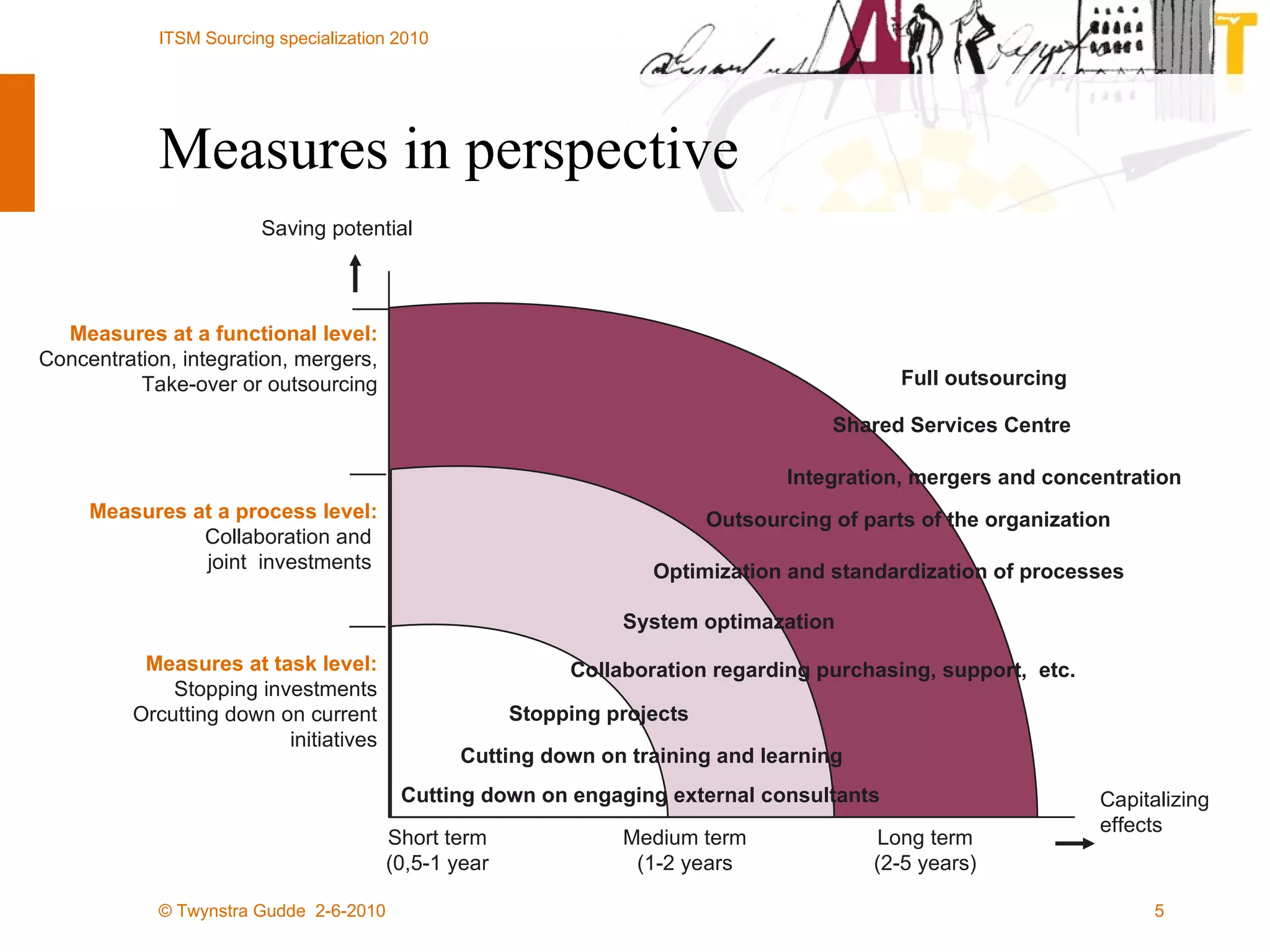
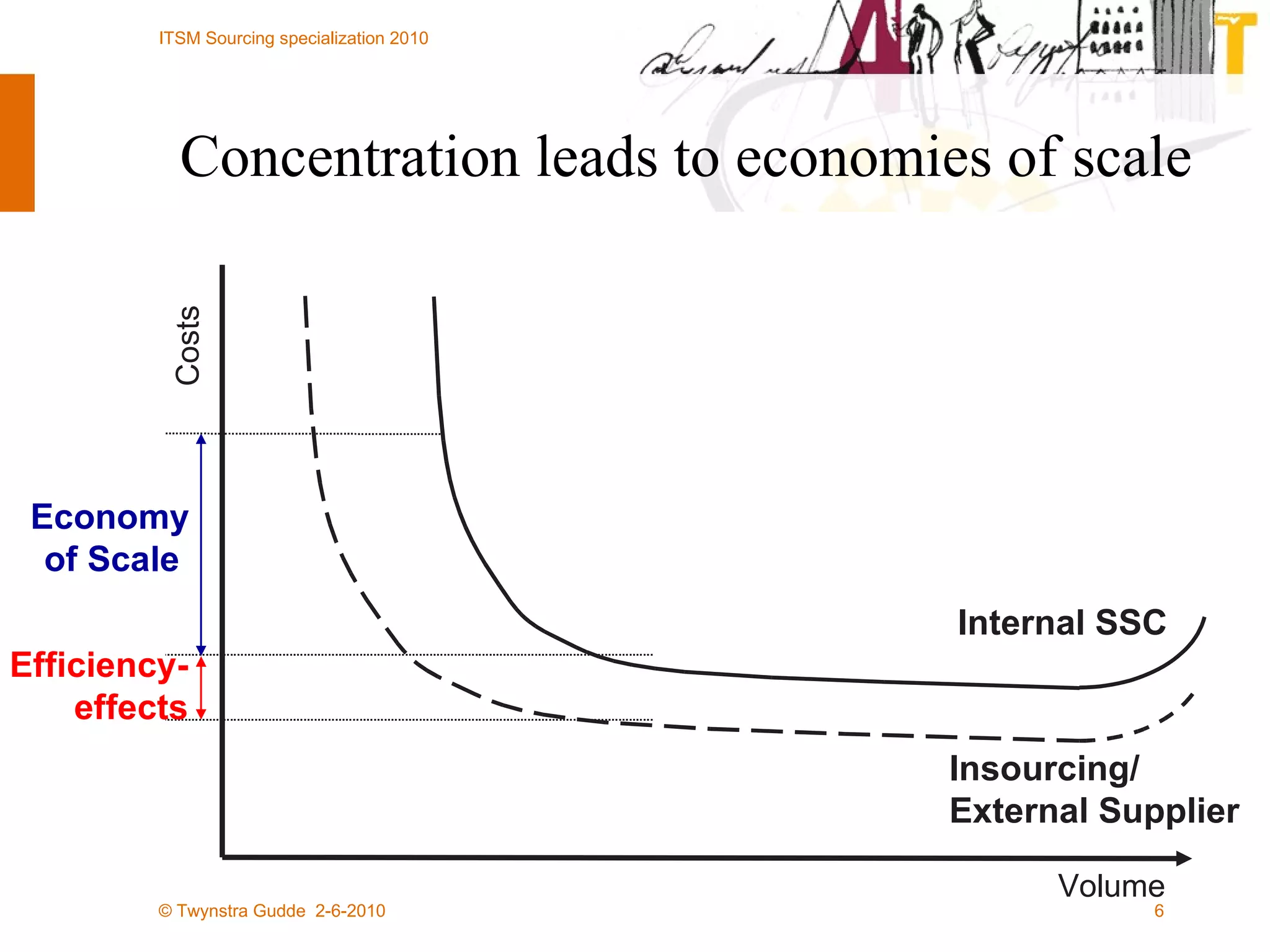
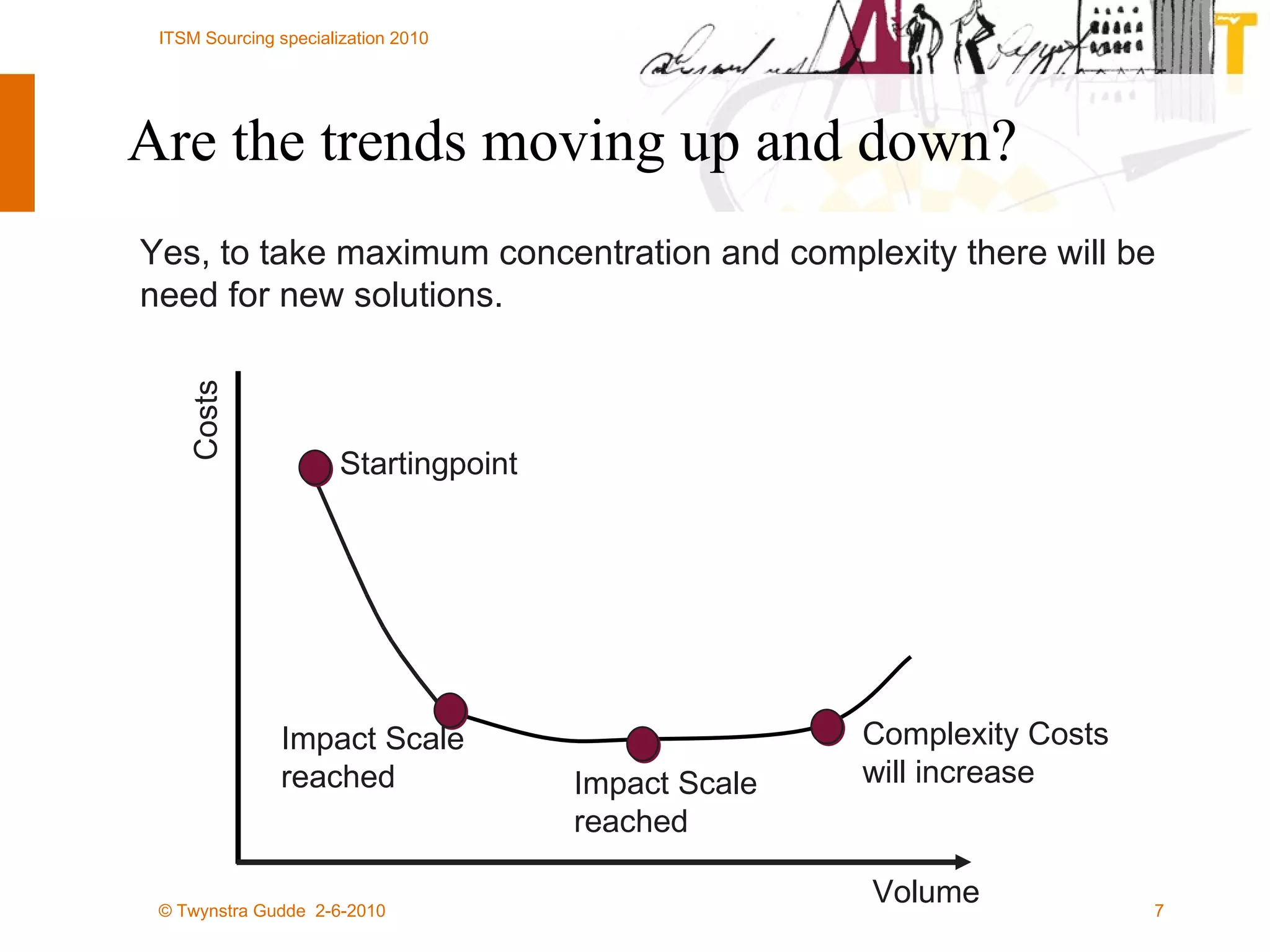
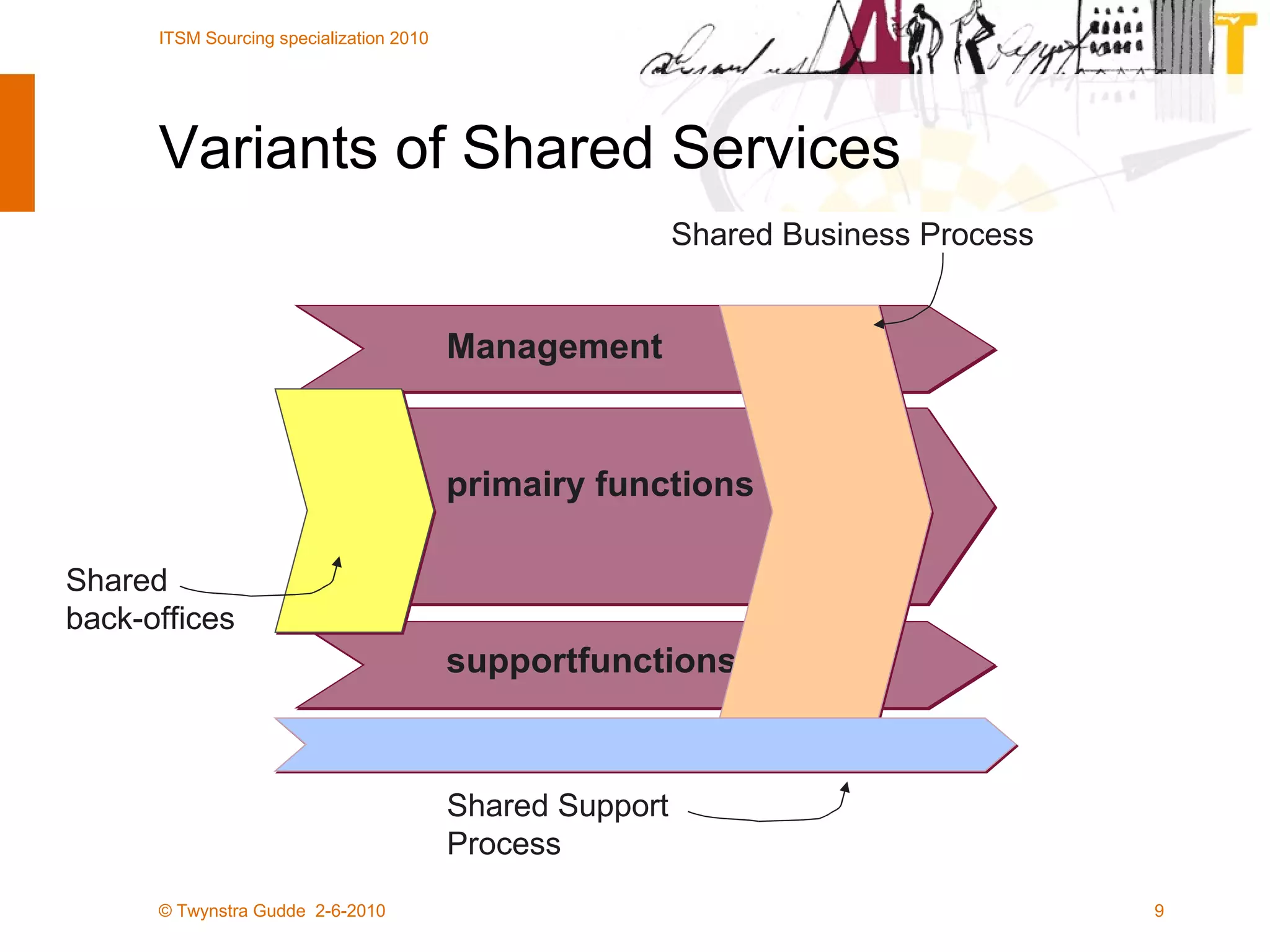
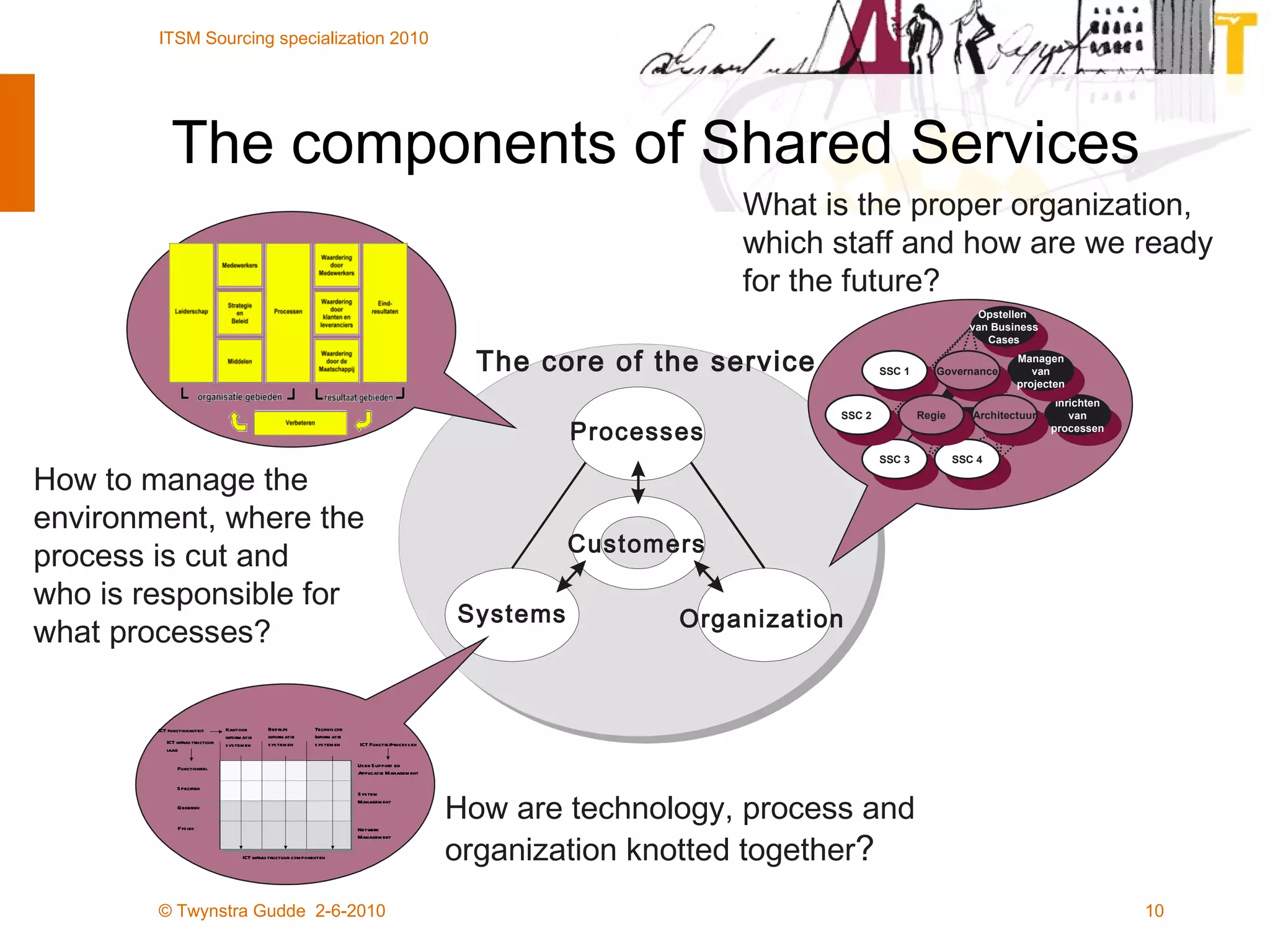
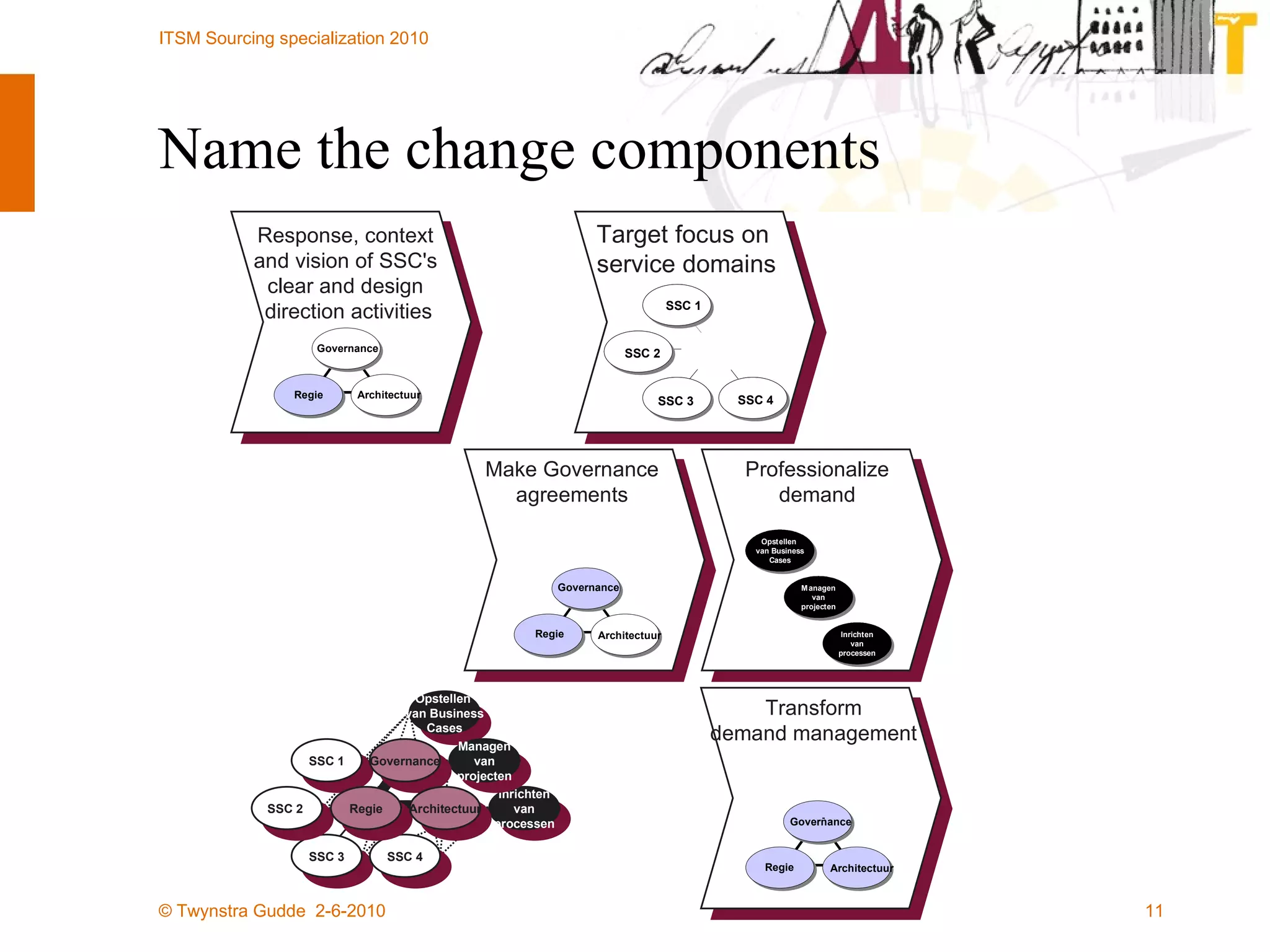
