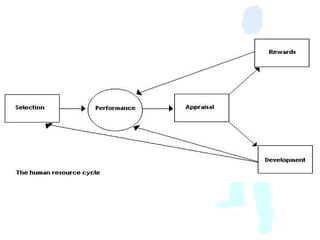
Human resource management involves attracting, selecting, training, assessing, and rewarding employees while ensuring compliance with employment laws. It can take either a "hard" or "soft" approach. The hard approach treats employees as resources to be hired and fired as needed with minimal communication and empowerment. The soft approach takes a long-term view of developing employees through training, delegation, and two-way communication to achieve corporate objectives. While the hard approach may be more cost-effective, the soft approach is likely to result in higher employee motivation, lower turnover, and a more successful recruitment through developing the workforce. The best approach depends on the organization's needs and goals.