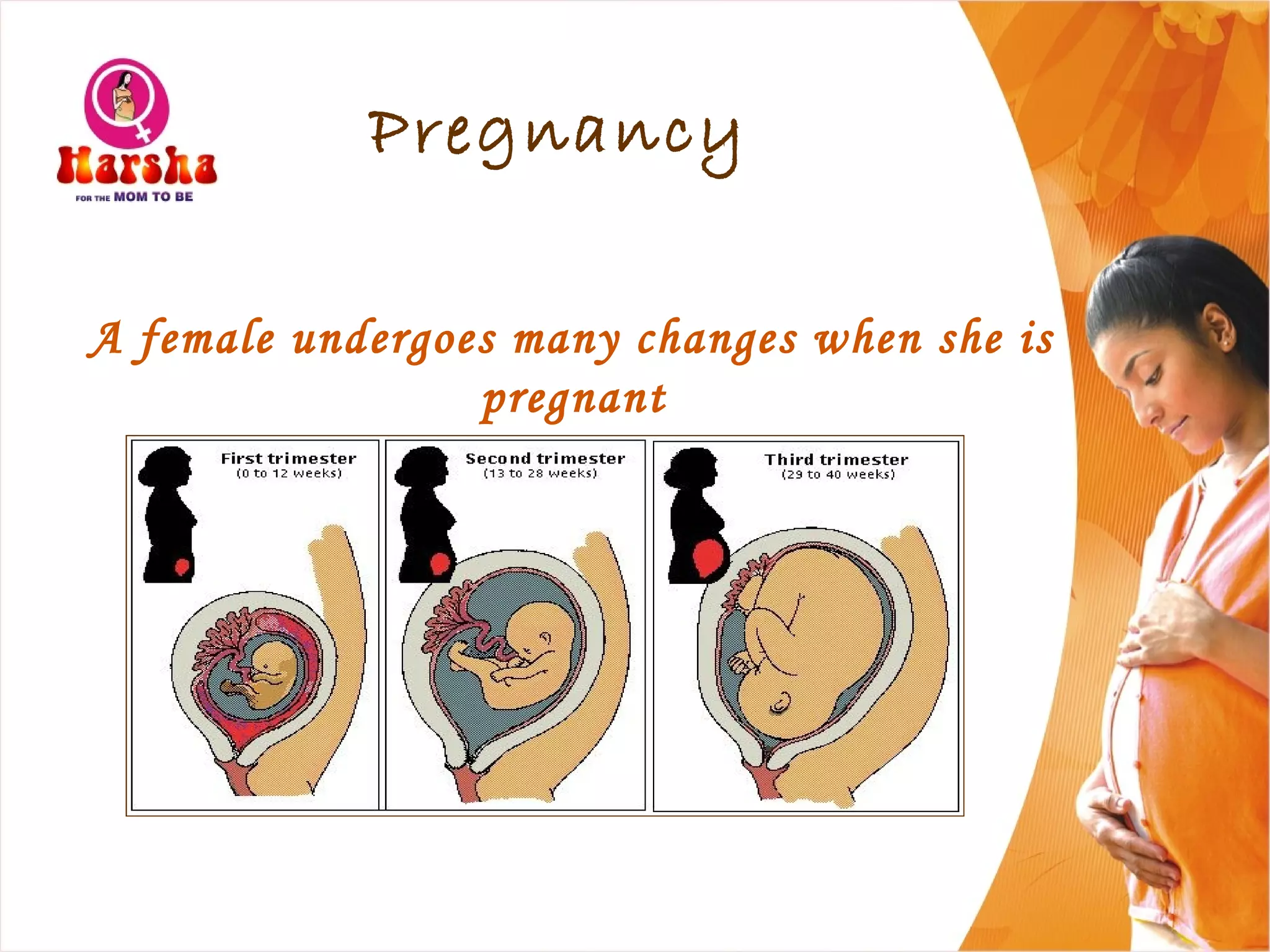
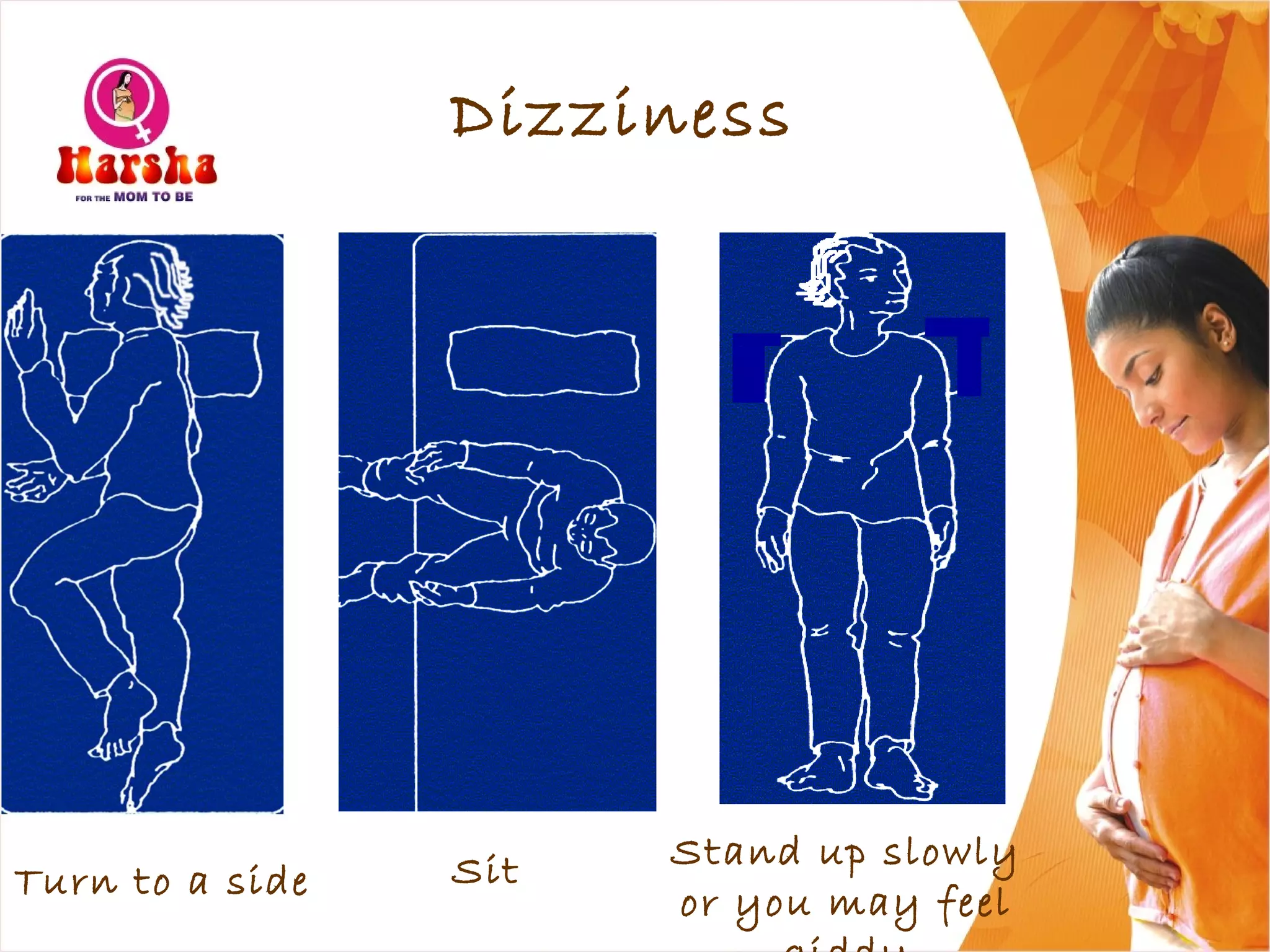
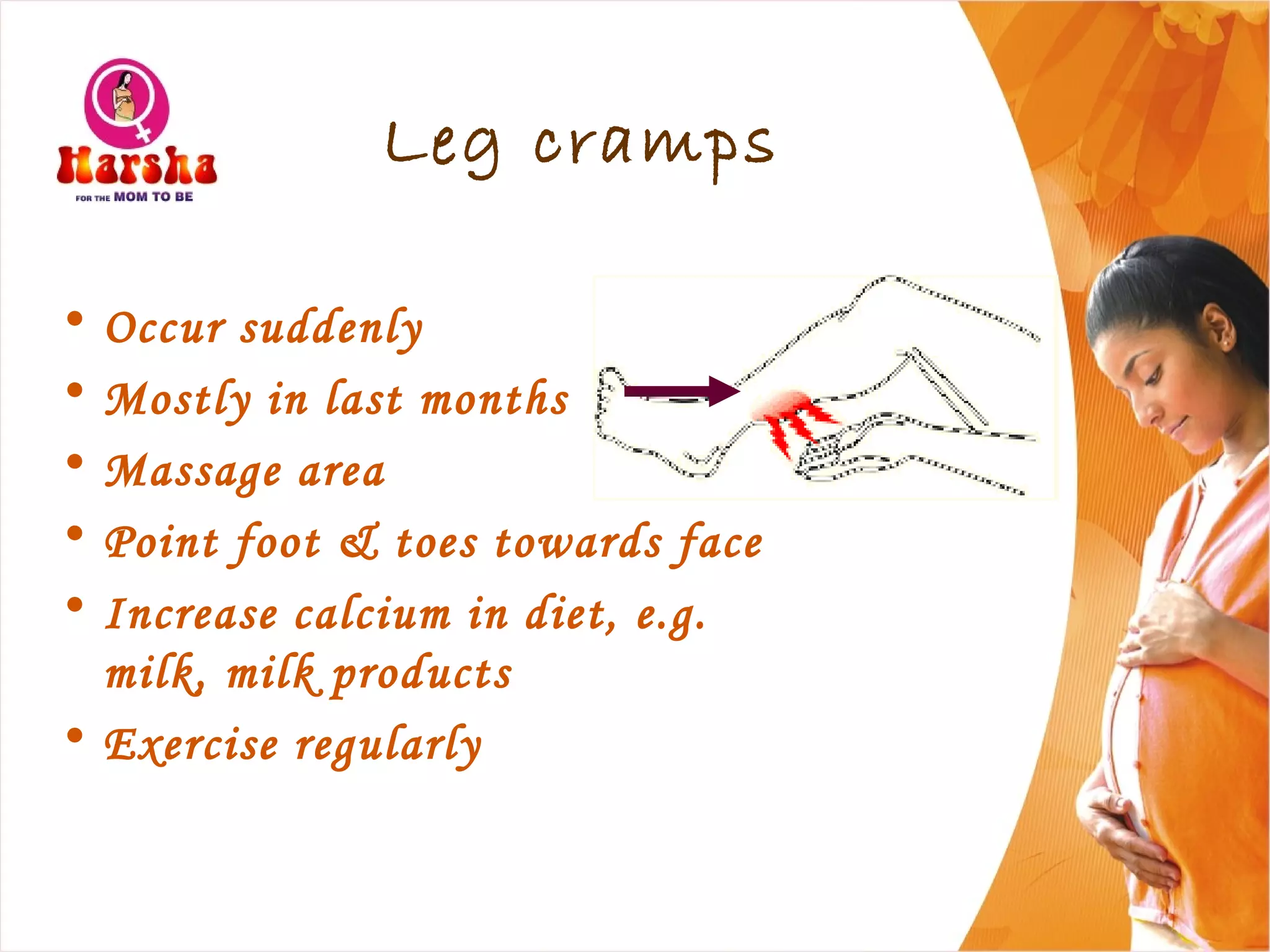
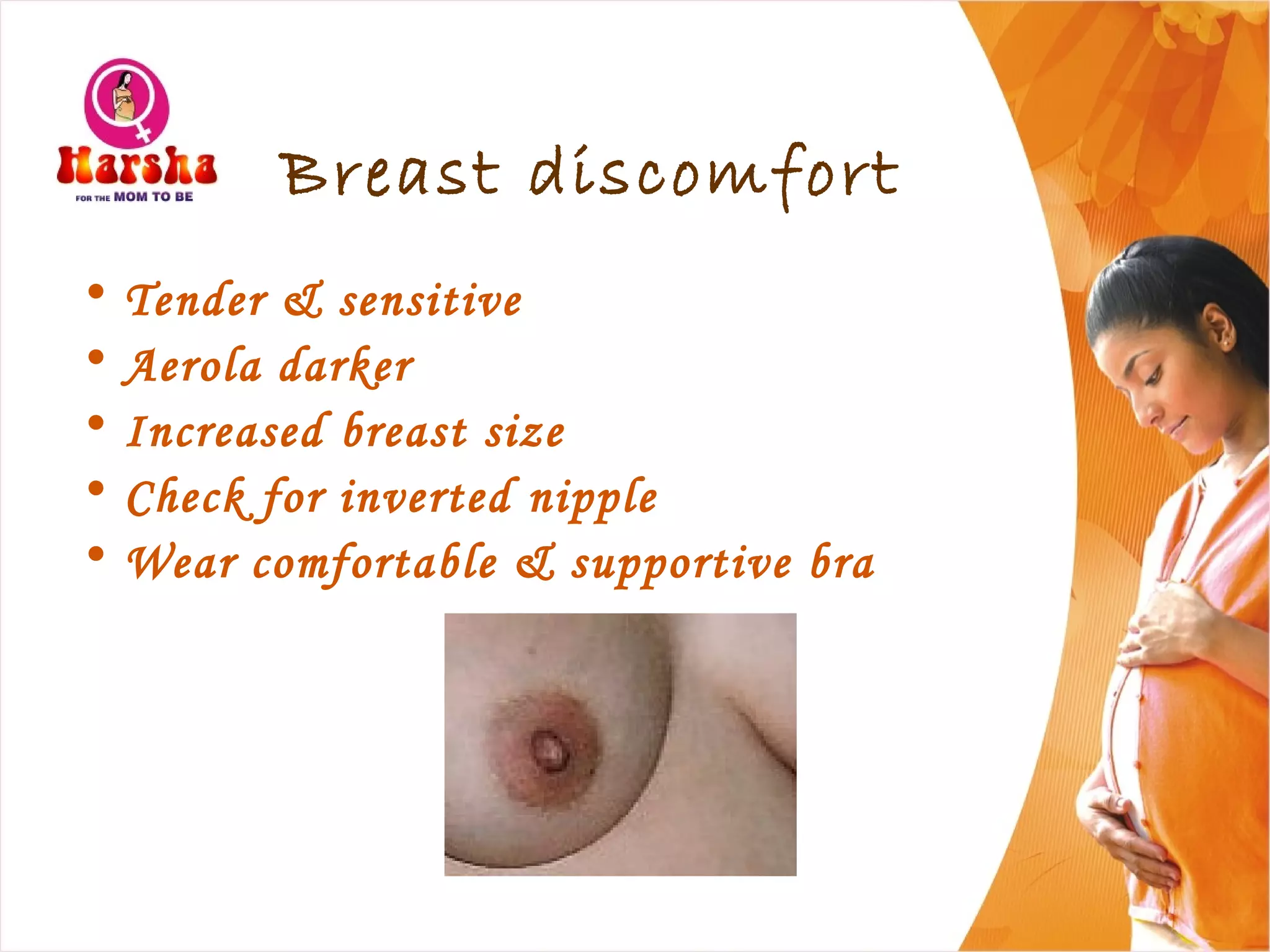