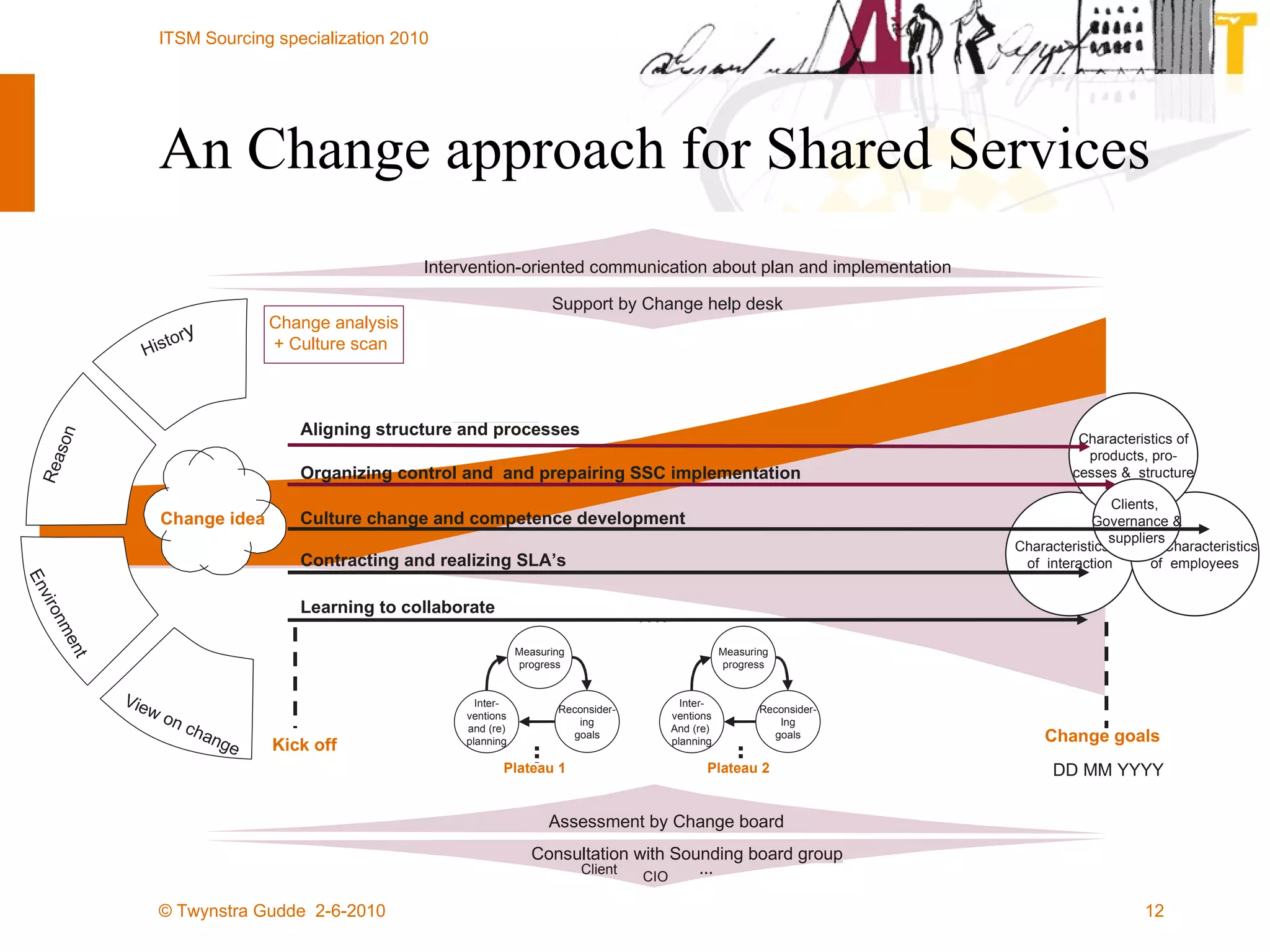
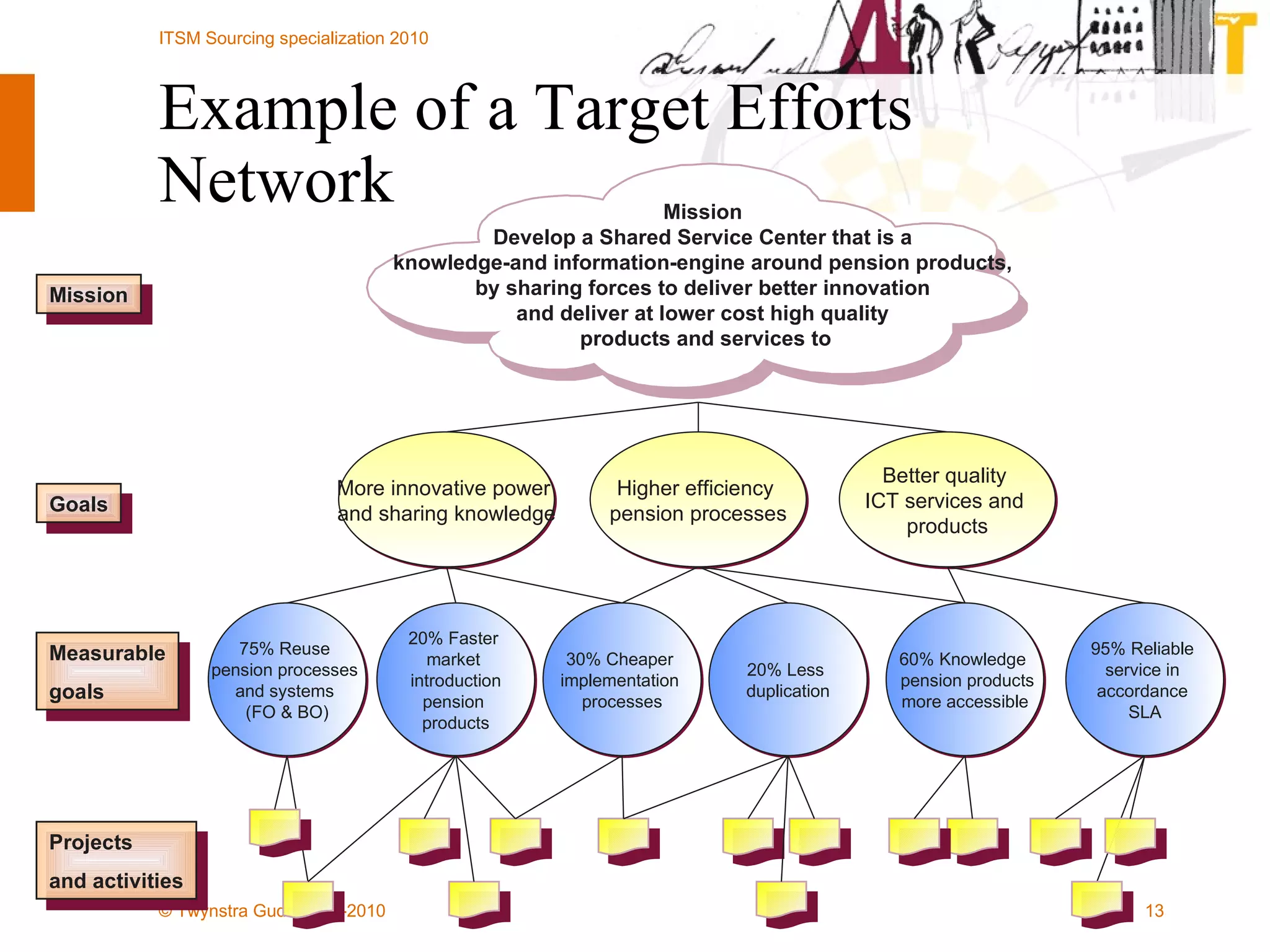
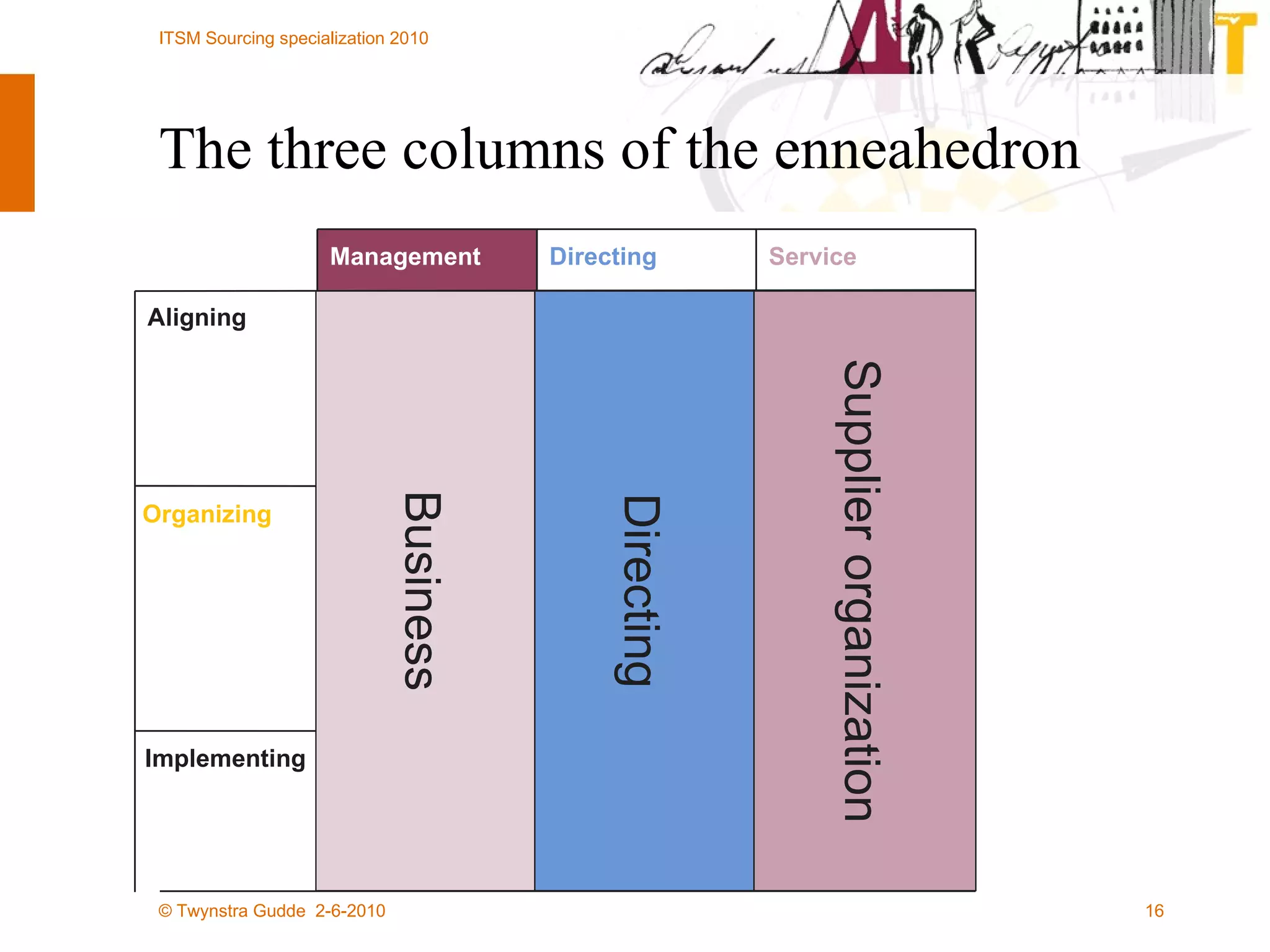
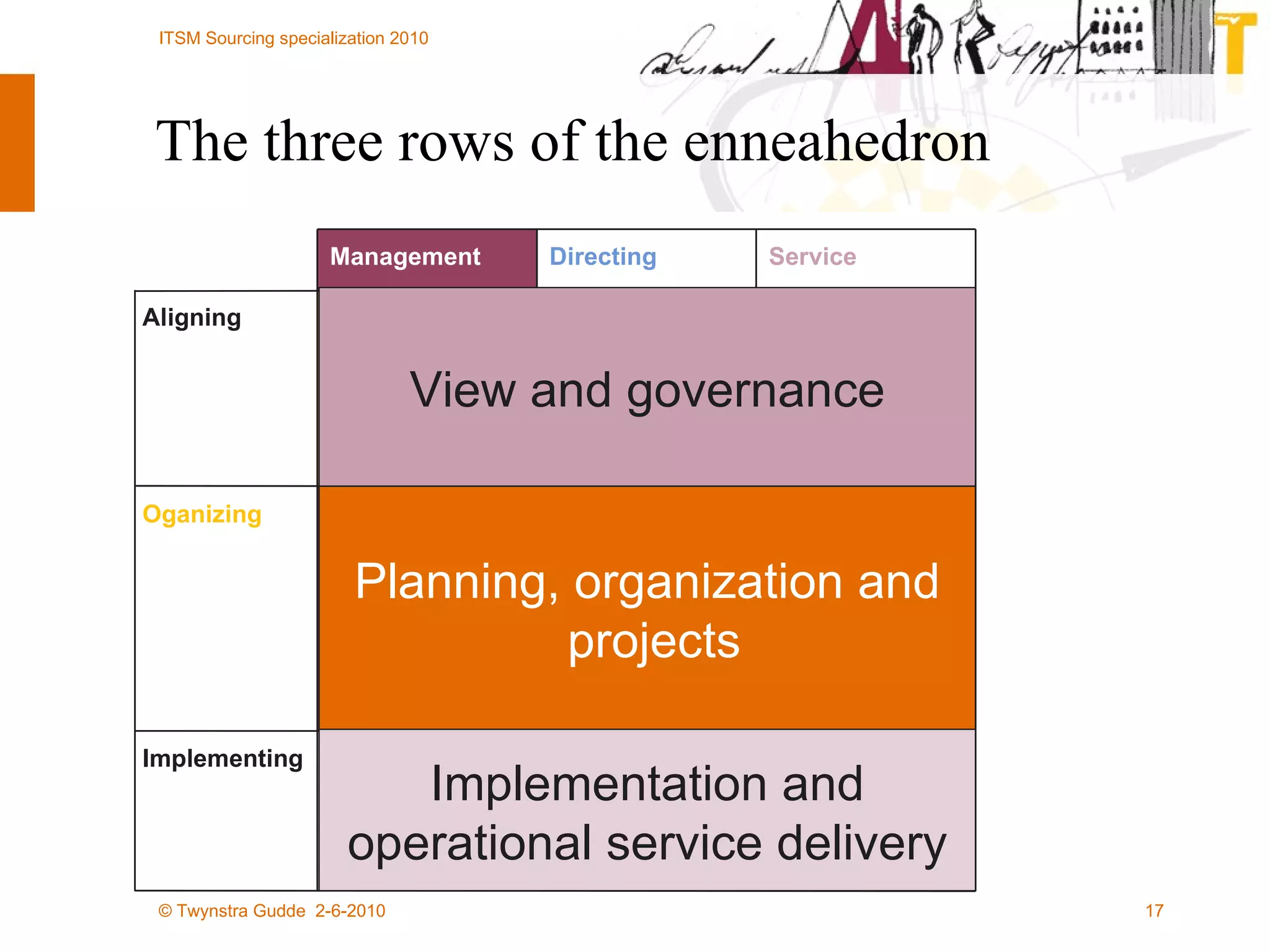
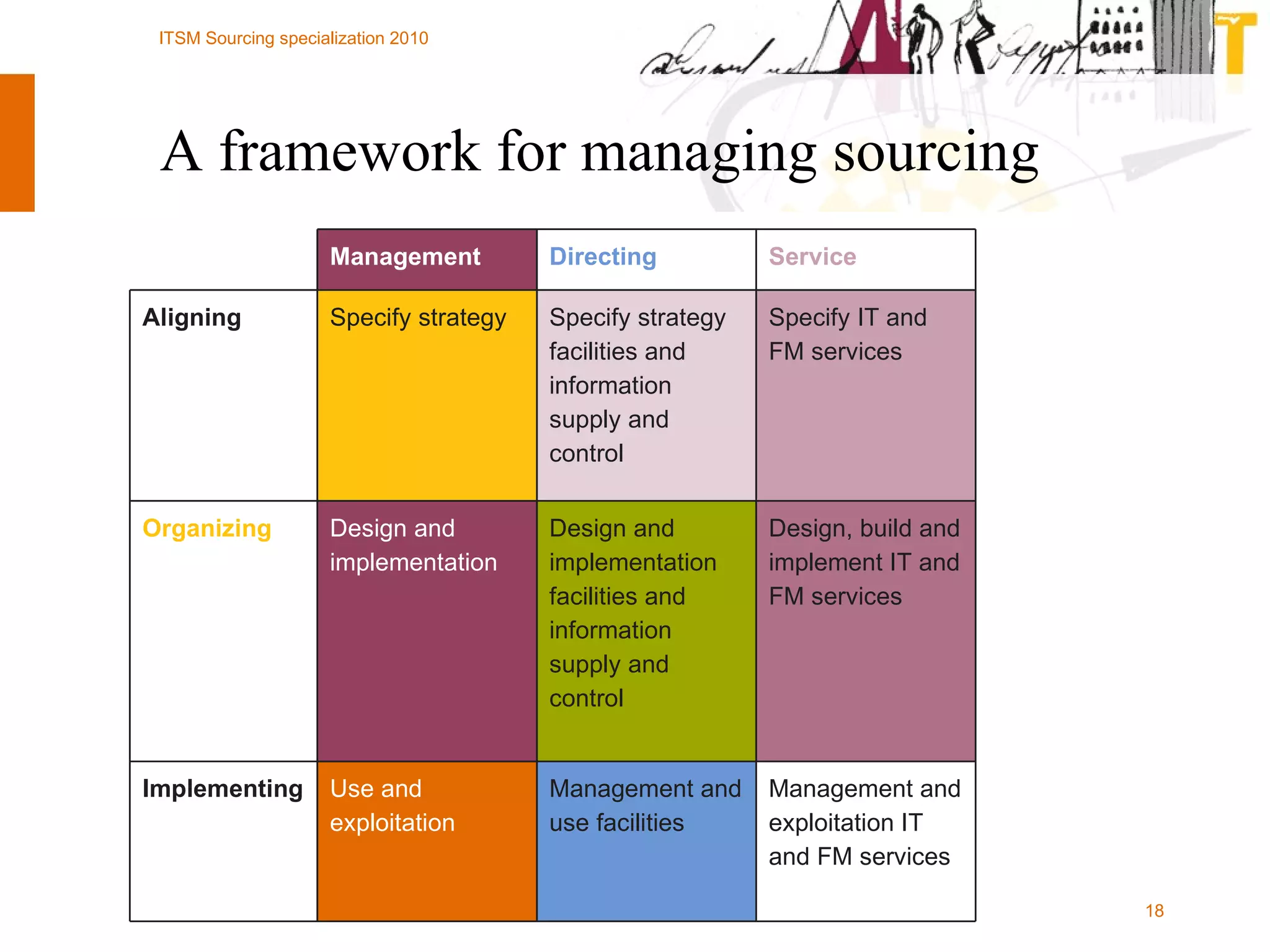
