The document discusses functional programming, particularly focusing on Haskell, its key features such as purity, laziness, strong typing, and its applications in real-world scenarios like quiz modeling and database systems. It contrasts functional programming with imperative programming, emphasizing the benefits of reduced code complexity and improved clarity. Additionally, it presents various Haskell examples and touches on the language's potential for mainstream adoption and its advantages for future programming paradigms.





![Imperative programming
●
records =
[ "one", "two", "three", "four", "five" ]
filtered = []; j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < length records; i++) {
if (records[i] matches “o”) {
filtered[j++] = records[i];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-6-320.jpg)
![Imperative programming
●
records =
[ "one", "two", "three", "four", "five" ]
filtered = []; j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < length records; i++) {
if (records[i] matches “o”) {
filtered[j++] = records[i];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-7-320.jpg)



![Your language has this construct
● Perl: my @filtered = grep /o/, @records;
● .Net: var filtered = from r in records
where r.match('o') select r
● Ruby: @filtered = @records.grep /o/
● Python: filtered = [x for x in records
if re.match('o', x)]
● etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-11-320.jpg)




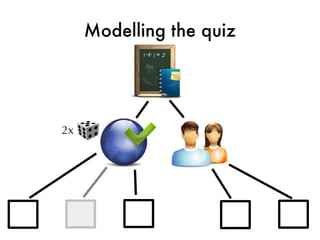
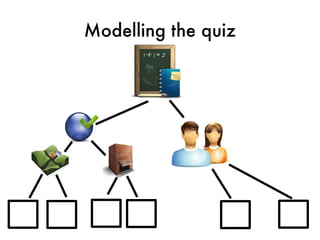
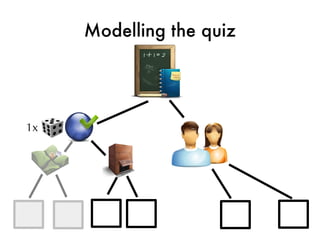