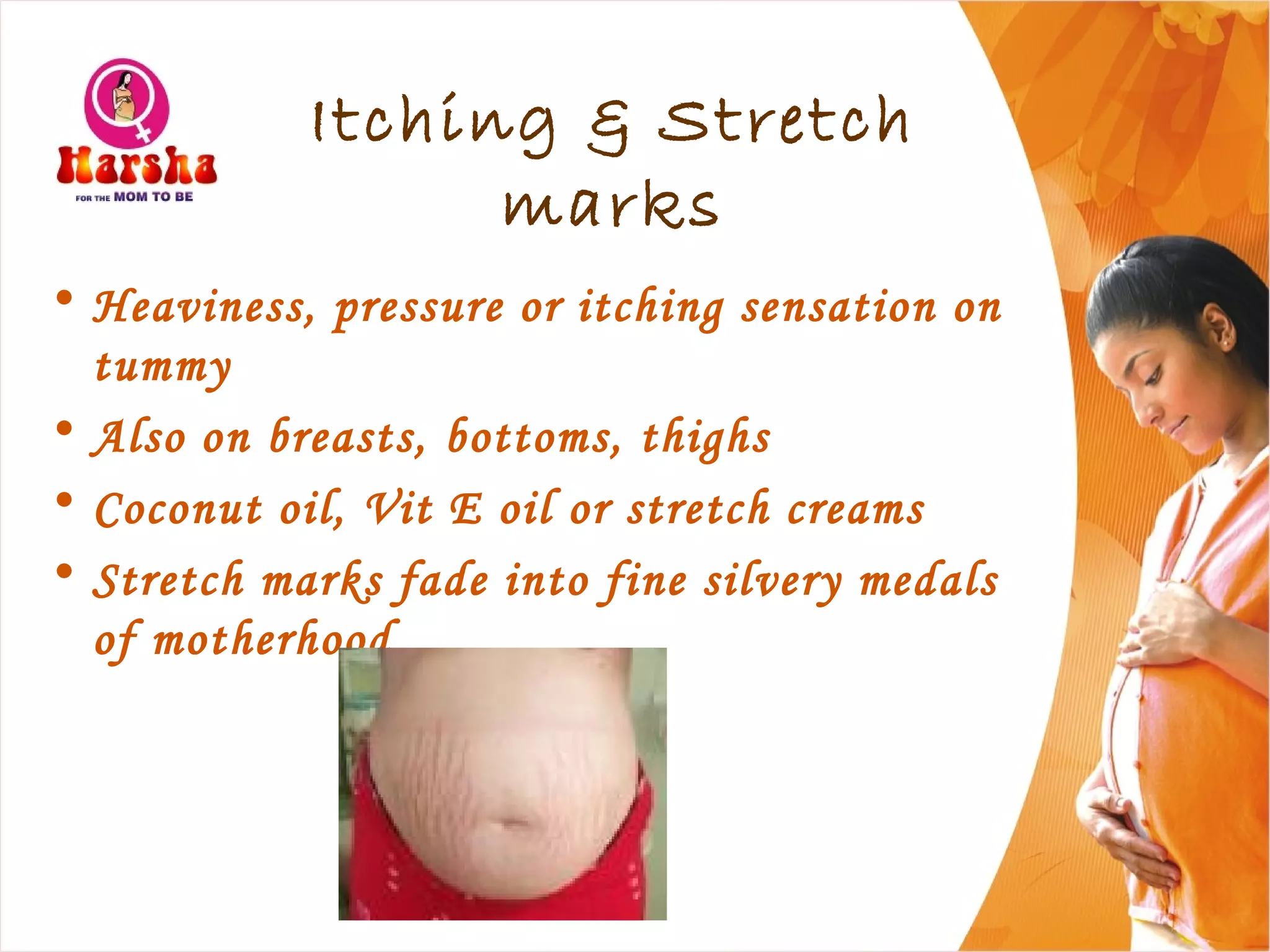
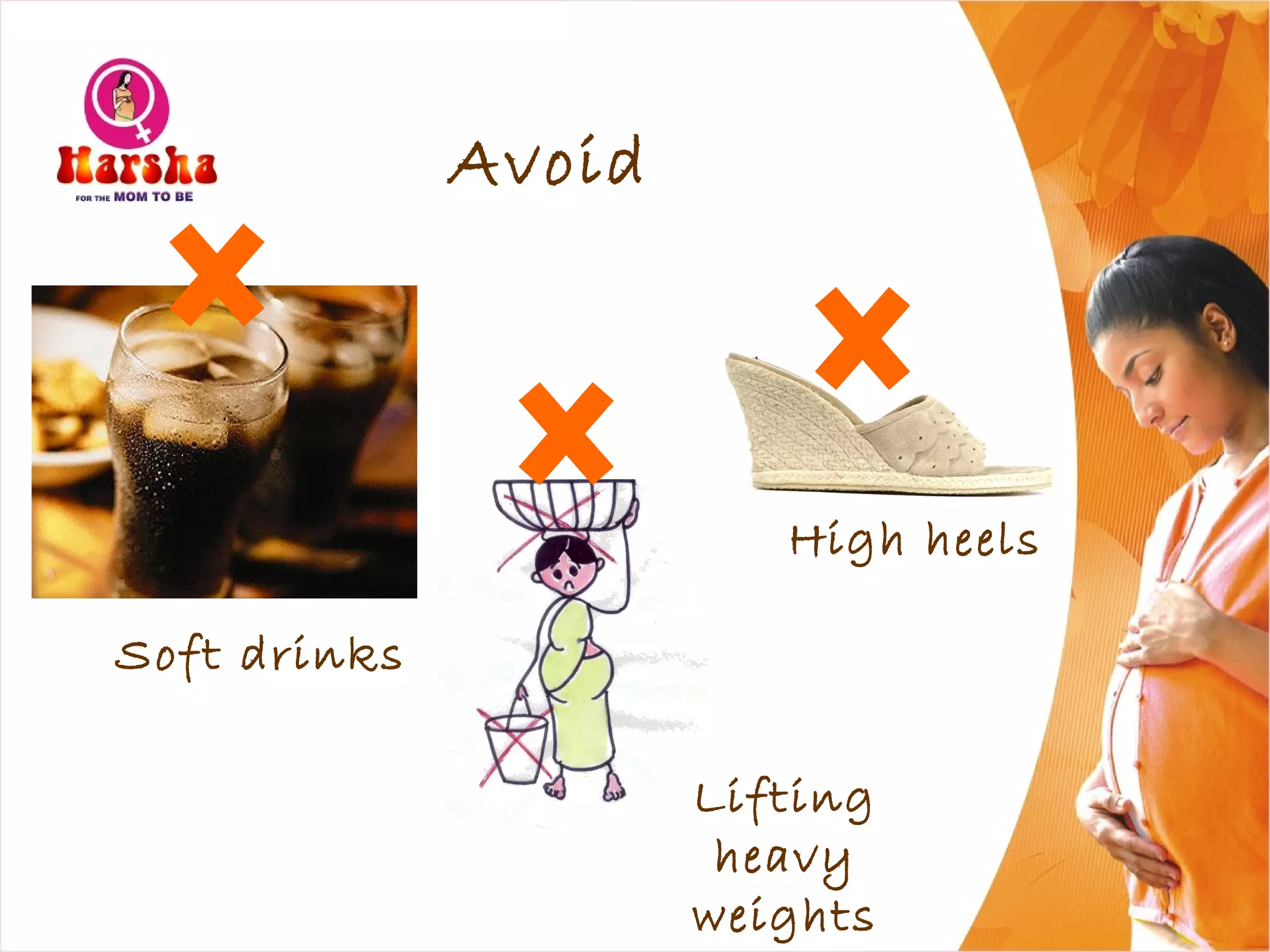
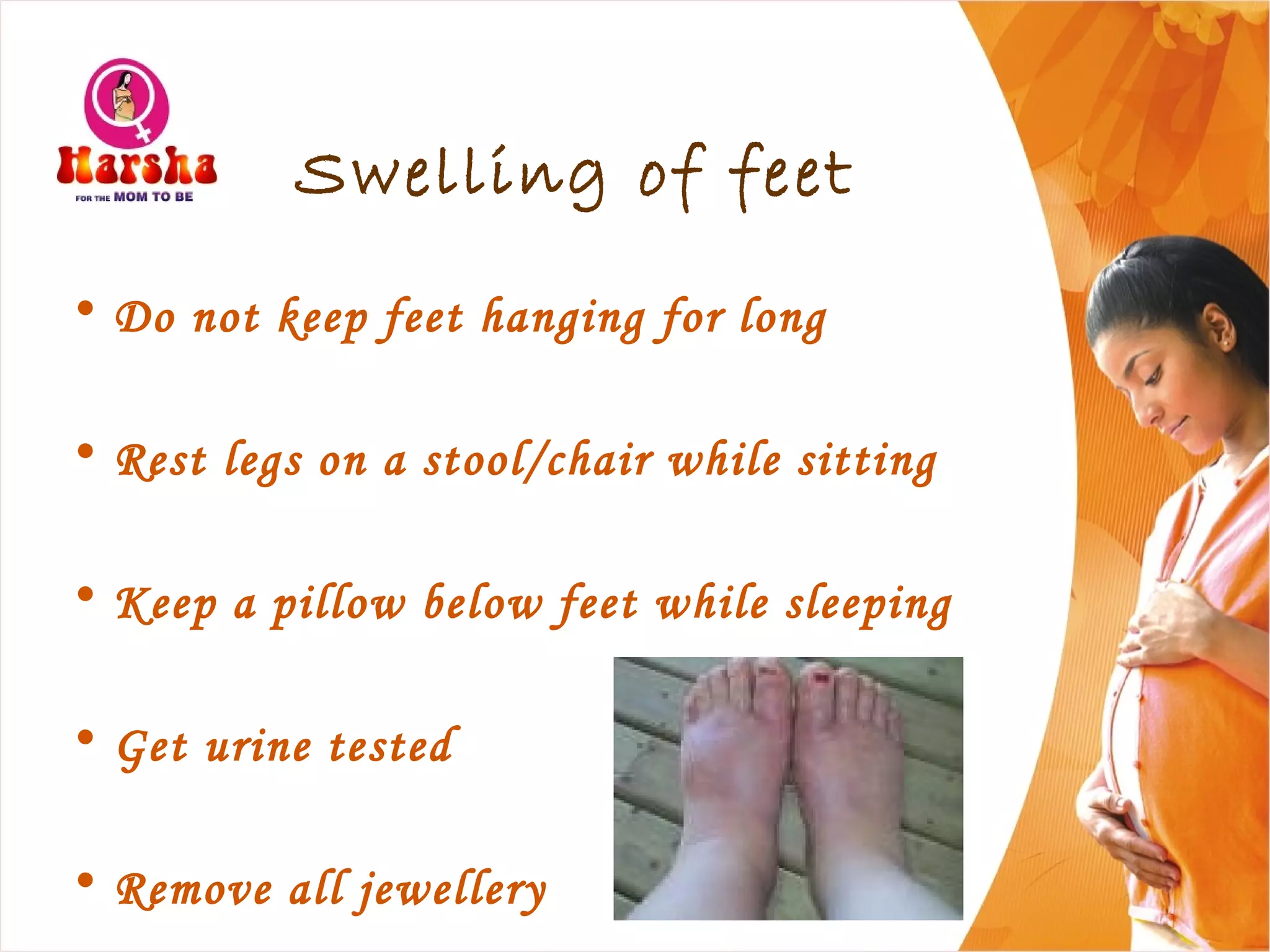
