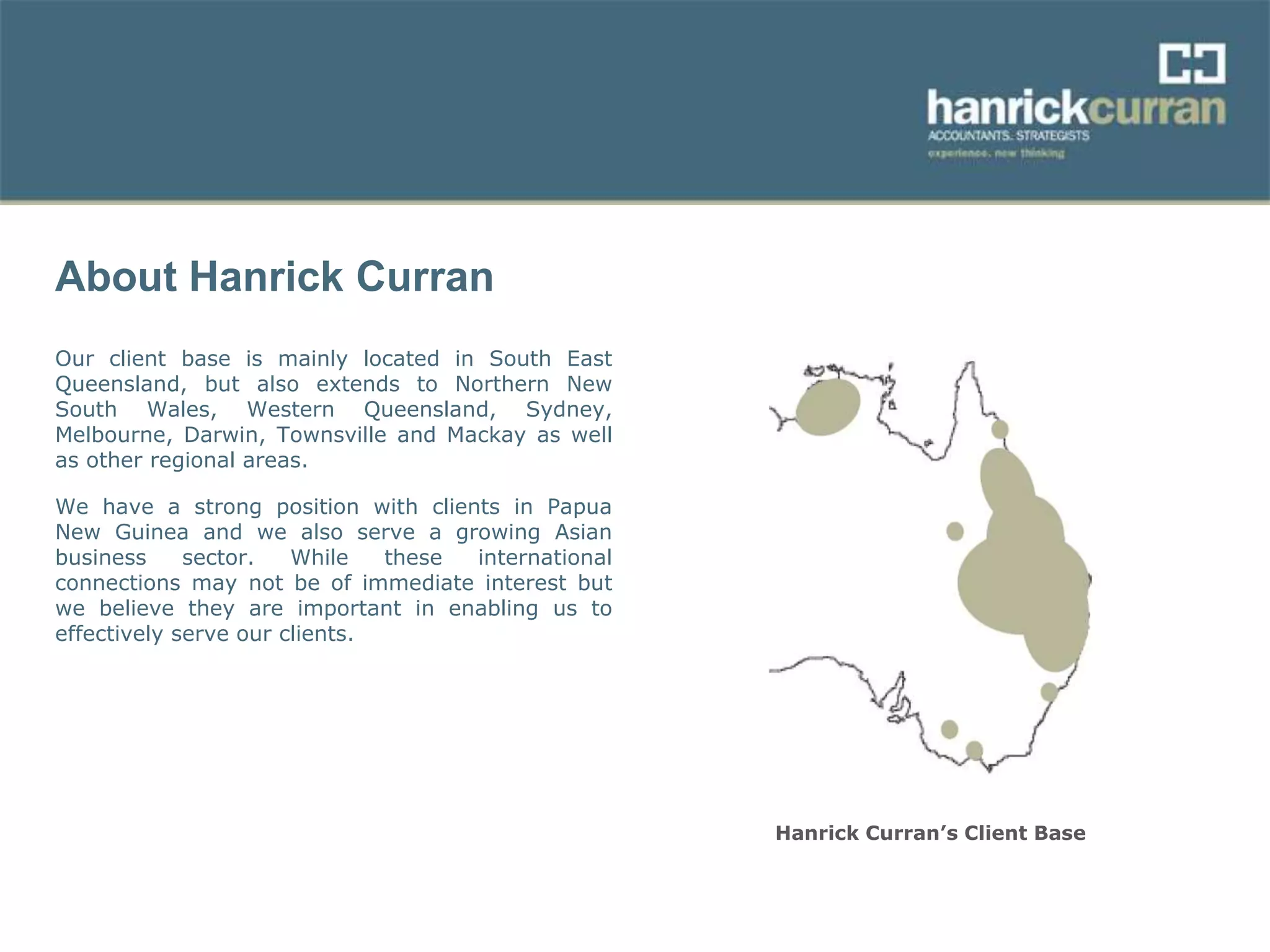