![Quiz data type
●
data QuizNode =
Quiz Name [QuizNode]
| Section Name Score [QuizNode]
| RandomSection Name Score Choose [QuizNode]
| Question Name Score Answer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-23-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
●
data QuizNode =
Quiz Name [QuizNode]
| Section Name Score [QuizNode]
| RandomSection Name Score Choose [QuizNode]
| Question Name Score Answer
●
type Name = String
type Score = Int
type Choose = Int](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-24-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
●
data QuizNode =
Quiz Name [QuizNode]
| Section Name Score [QuizNode]
| RandomSection Name Score Choose [QuizNode]
| Question Name Score Answer
●
data Answer = MultiChoice [BoolAnswer]
| StringChoice [String]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-25-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
●
data QuizNode =
Quiz Name [QuizNode]
| Section Name Score [QuizNode]
| RandomSection Name Score Choose [QuizNode]
| Question Name Score Answer
●
data Answer = MultiChoice [BoolAnswer]
| StringChoice [String]
●
data BoolAnswer = BoolAnswer Bool String](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-26-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
quiz,geo,pop :: QuizNode
quiz = Quiz “General Knowledge Quiz” [ pop, geo ]
geo = RandomSection “Geography” 40 2 [
Question “What is the capital of England?”
2 $ StringChoice [“London”],
Question “What is the capital of France?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Paris”],
Question “What is the capital of Finland?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Helsinki”],
Question “What is the capital of Italy?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Rome”, “Roma”],
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-27-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
quiz,geo,pop :: QuizNode
quiz = Quiz “General Knowledge Quiz” [ pop, geo ]
geo = RandomSection “Geography” 40 2 [
Question “What is the capital of England?”
2 $ StringChoice [“London”],
Question “What is the capital of France?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Paris”],
Question “What is the capital of Finland?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Helsinki”],
Question “What is the capital of Italy?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Rome”, “Roma”],
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-28-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
quiz,geo,pop :: QuizNode
quiz = Quiz “General Knowledge Quiz” [ pop, geo ]
geo = RandomSection “Geography” 40 2 [
Question “What is the capital of England?”
2 $ StringChoice [“London”],
Question “What is the capital of France?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Paris”],
Question “What is the capital of Finland?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Helsinki”],
Question “What is the capital of Italy?”
2 $ StringChoice [“Rome”, “Roma”],
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-29-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
pop = Section “Pop music” 60 [
Question “Which of these are Beatles?” 5
$ MultiChoice [
y “John”,
y “Paul”,
y “George”,
y “Ringo”,
n “Bob”,
n “Jason” ],
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-30-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
pop = Section “Pop music” 60 [
Question “Which of these are Beatles?” 5
$ MultiChoice [
BoolAnswer True “John”,
BoolAnswer True “Paul”,
BoolAnswer True “George”,
BoolAnswer True “Ringo”,
BoolAnswer False “Bob”,
BoolAnswer False “Jason” ],
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-31-320.jpg)
![Quiz data type
pop = Section “Pop music” 60 [
Question “Which of these are Beatles?” 5
$ MultiChoice [
y “John”,
y “Paul”,
y “George”,
y “Ringo”,
n “Bob”,
n “Jason” ],
...
y,n :: String -> BoolAnswer
y = BoolAnswer True
n = BoolAnswer False](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-32-320.jpg)
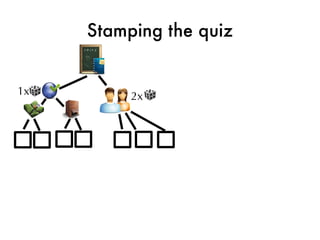
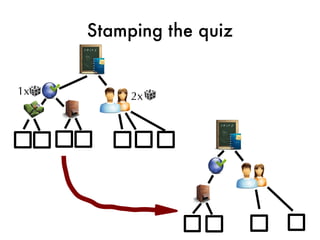
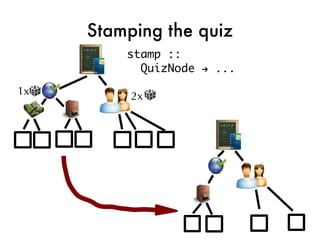
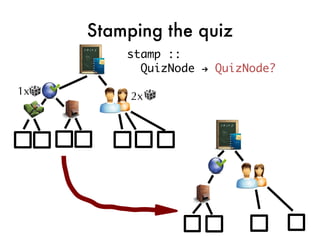
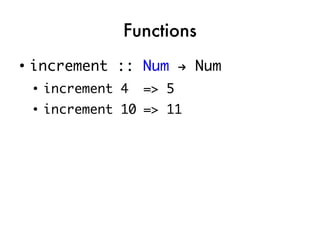
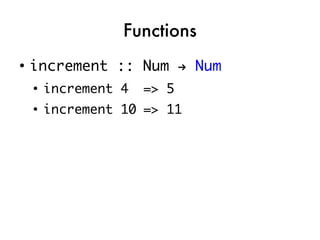
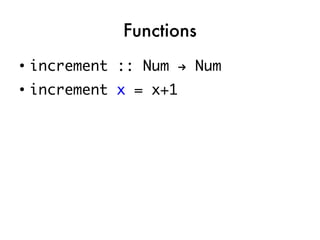
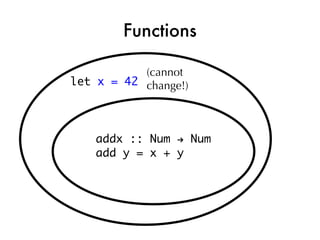
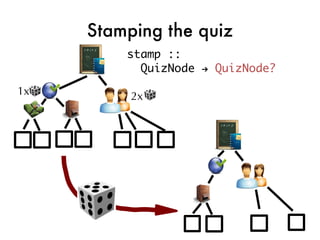
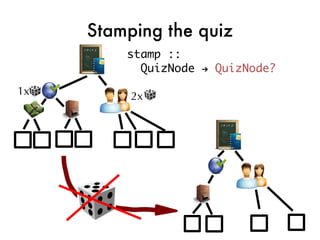
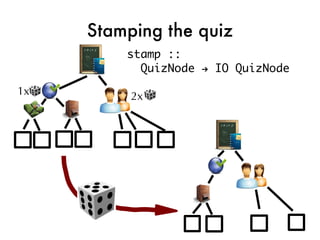