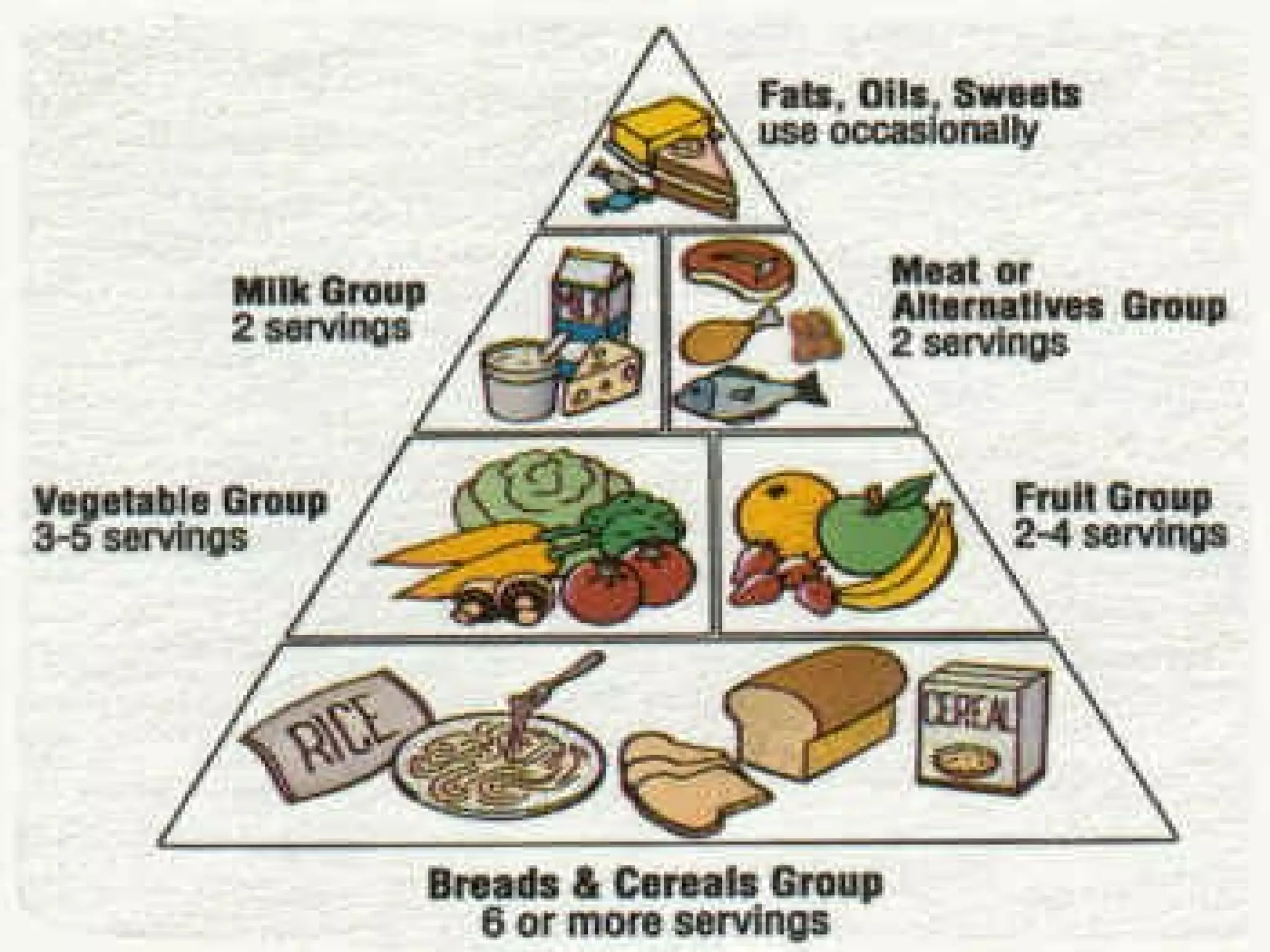
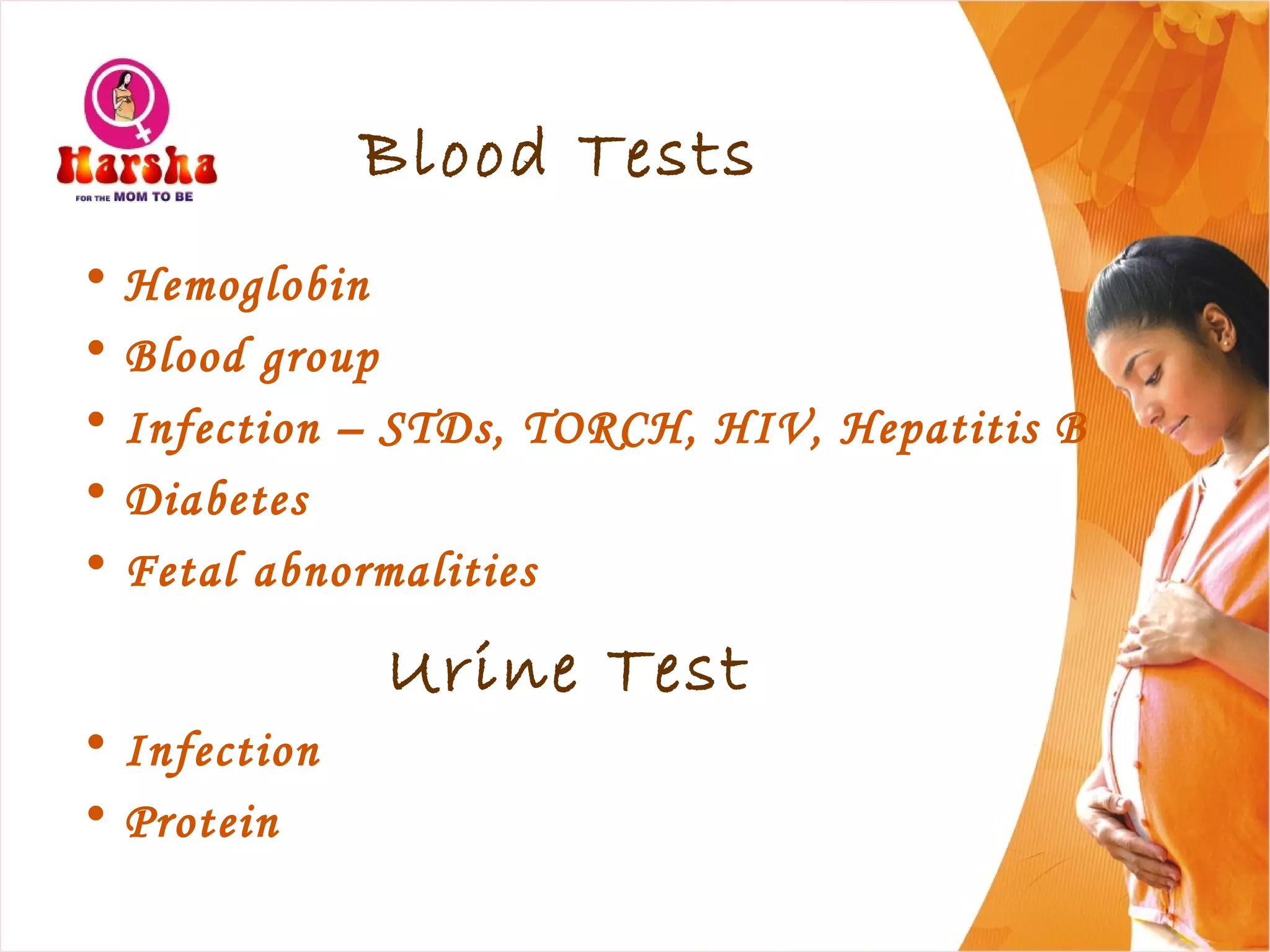
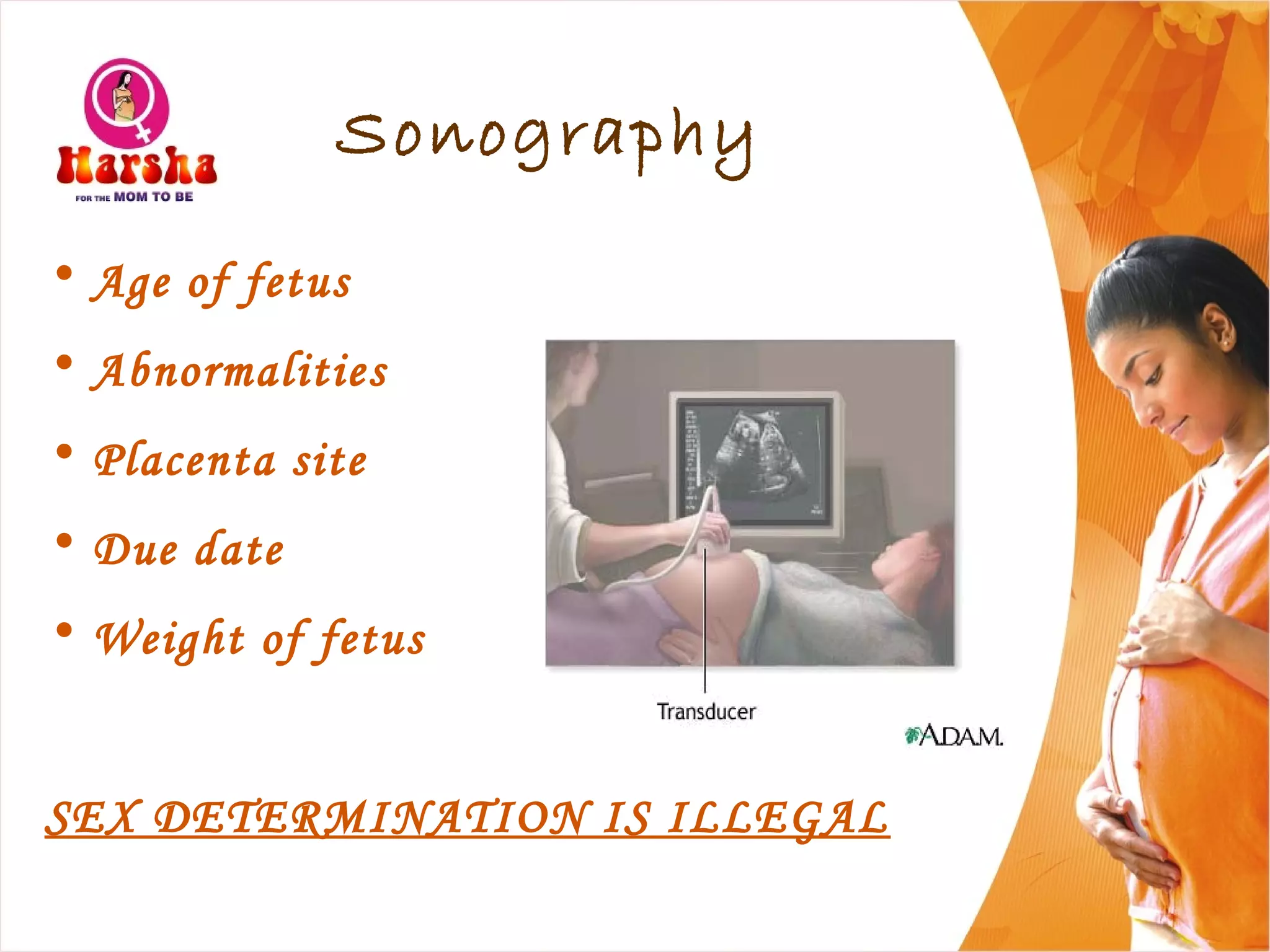
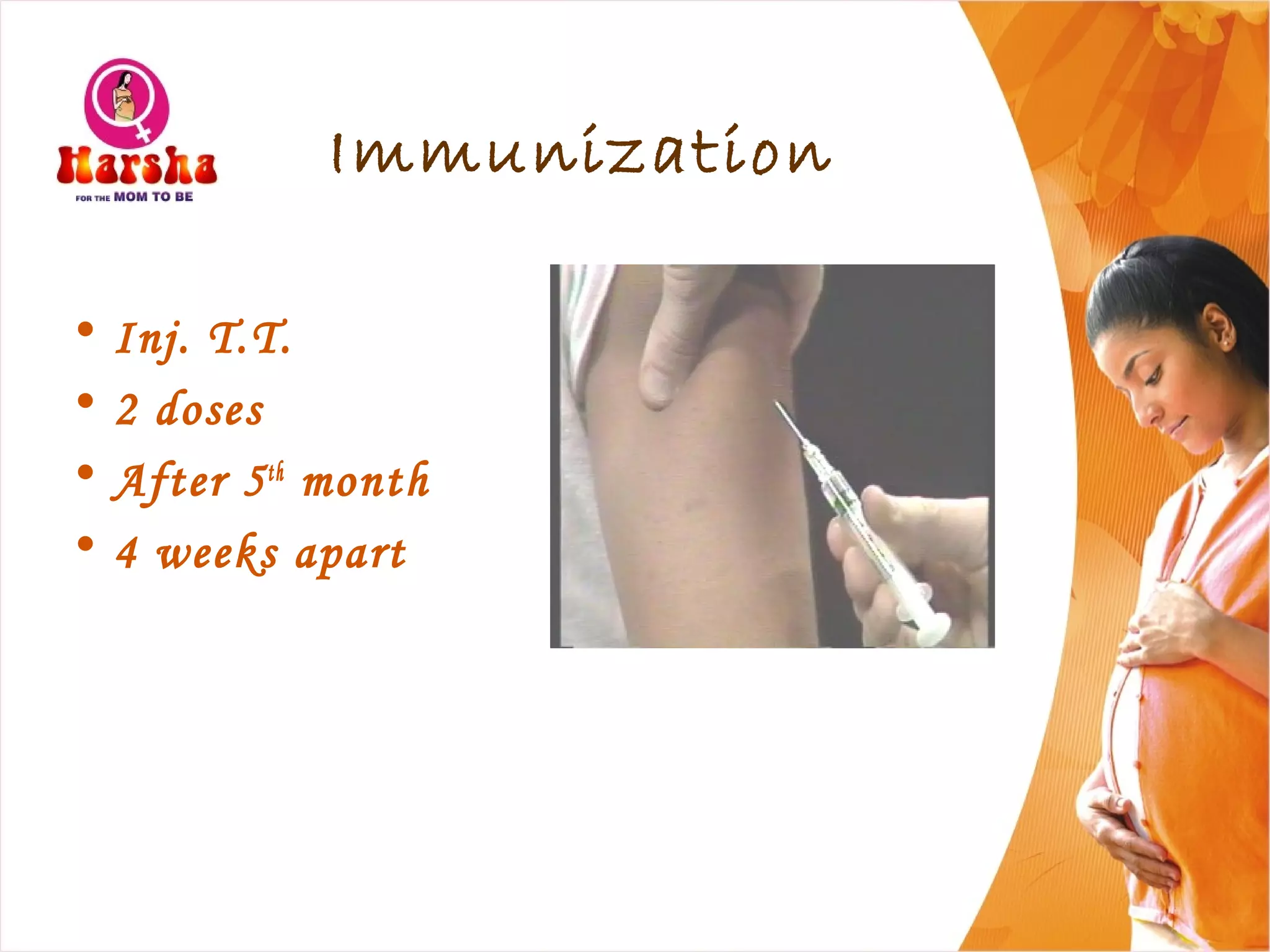
