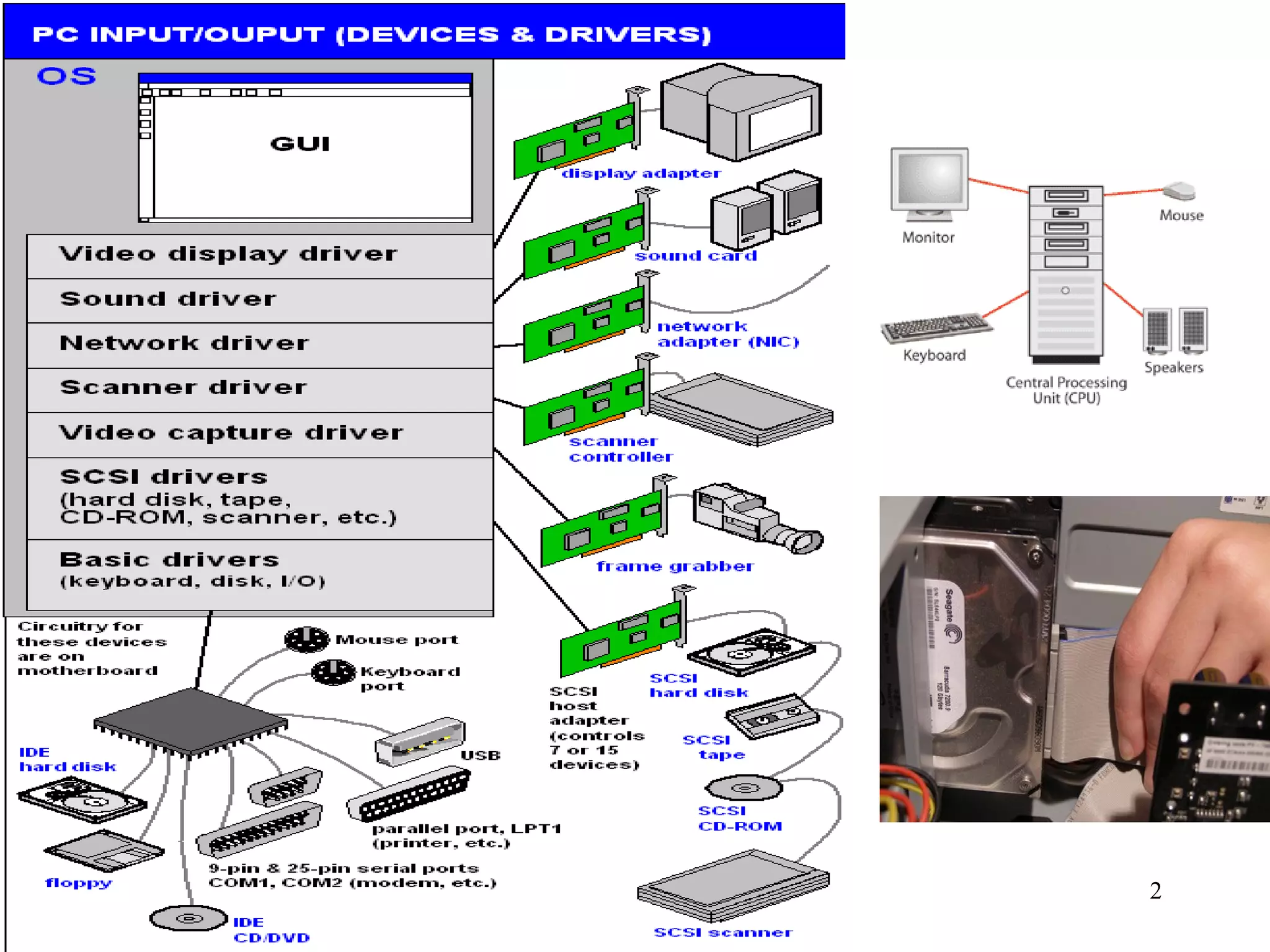
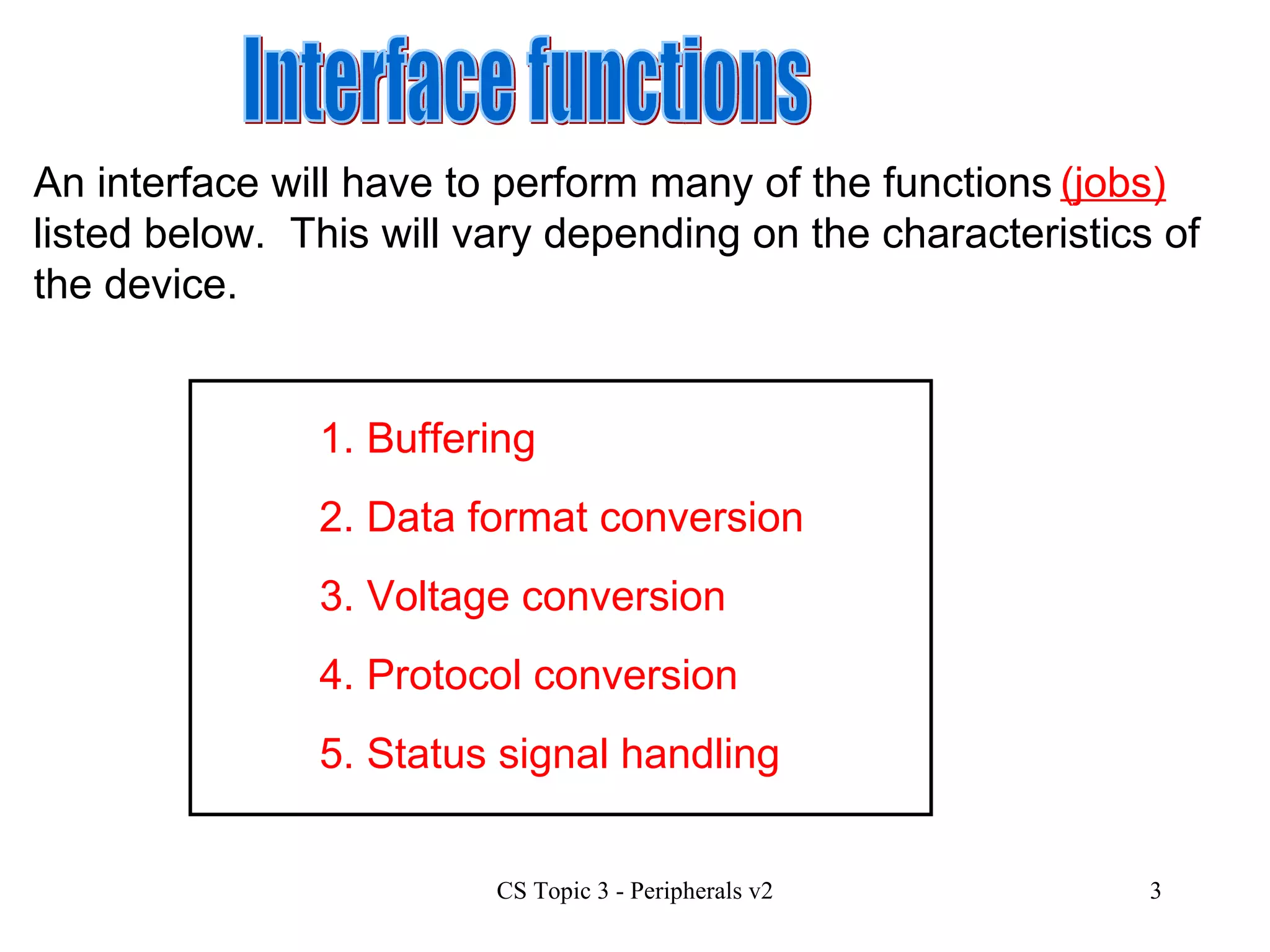
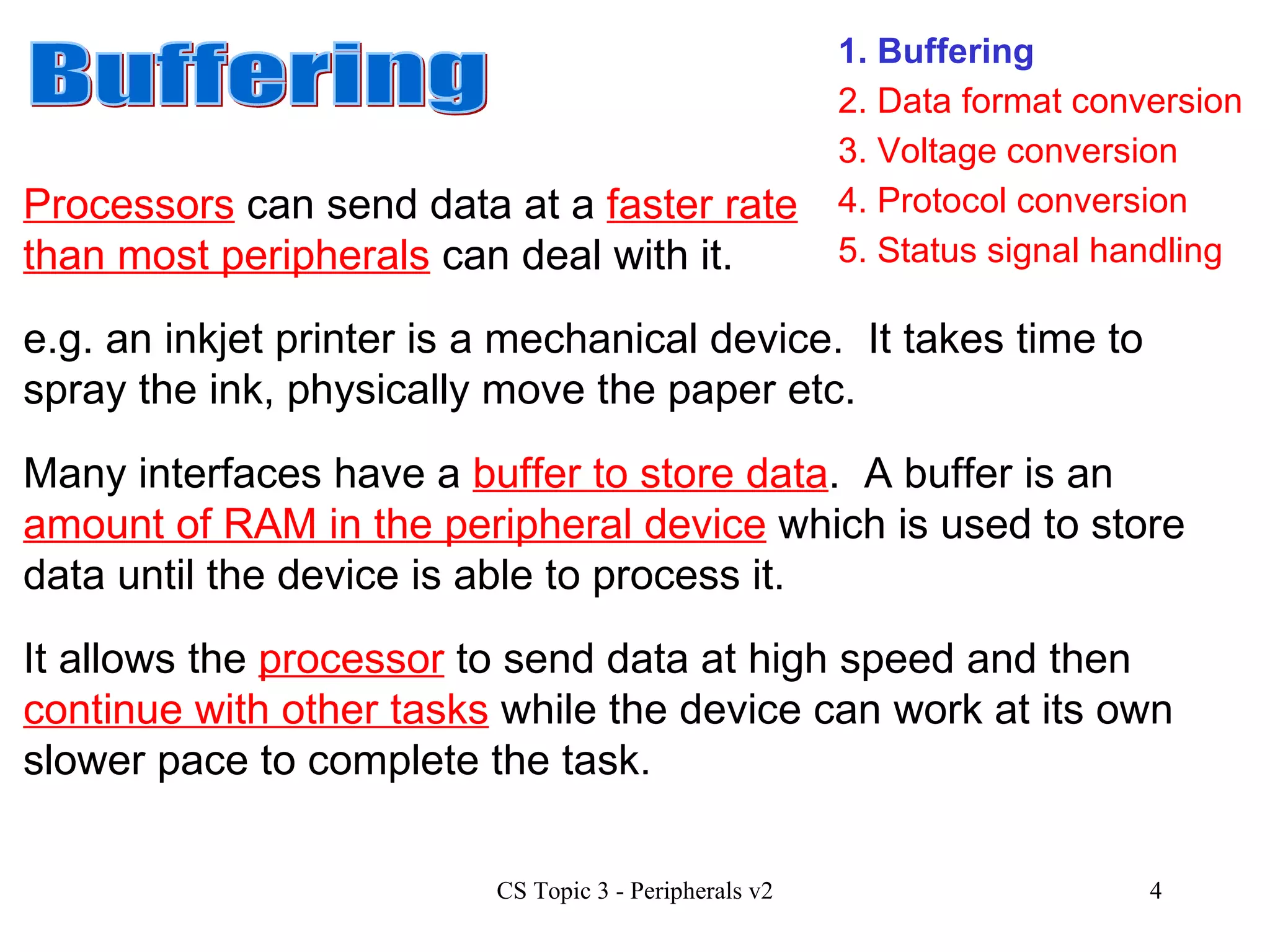
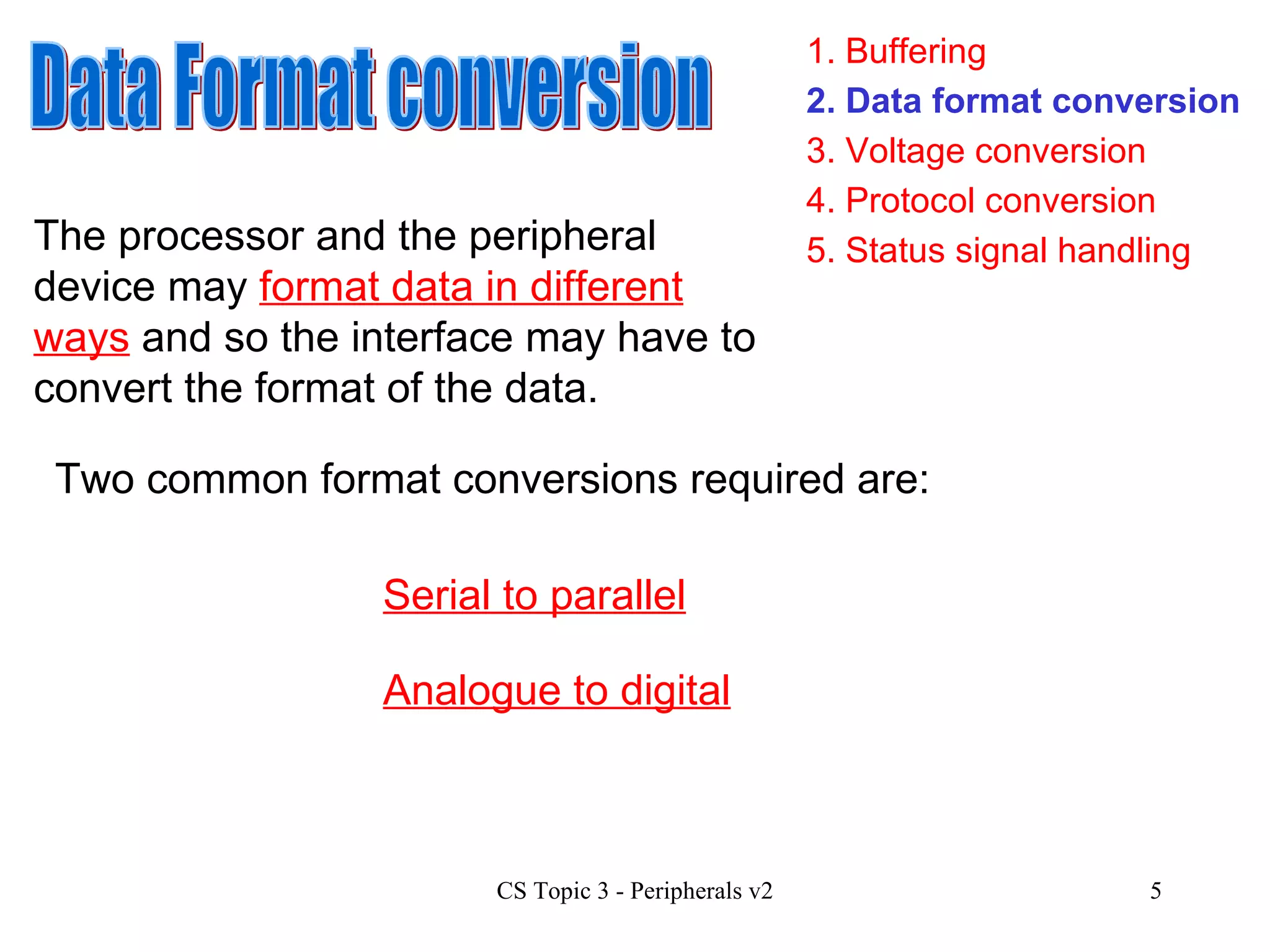
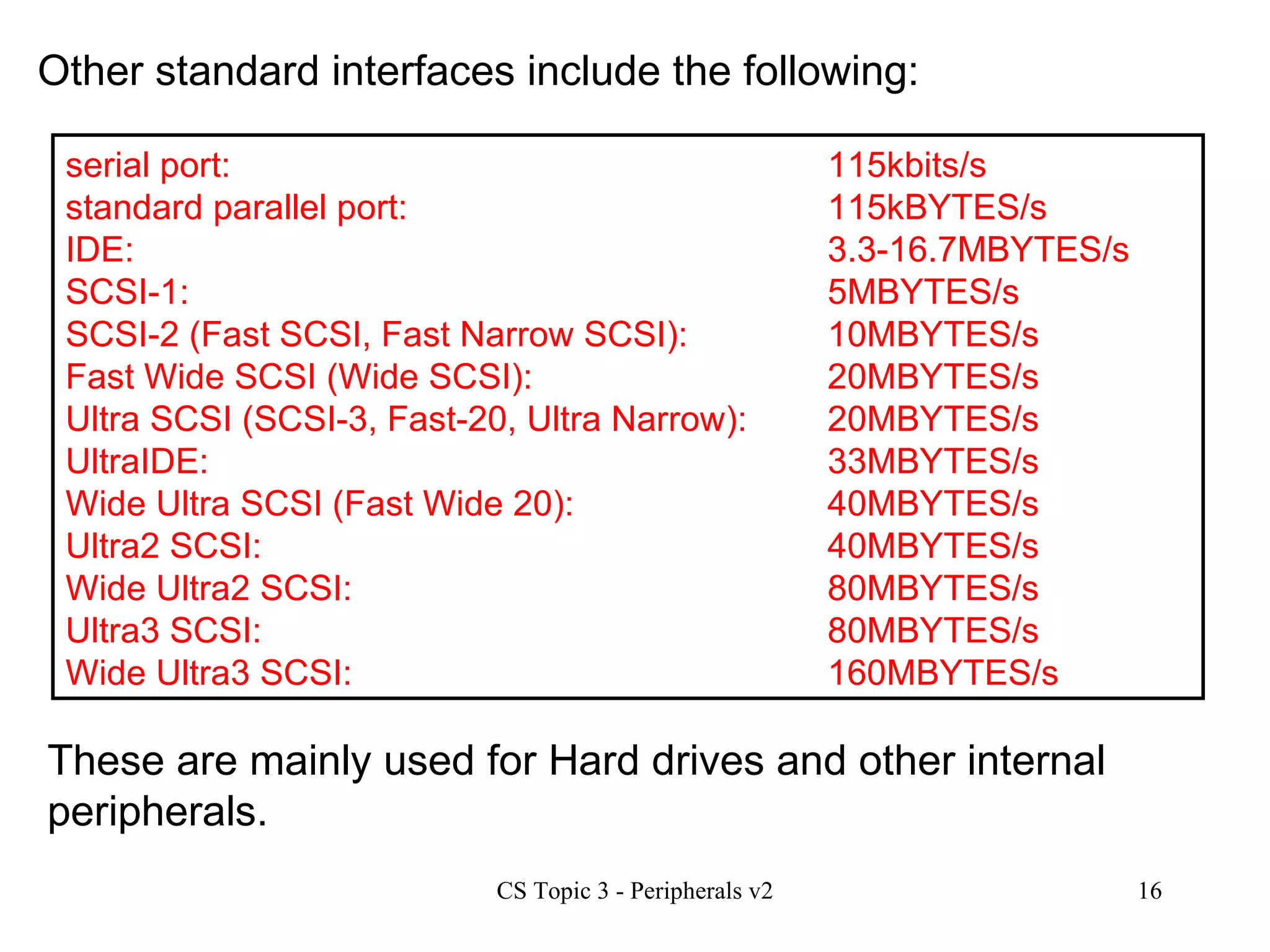
An interface allows a processor and peripheral device to communicate correctly by compensating for differences in their operating characteristics such as speed, data format, and voltages. Key interface functions include buffering, data format conversion, voltage conversion, protocol conversion, and status signal handling. Buffering uses RAM in the peripheral to store data until it can be processed. Data format conversion deals with differences in serial/parallel and analog/digital data. Voltage conversion adjusts voltages between the processor and device. Protocol conversion ensures communication follows agreed rules. Status signals indicate the device's readiness. Common interfaces today include USB, FireWire, and Bluetooth.