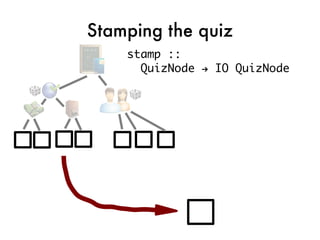
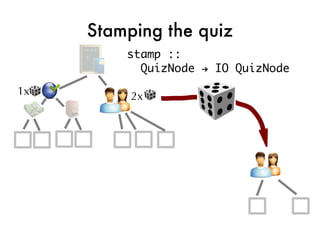
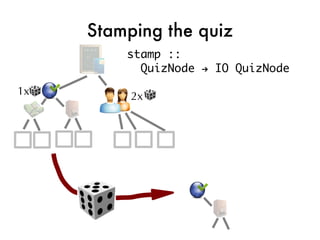
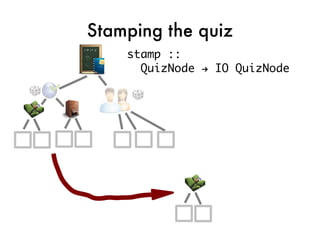
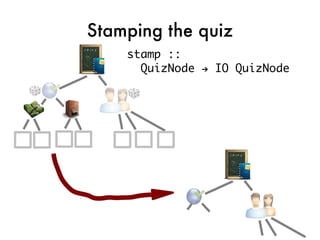
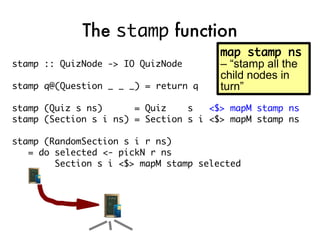
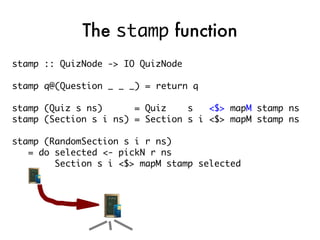
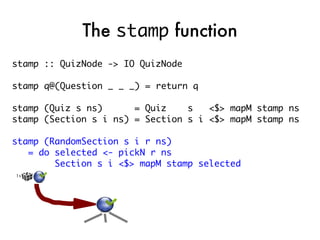
![Taking the quiz!
●
takeNode ::
QuizNode -> IO CompletedNode
●
printQuestion ::
QuizNode -> IO ()
●
showBoolTextAnswers ::
[BoolAnswer] -> String
●
checkAnswer ::
String -> Answer -> Bool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-58-320.jpg)
![Taking the quiz!
●
takeNode ::
QuizNode -> IO CompletedNode
●
printQuestion ::
QuizNode -> IO ()
●
showBoolTextAnswers ::
[BoolAnswer] -> String
●
checkAnswer ::
String -> Answer -> Bool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-59-320.jpg)
![Taking the quiz!
●
takeNode ::
QuizNode -> IO CompletedNode
●
printQuestion ::
QuizNode -> IO ()
●
showBoolTextAnswers ::
[BoolAnswer] -> String
●
checkAnswer ::
String -> Answer -> Bool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-60-320.jpg)
![Taking the quiz!
●
takeNode ::
QuizNode -> IO CompletedNode
●
printQuestion ::
QuizNode -> IO ()
●
showBoolTextAnswers ::
[BoolAnswer] -> String
●
checkAnswer ::
String -> Answer -> Bool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-61-320.jpg)
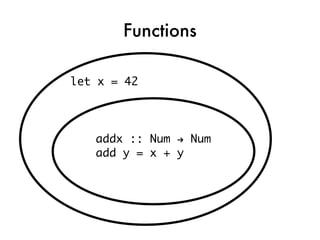
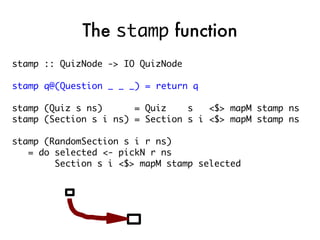
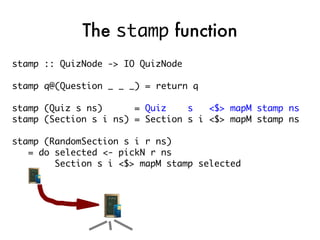
![takeNode
takeNode node@(Question s i a) = do
printQuestion node
ans <- getLine
let correct = checkAnswer ans a
let score = if correct
then (i,i) else (0,i)
putStrLn $ if correct
then “Correct!” else “Wrong!”
return $
CompletedNode ans score [] node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fptalk-110605060436-phpapp01/85/Haskell-in-the-Real-World-62-320.jpg)