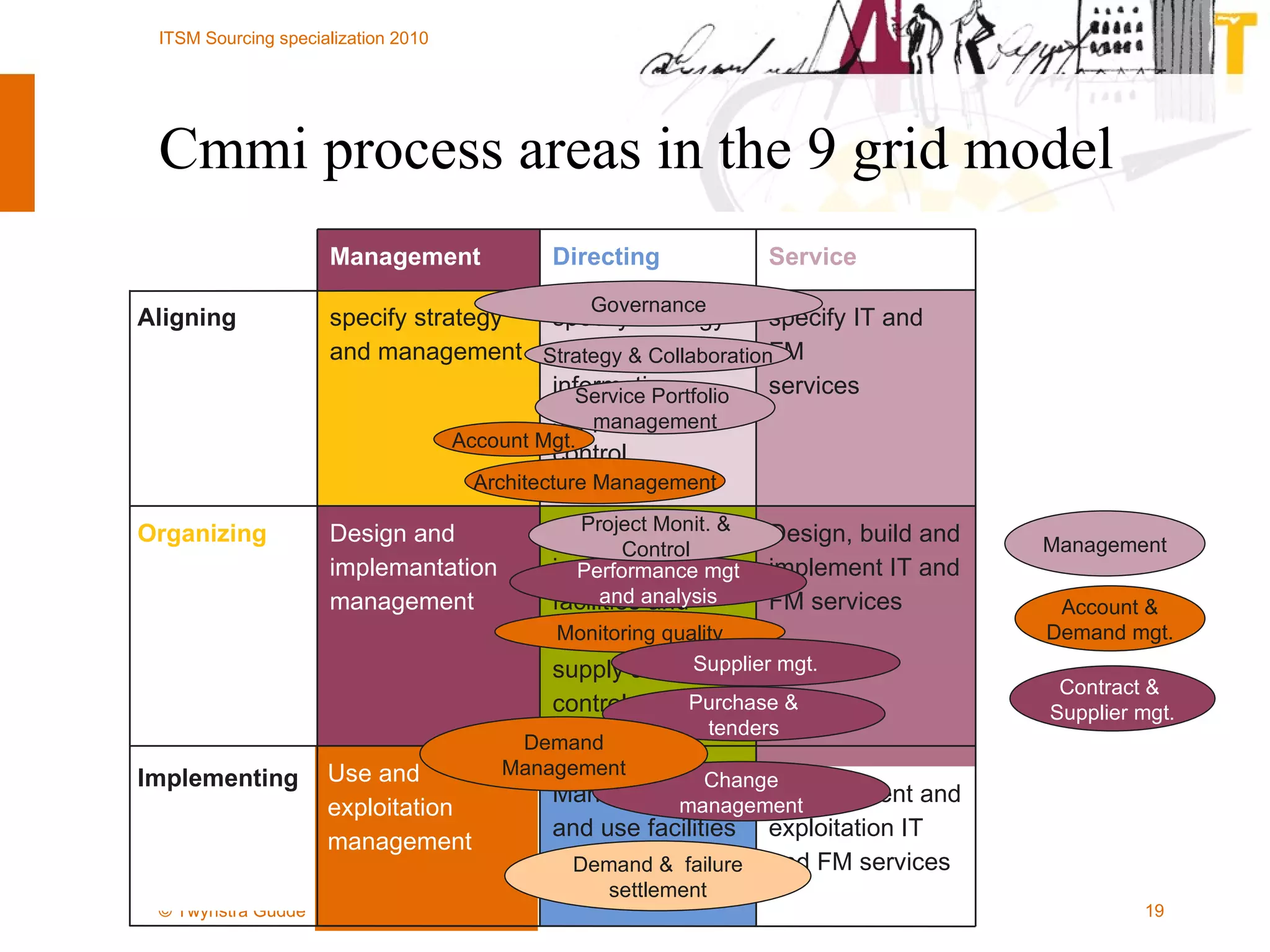
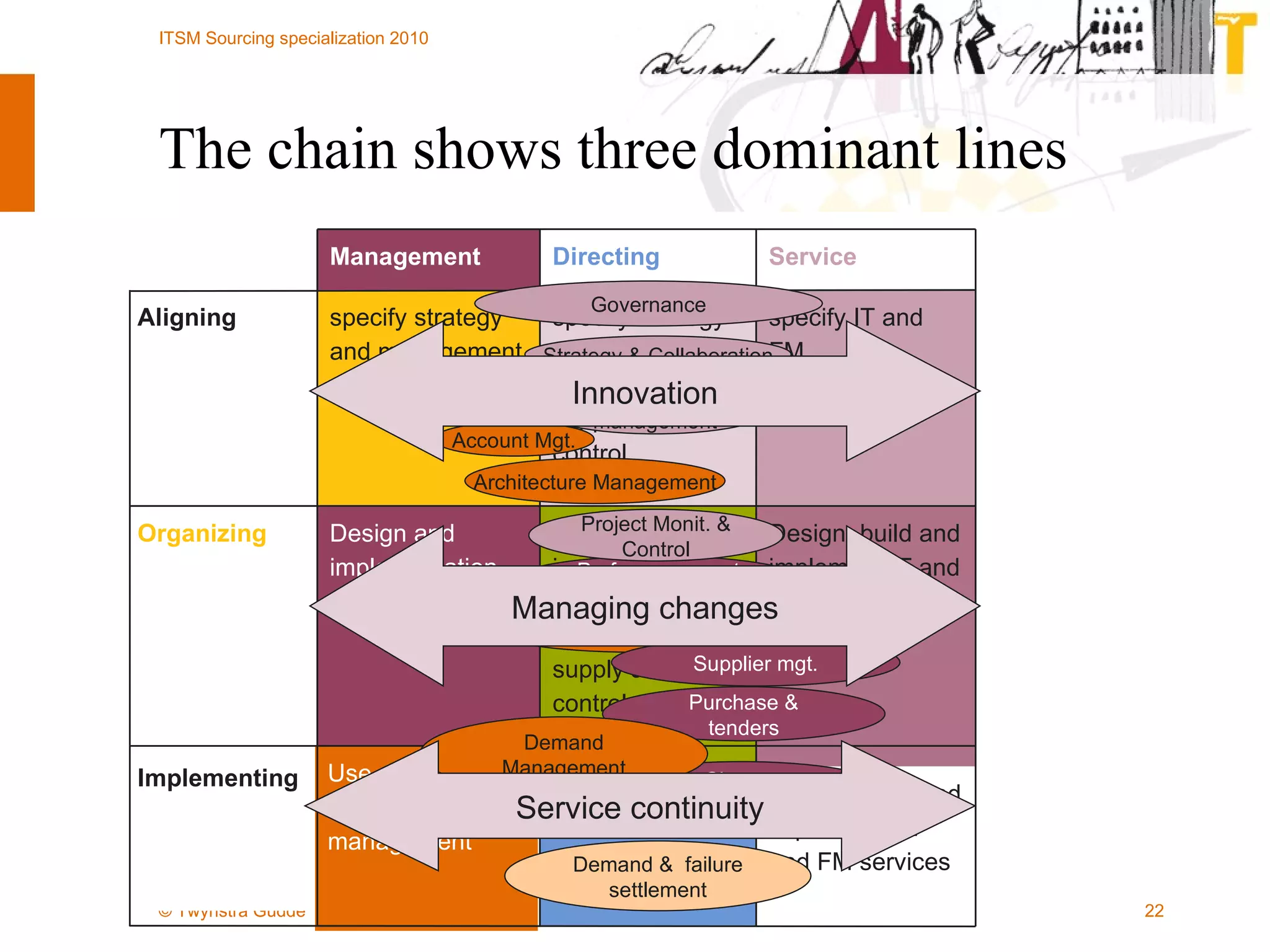
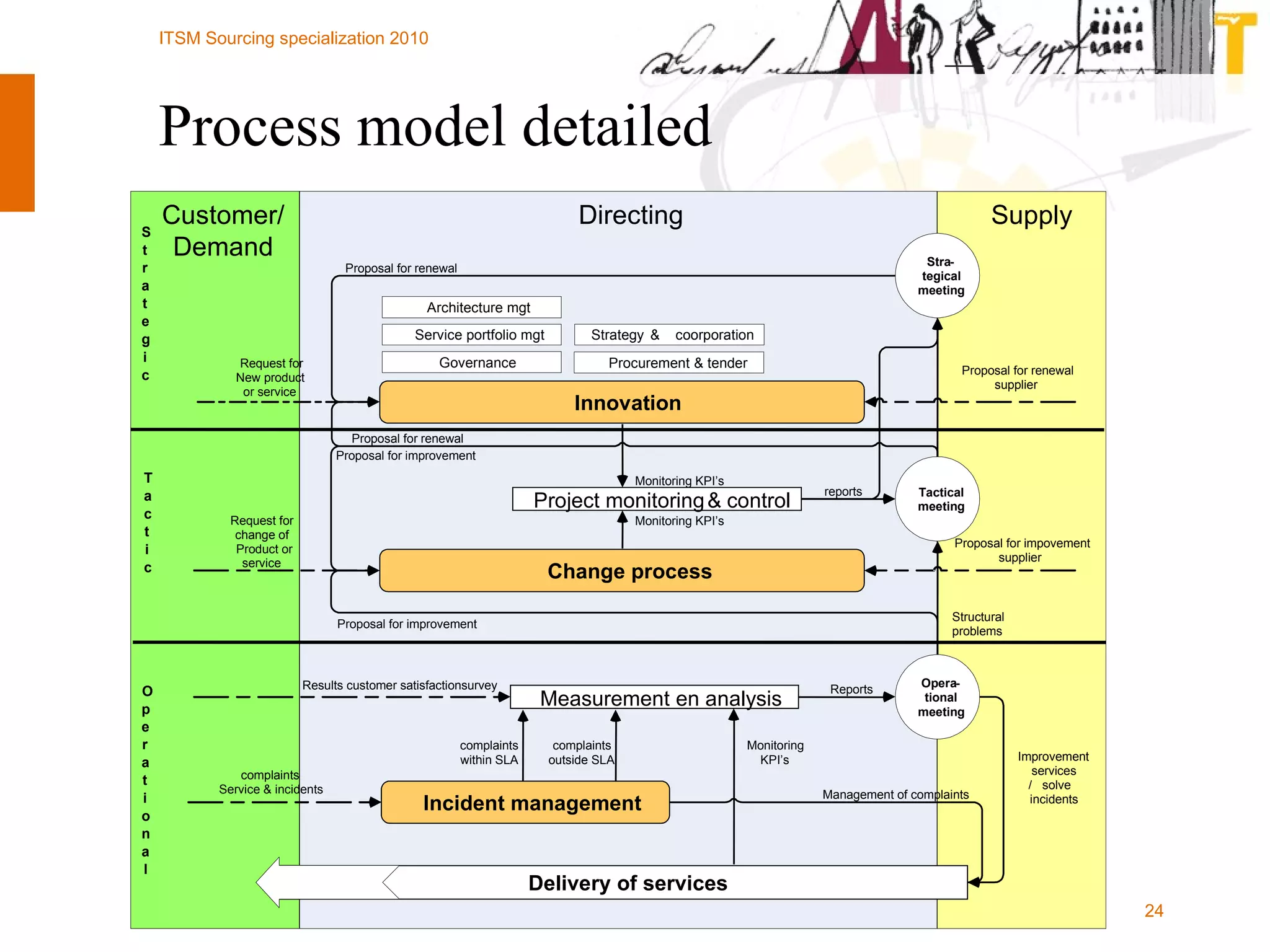
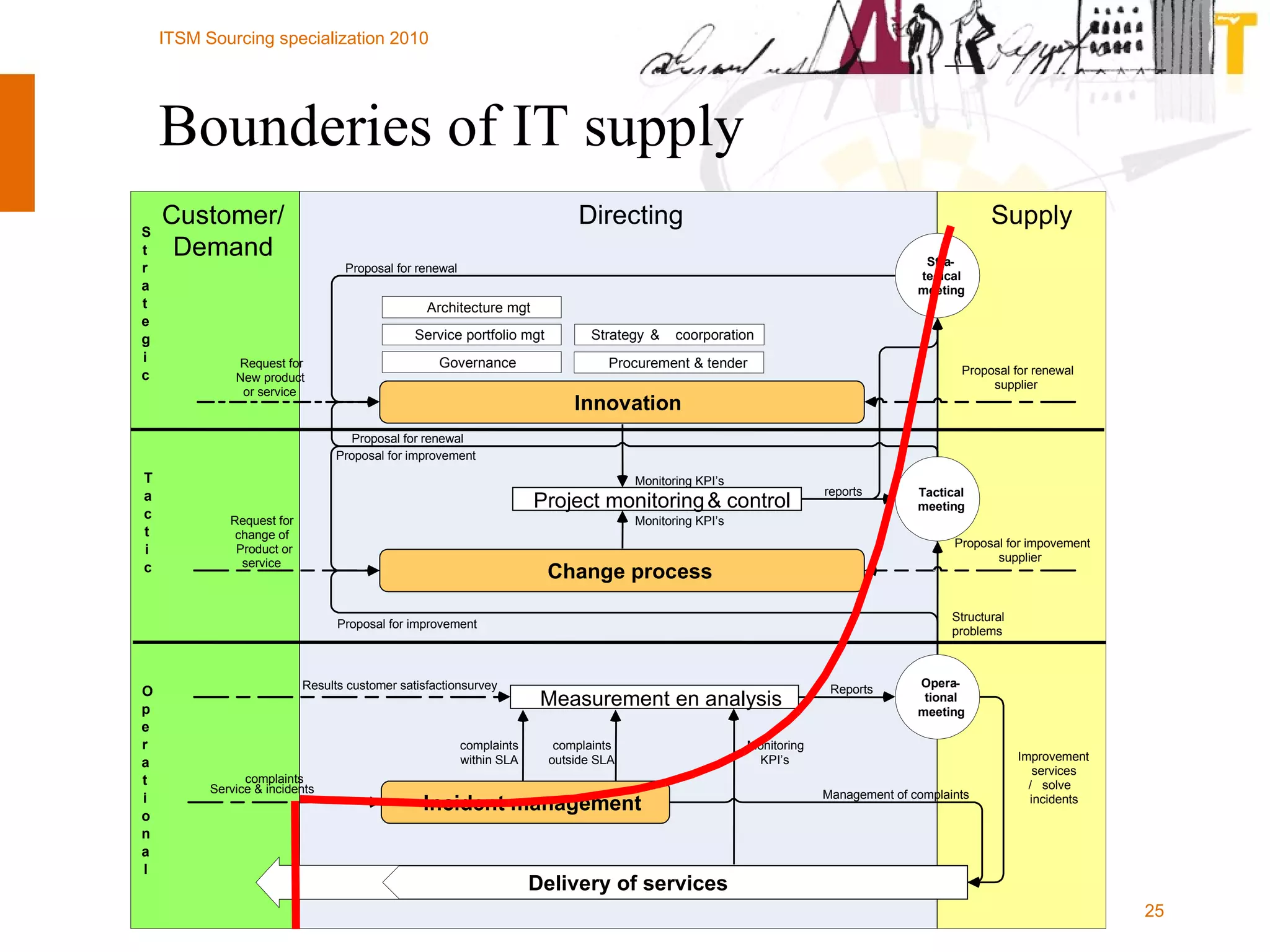
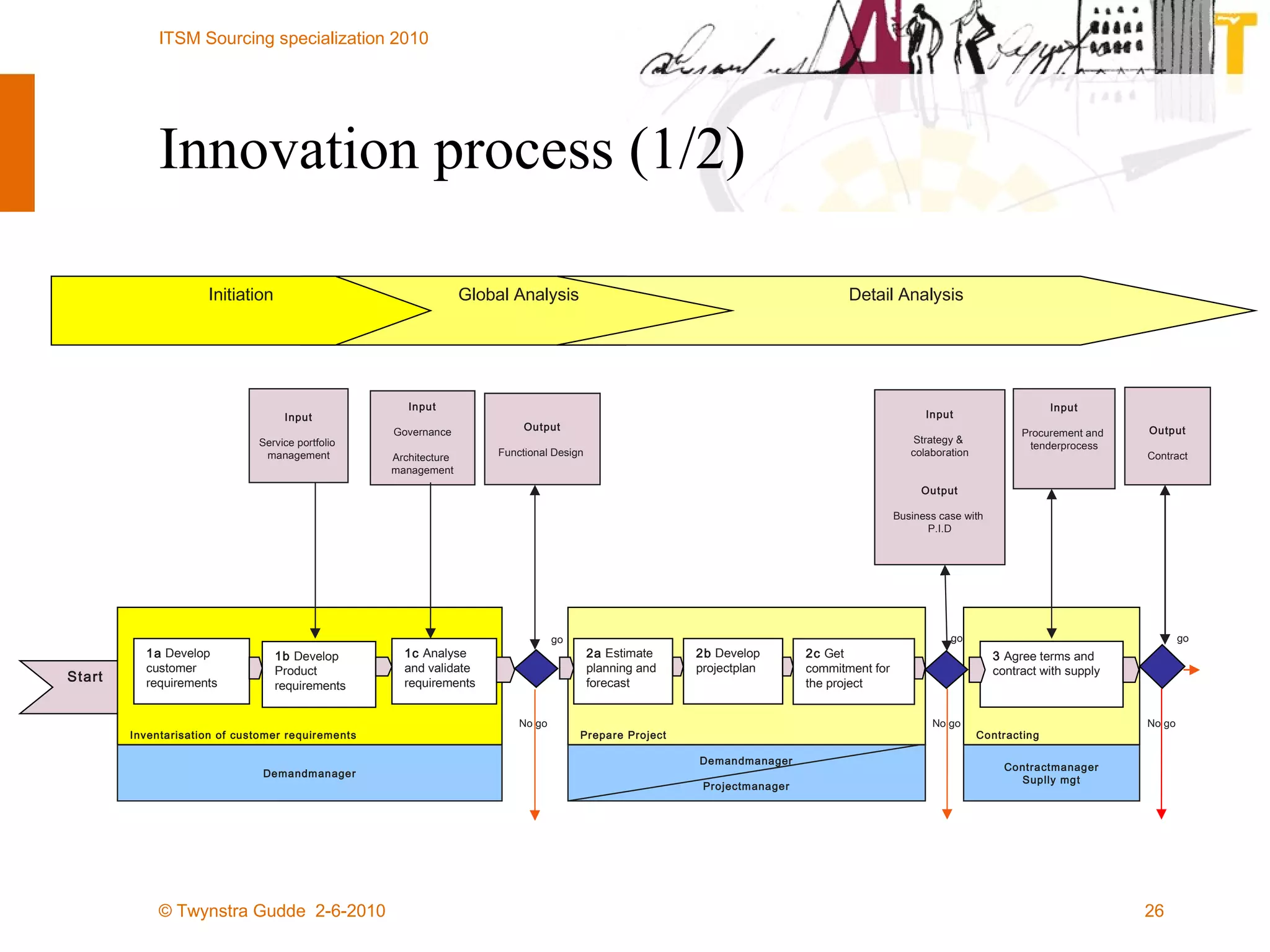
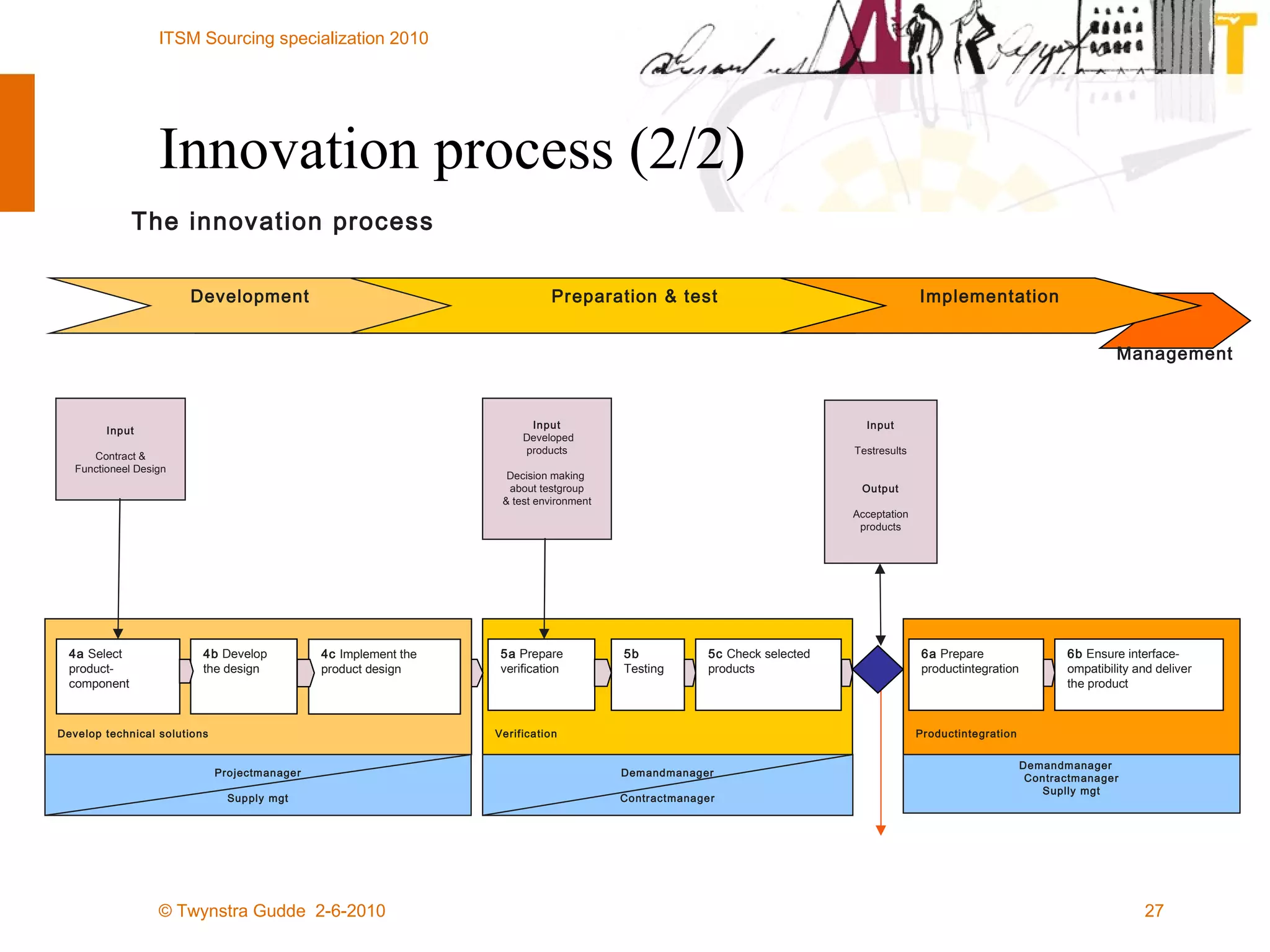
