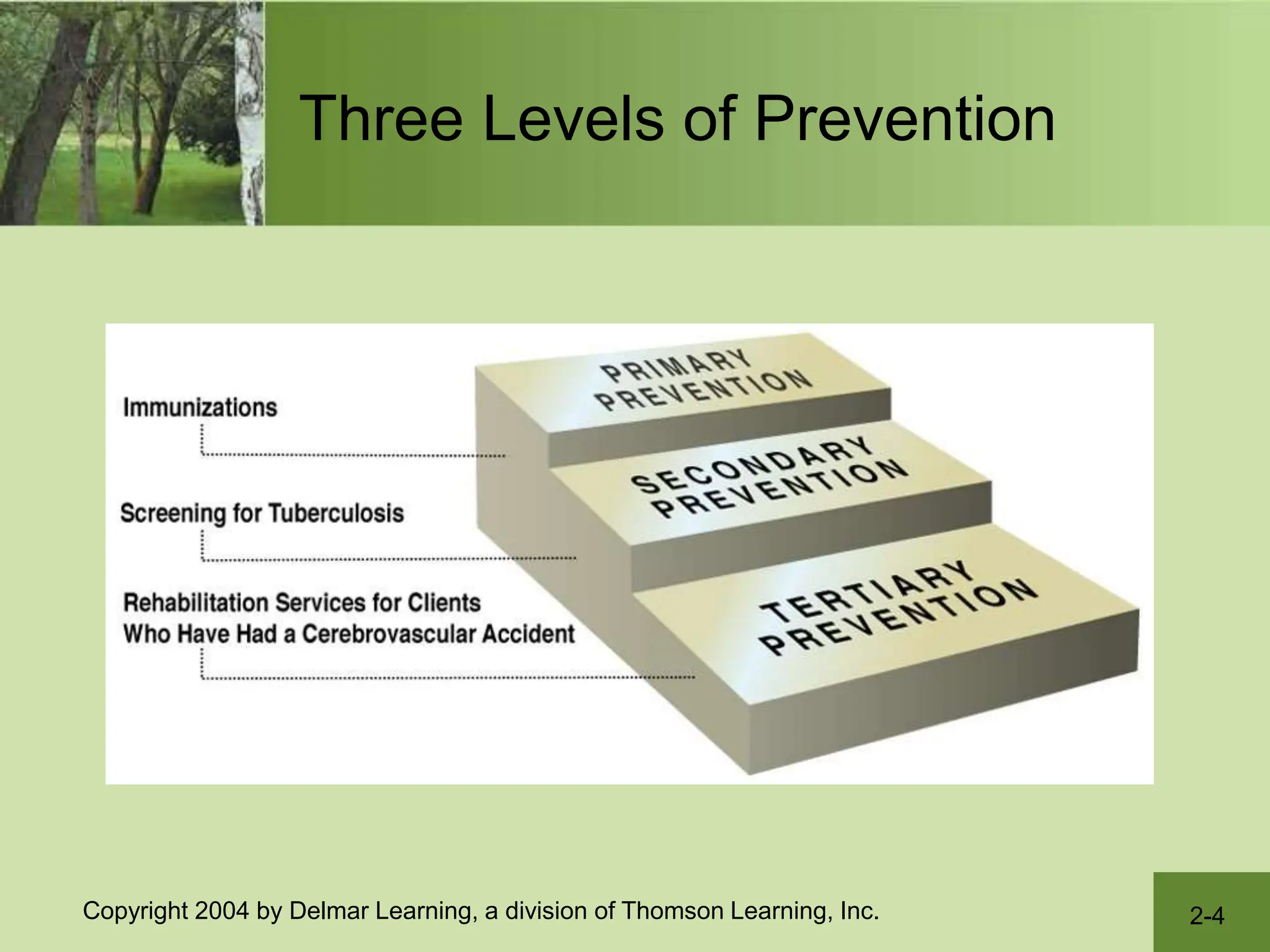
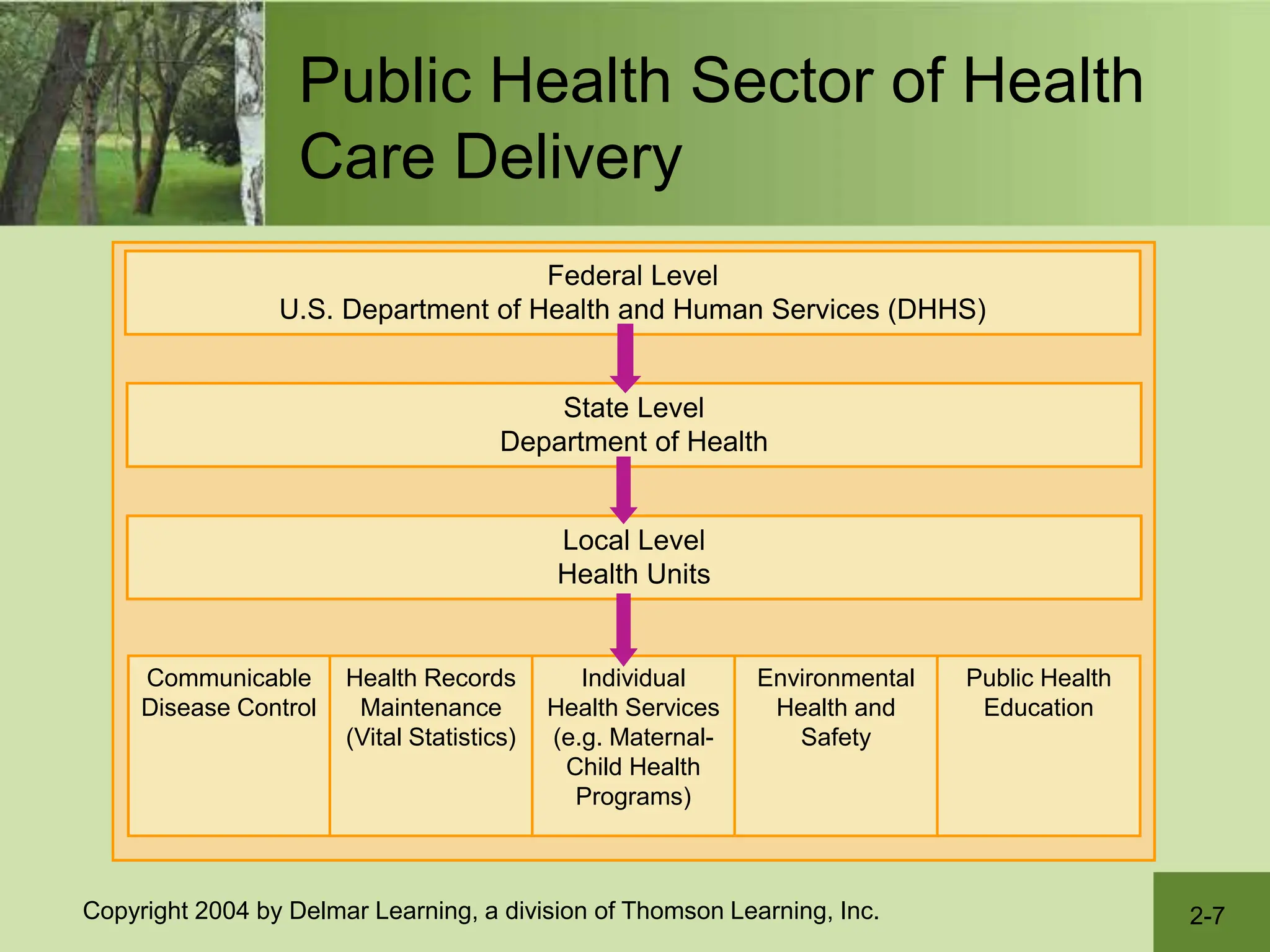
The document describes the US health care delivery system. It discusses that nursing is a major component and outlines the various levels of care - primary, secondary, and tertiary. It also outlines the public and private sectors of health care settings and lists the various roles that make up the health care team. Finally, it discusses challenges facing the system like rising costs, access and quality issues, and vulnerable populations.