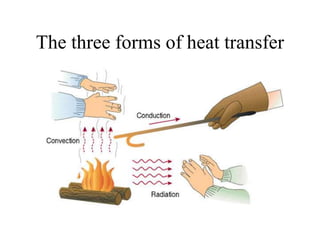
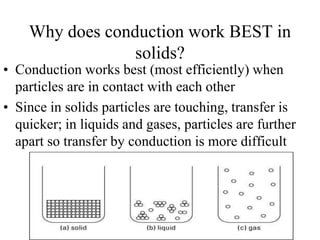
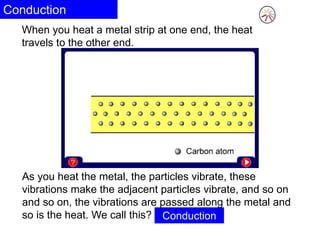
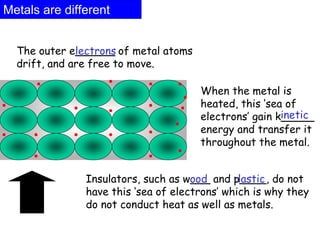
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from a warmer object to a cooler one. It is a process, not a physical thing that can be contained. Thermal energy is the total kinetic and potential energy of an object's molecules. Heat transfer occurs through three main methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the direct transfer of heat between objects in contact through particle vibration; it is most effective in solids and fluids.