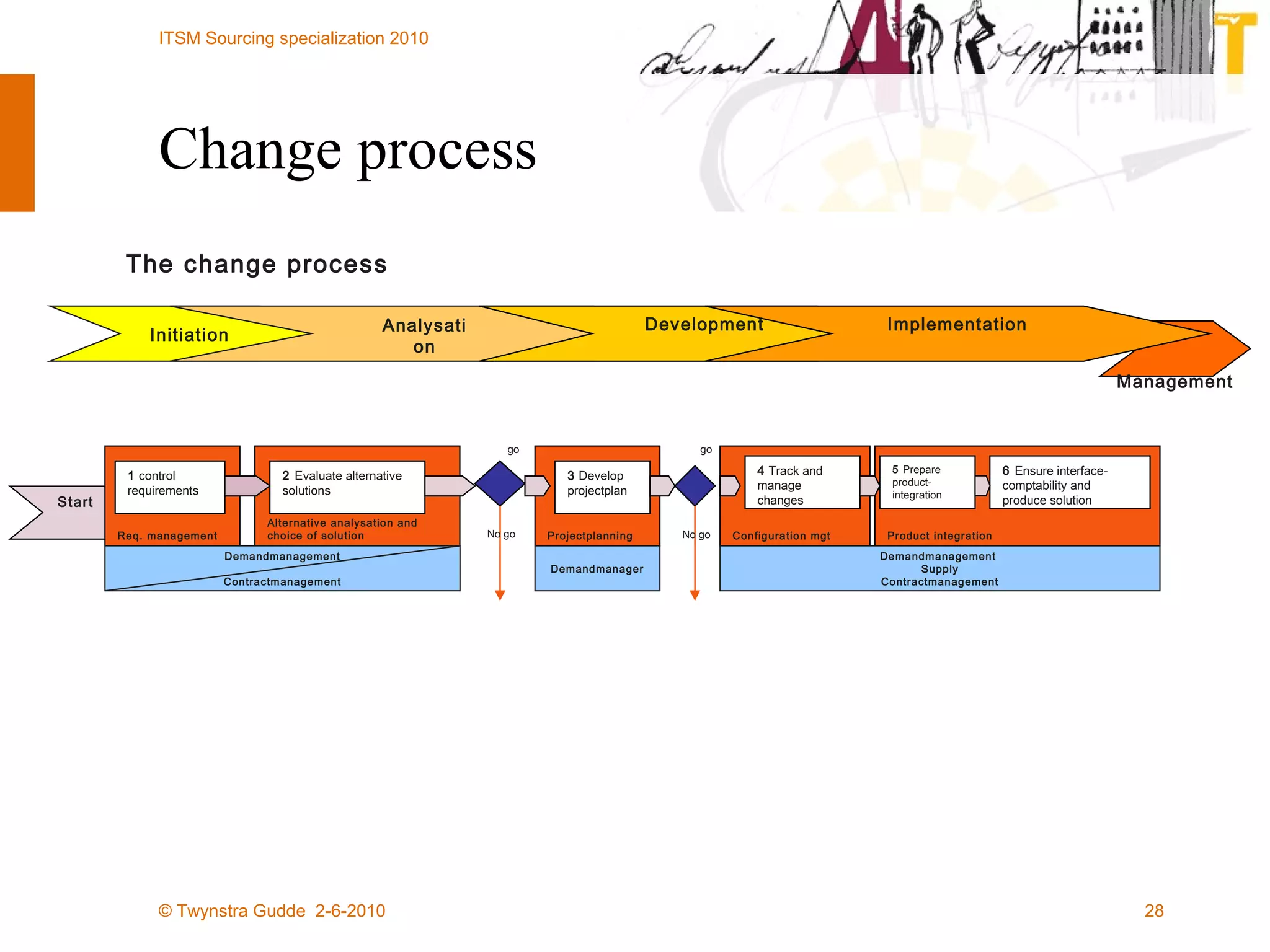
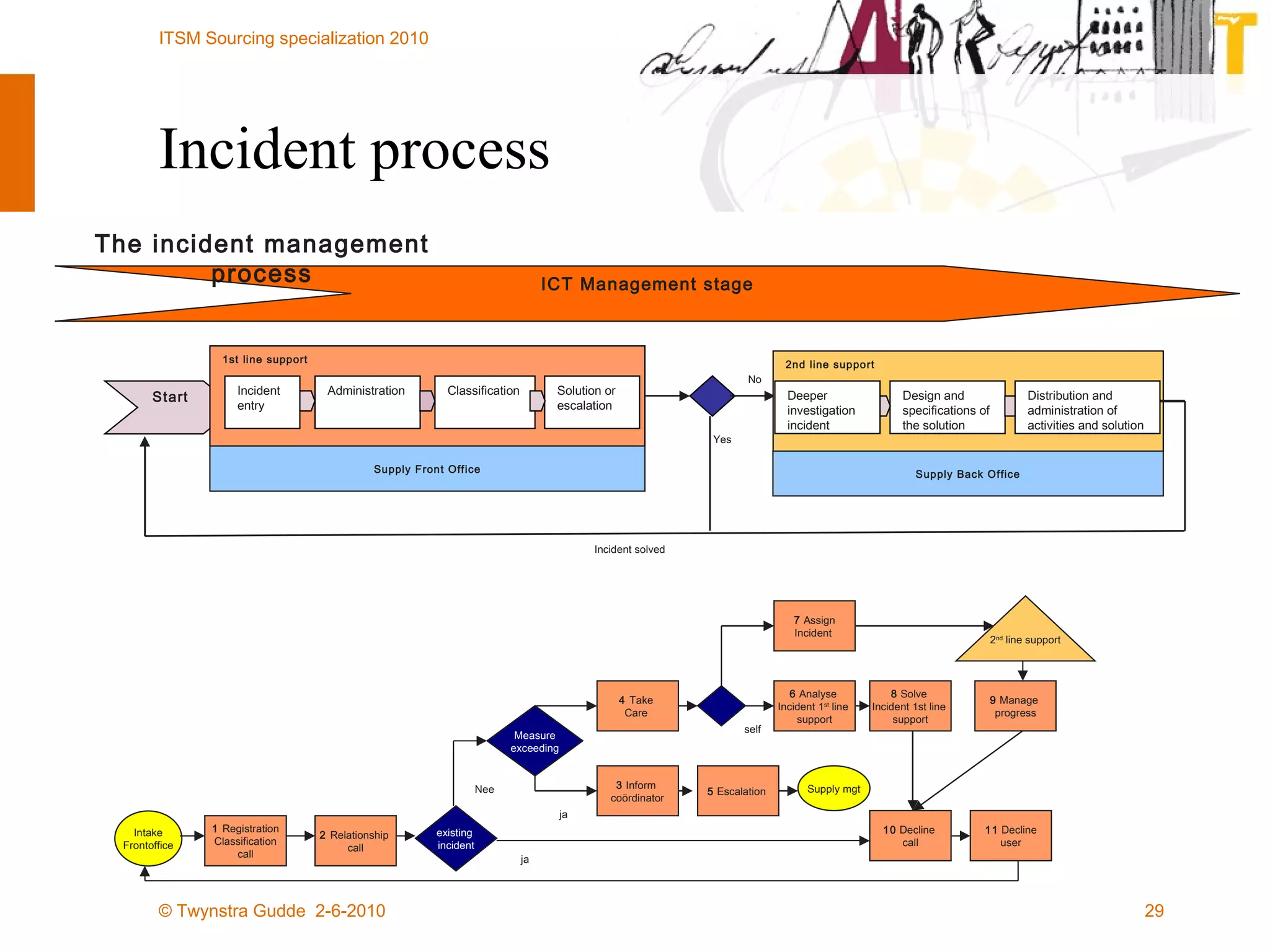
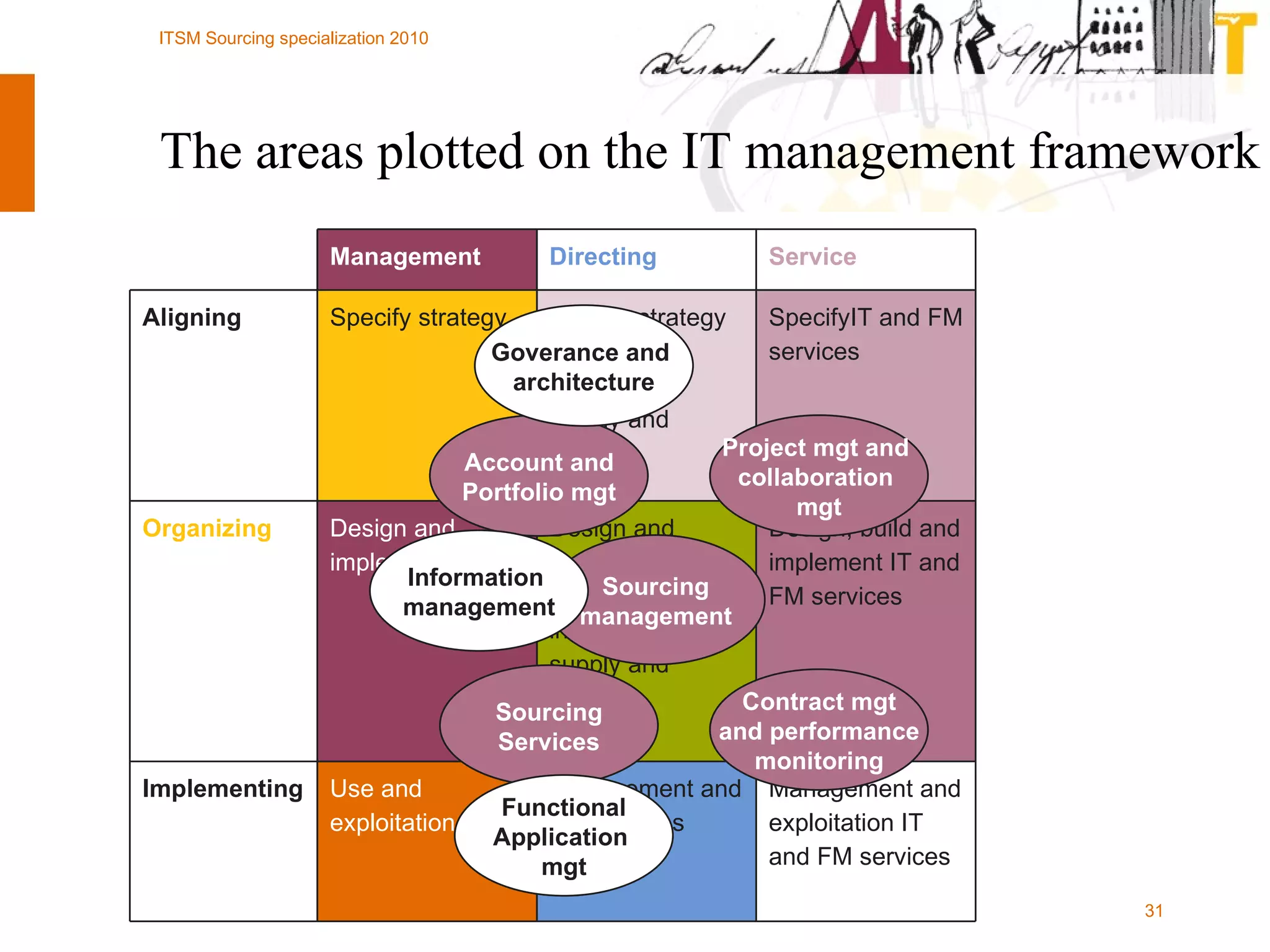
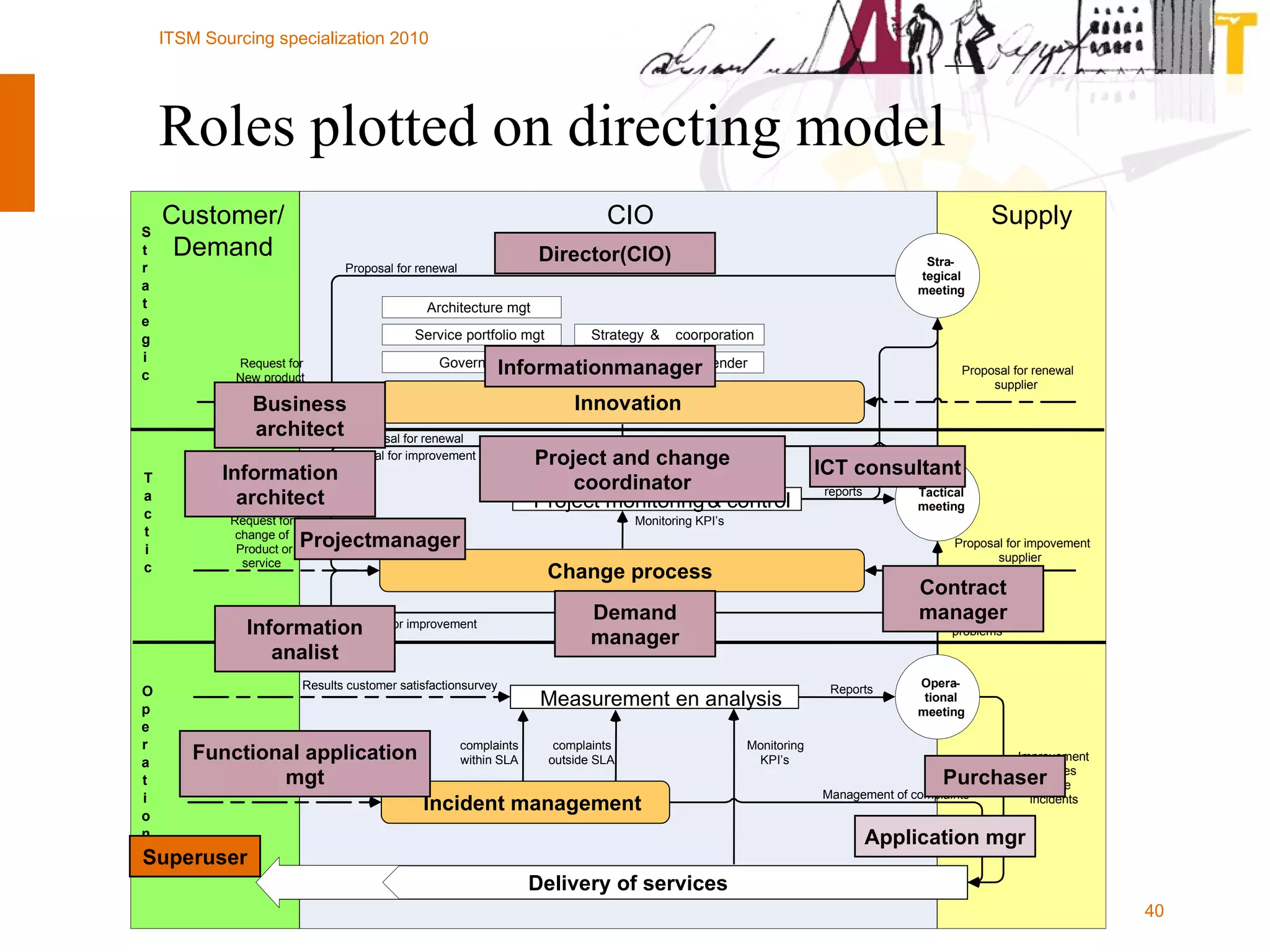
The document outlines the framework for establishing and managing shared service centers (SSCs) within organizations, emphasizing the importance of improving service quality while reducing costs. It discusses the roles and responsibilities involved in directing and sourcing services, including management structures, process models, and the integration of technology. Additionally, it highlights the need for strategic alignment and effective governance in the implementation of SSCs to ensure operational efficiency and innovation.





















![All rights reserved. No part of this presentation may be reproduced or published in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Twynstra Gudde. Frank Willems [email_address] www.twynstragudde.nl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hg-itsm-sourcing-lecture-5-directing-sourcing-and-services-1232313808559843-2/75/Sourcing-Lecture-5-Directing-Sourcing-And-Services-43-2048.jpg)