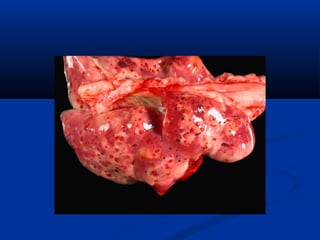
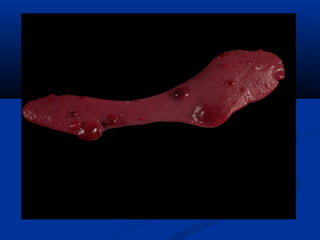
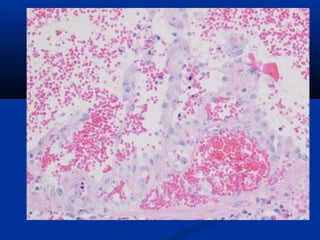
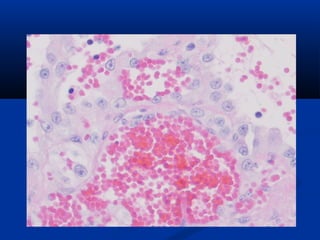
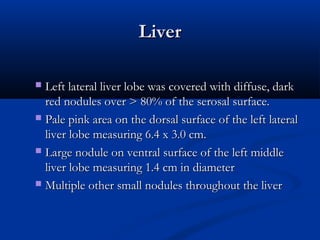
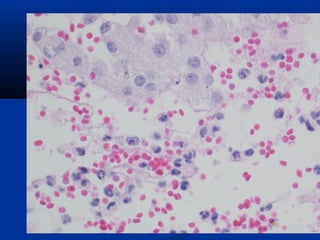
Hemangiosarcoma is a malignant tumor that arises from blood vessel cells. It is more common in dogs than cats and occurs most often in the spleen, heart, and skin. Clinical signs depend on the location of the tumor and may include weakness, collapse, or abdominal swelling. Diagnosis is made through biopsy and histopathology. Prognosis is generally poor but may be extended through surgery and chemotherapy. Treatment is aimed at completely removing single tumors when possible or managing clinical signs.