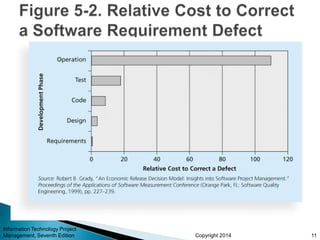
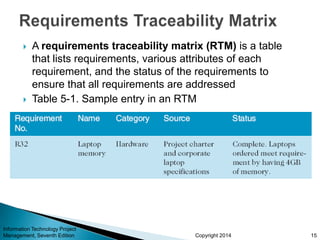
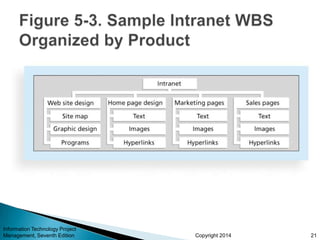
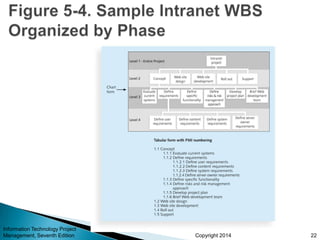
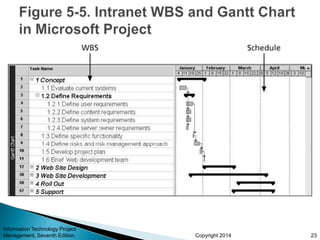
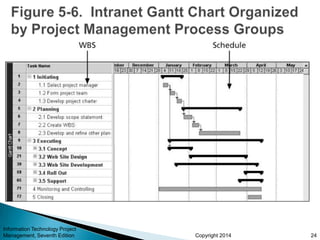
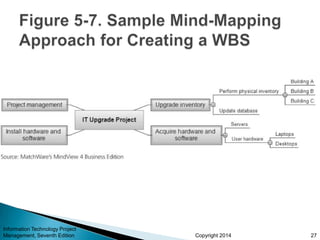
This document provides an overview of scope management for IT projects. It discusses planning scope management, collecting requirements, defining scope, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), validating scope, and controlling scope. A WBS decomposes project deliverables into smaller components to aid in planning, scheduling, resource allocation, and change management. Maintaining a WBS dictionary with detailed descriptions of each item is important. Scope management aims to formally accept completed project deliverables and control any changes to the agreed-upon scope.