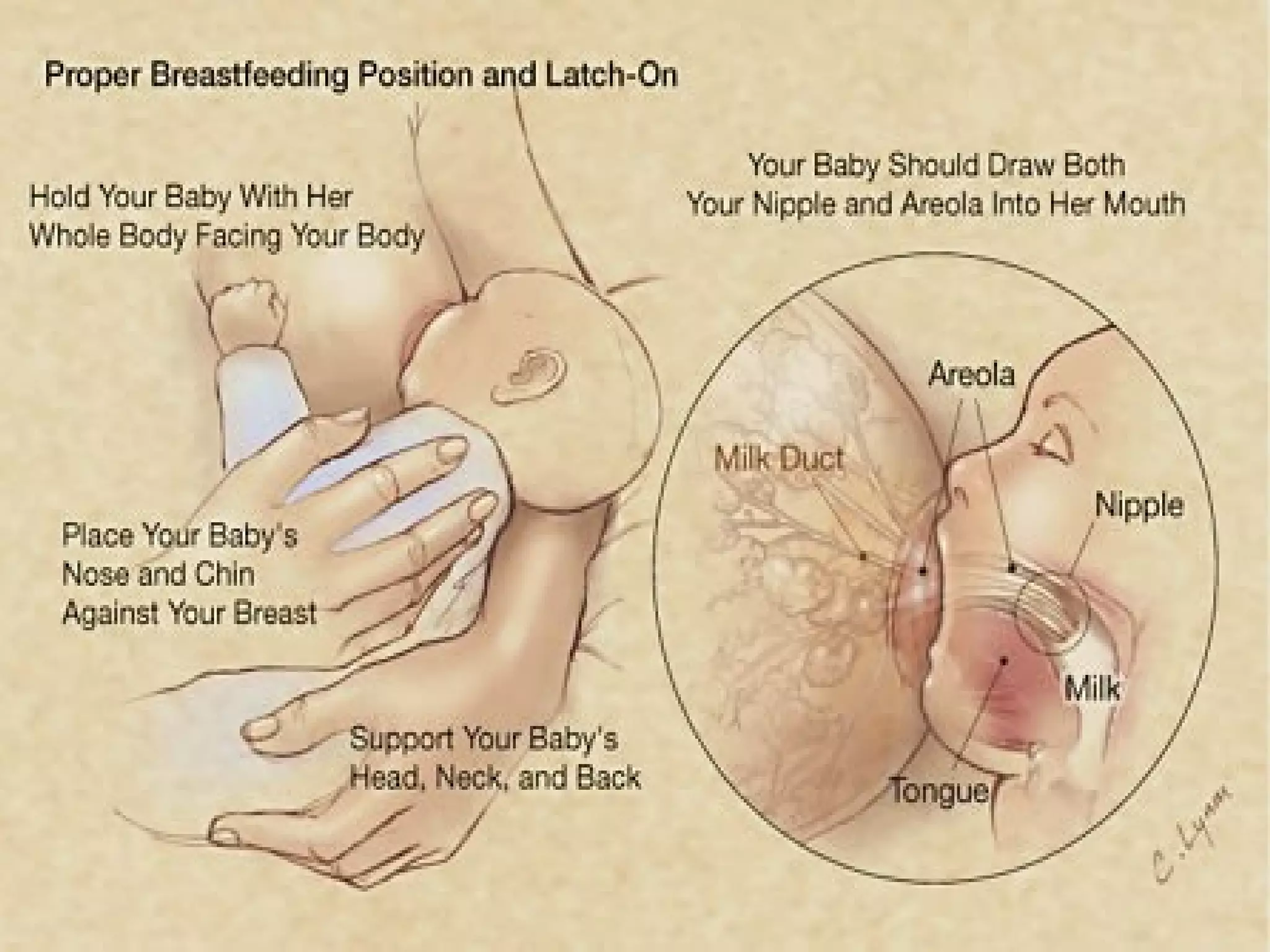
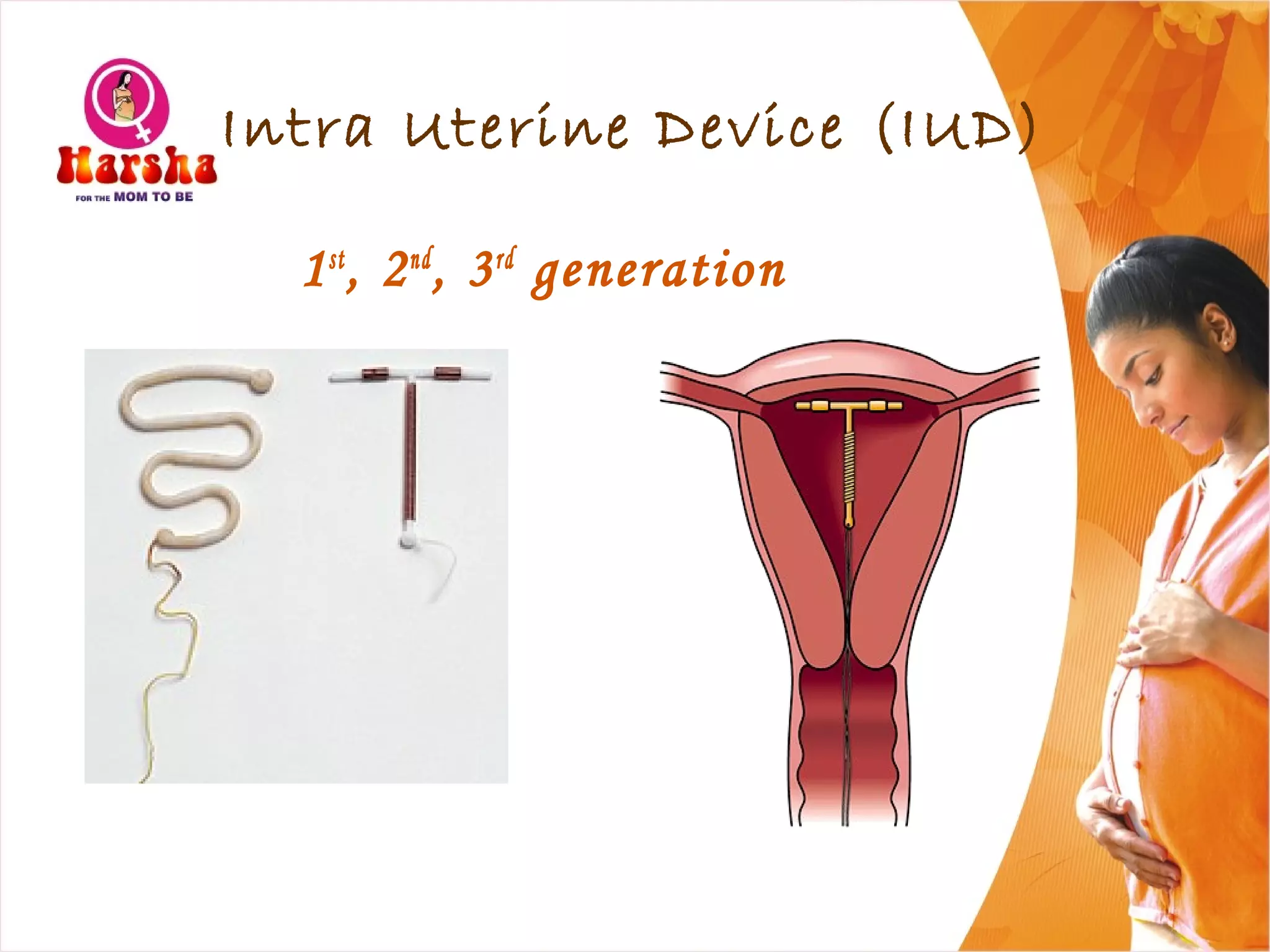
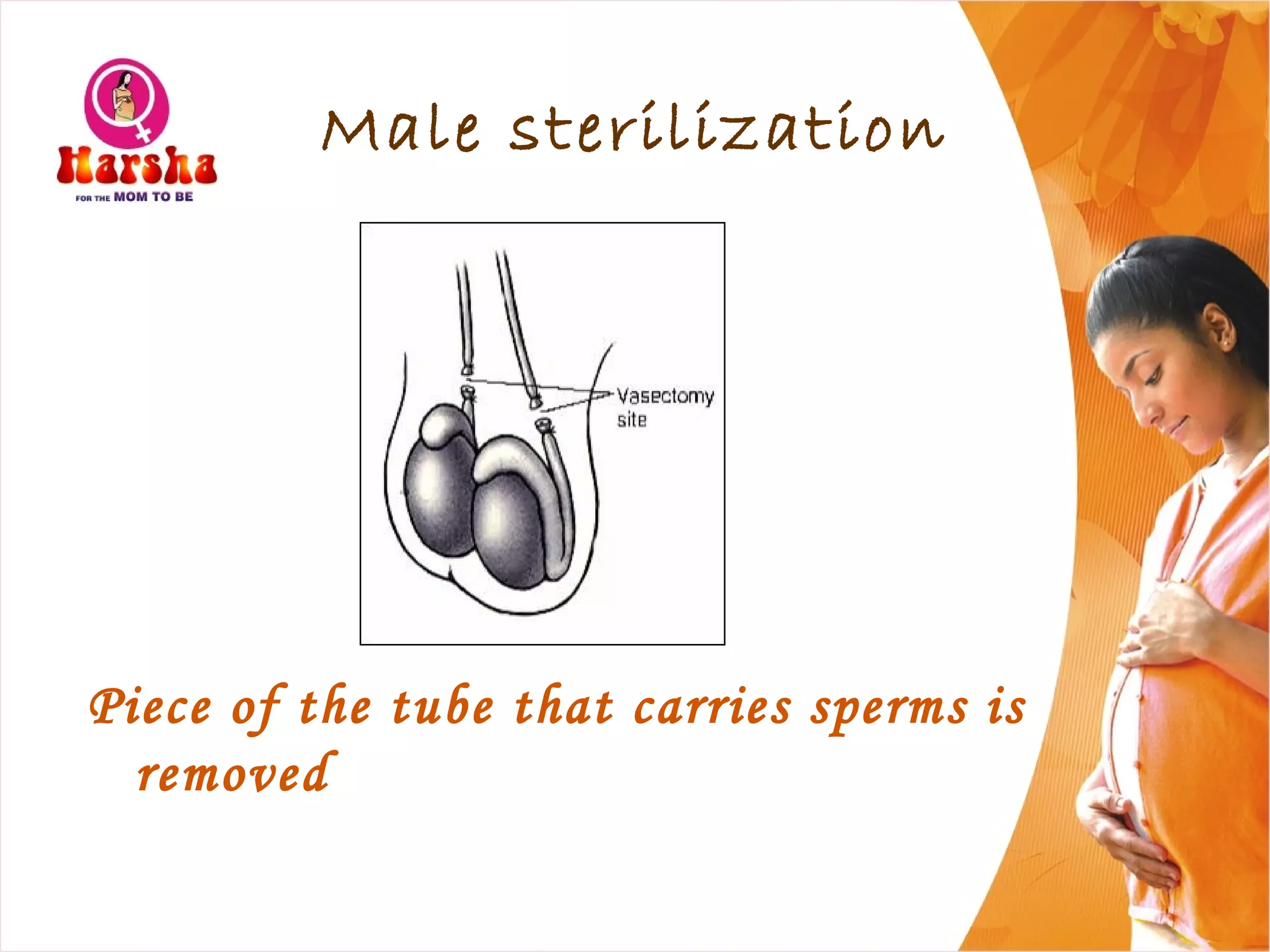
