The document outlines key aspects of human resource management and job design discussed in Chapter 10, including:
1. It discusses employment stability policies like following demand exactly or holding employment constant.
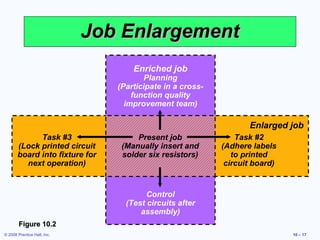
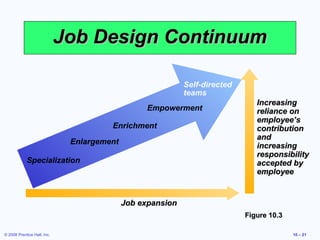
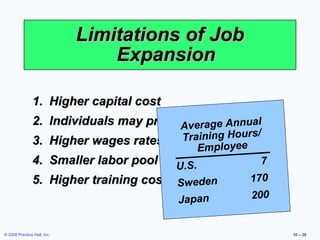
2. It covers topics like job classification, work schedules, job design approaches like specialization and expansion.
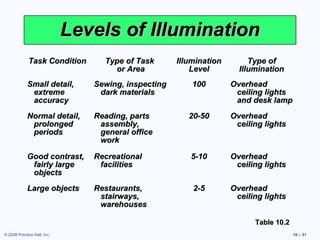
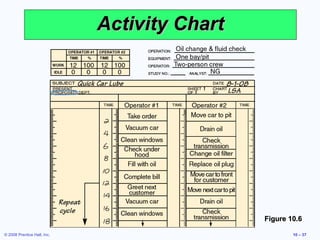
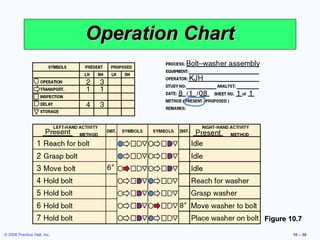
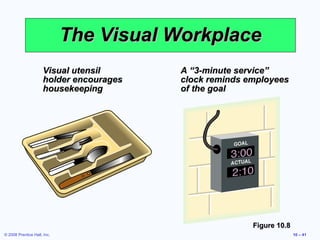
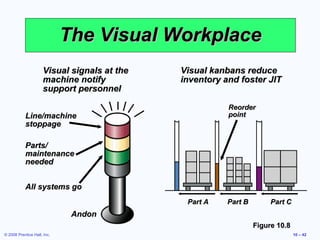
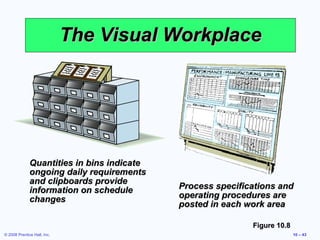
3. It also discusses ergonomics, motivation systems, and the use of visual tools in the workplace.