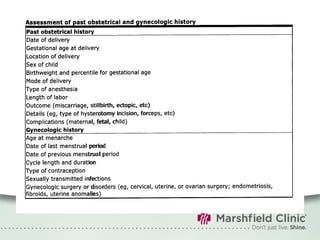
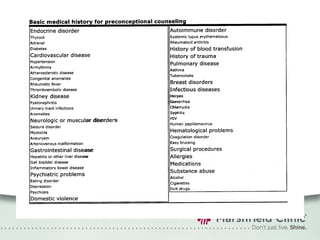
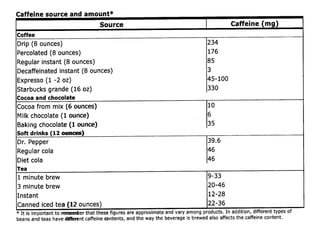
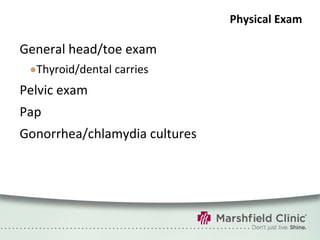
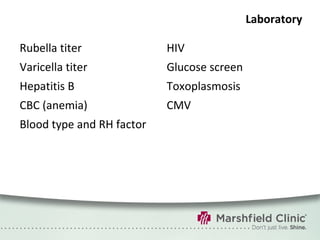
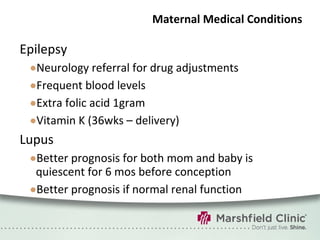
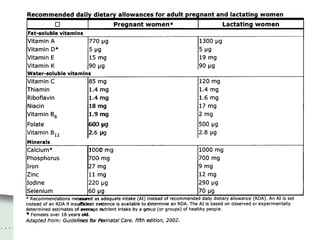
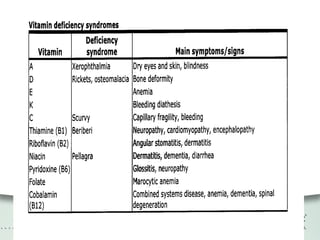
The document provides a comprehensive overview of preconceptual counseling aimed at improving maternal and fetal health through the identification and management of health risks before pregnancy. It highlights the importance of medical history, dietary considerations, exercise, substance use, and weight management in optimizing pregnancy outcomes. Additionally, it addresses various maternal medical conditions and emphasizes the need for prenatal education to ensure better self-care and pregnancy results.