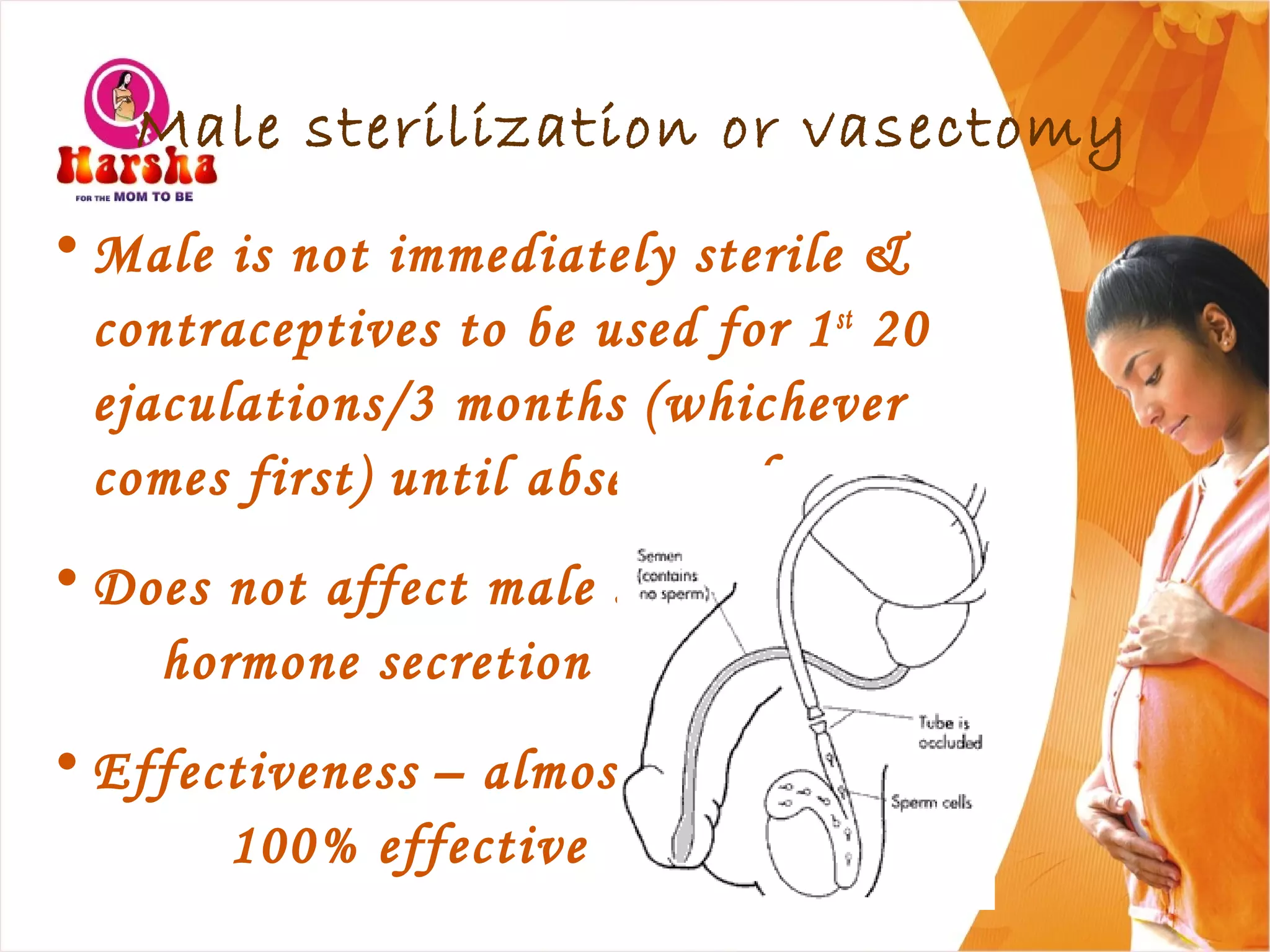
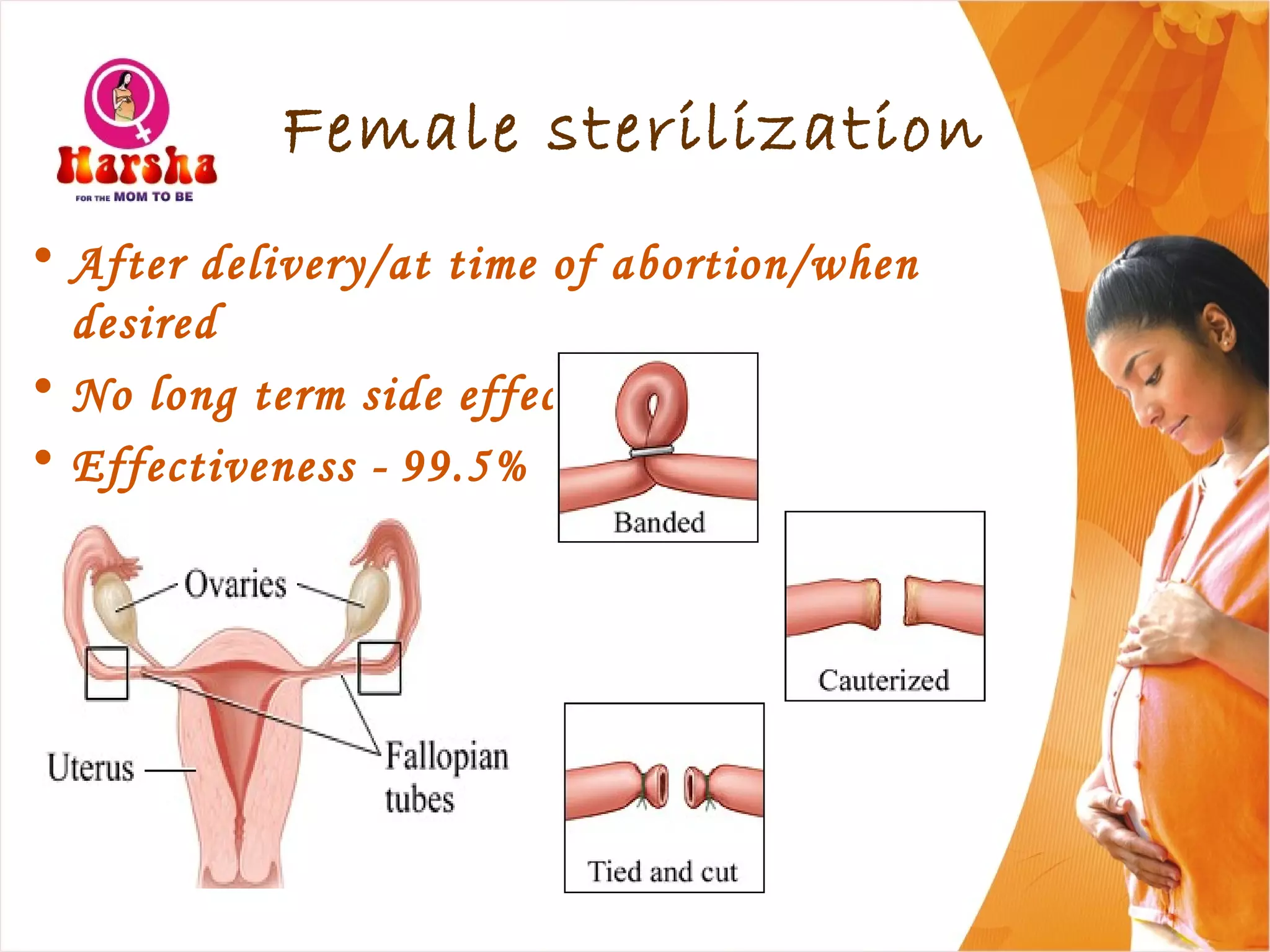
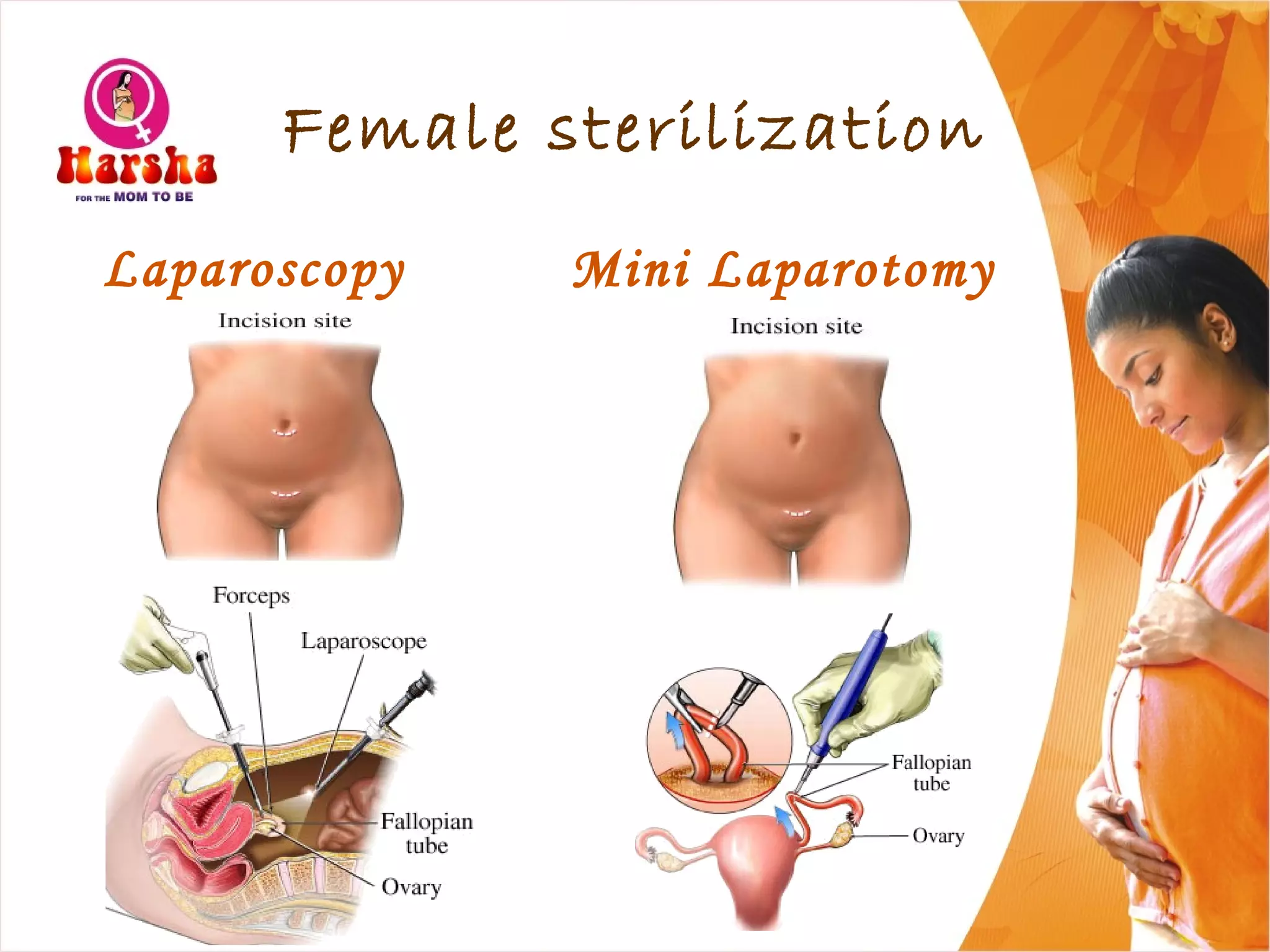
Pregnancy involves many physical and lifestyle changes for the mother. The document provides information on common symptoms during pregnancy like nausea and backaches. It discusses the importance of a healthy, balanced diet with sufficient calcium, iron and proteins. Self-care recommendations include proper hygiene, exercise and getting sufficient medical care and checkups. The post-pregnancy section covers breastfeeding, post-delivery recovery, family planning and contraceptive options.