing and color change.