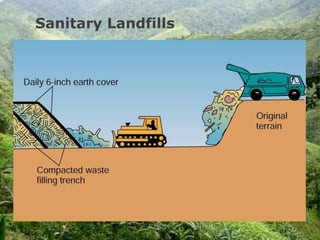
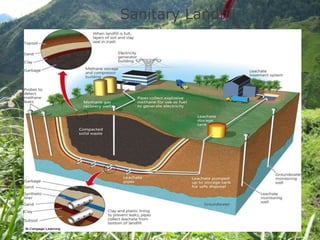
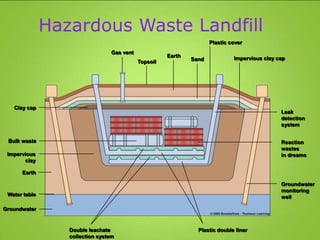
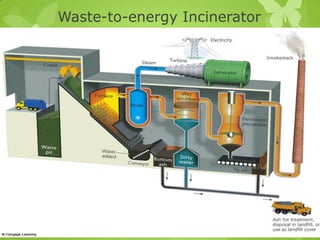
This document discusses hazardous and toxic wastes. Hazardous wastes are materials that are capable of harming people and the environment, such as acids, heavy metals, and radioactive materials. Toxic wastes are materials that can cause death, injury, or birth defects and include dioxins, heavy metals, and radioactive waste. Common methods of disposal for hazardous and toxic wastes include landfilling, incineration, and recycling. Reducing, reusing, and recycling are presented as better alternatives to disposal to reduce waste.