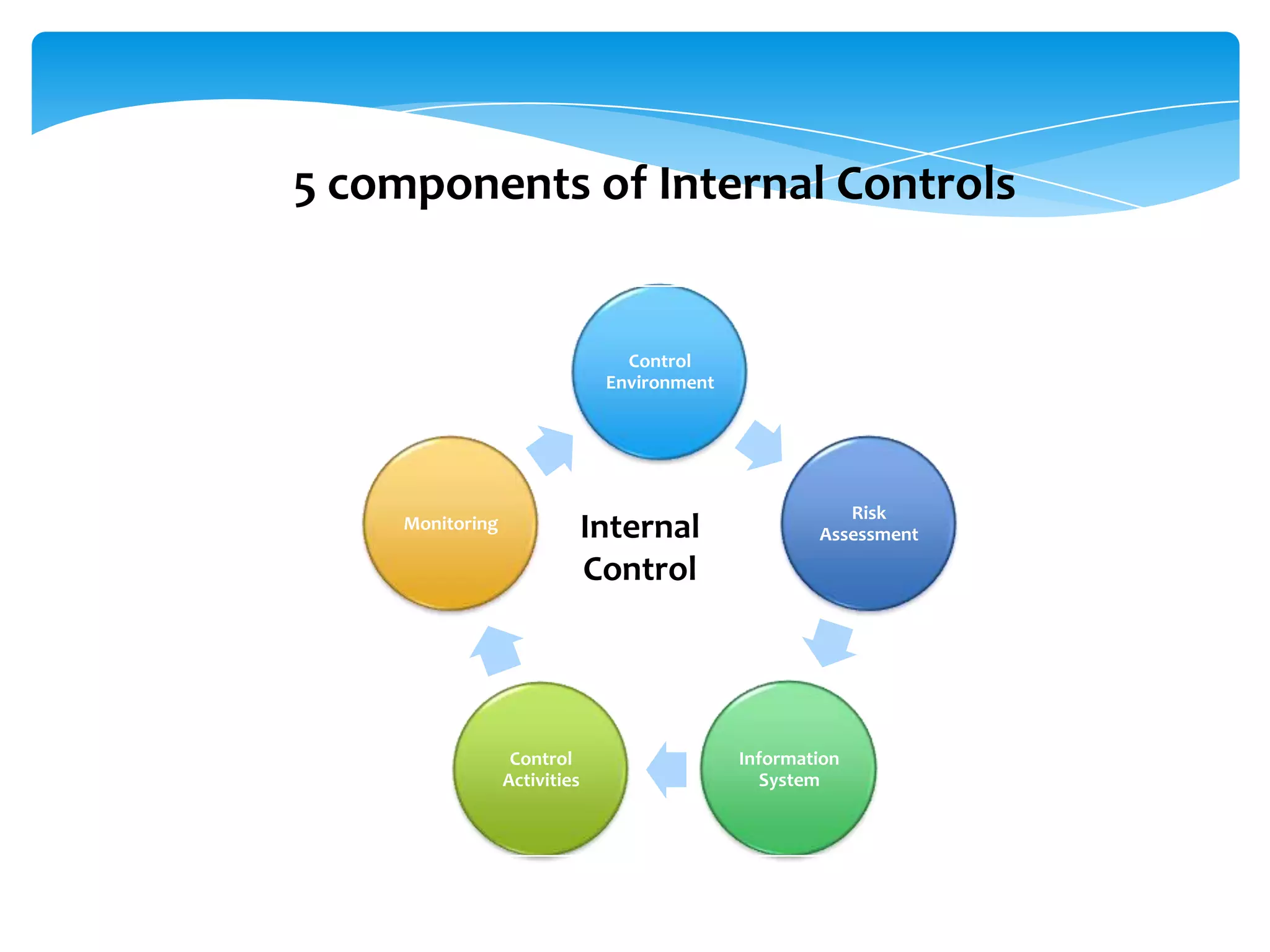
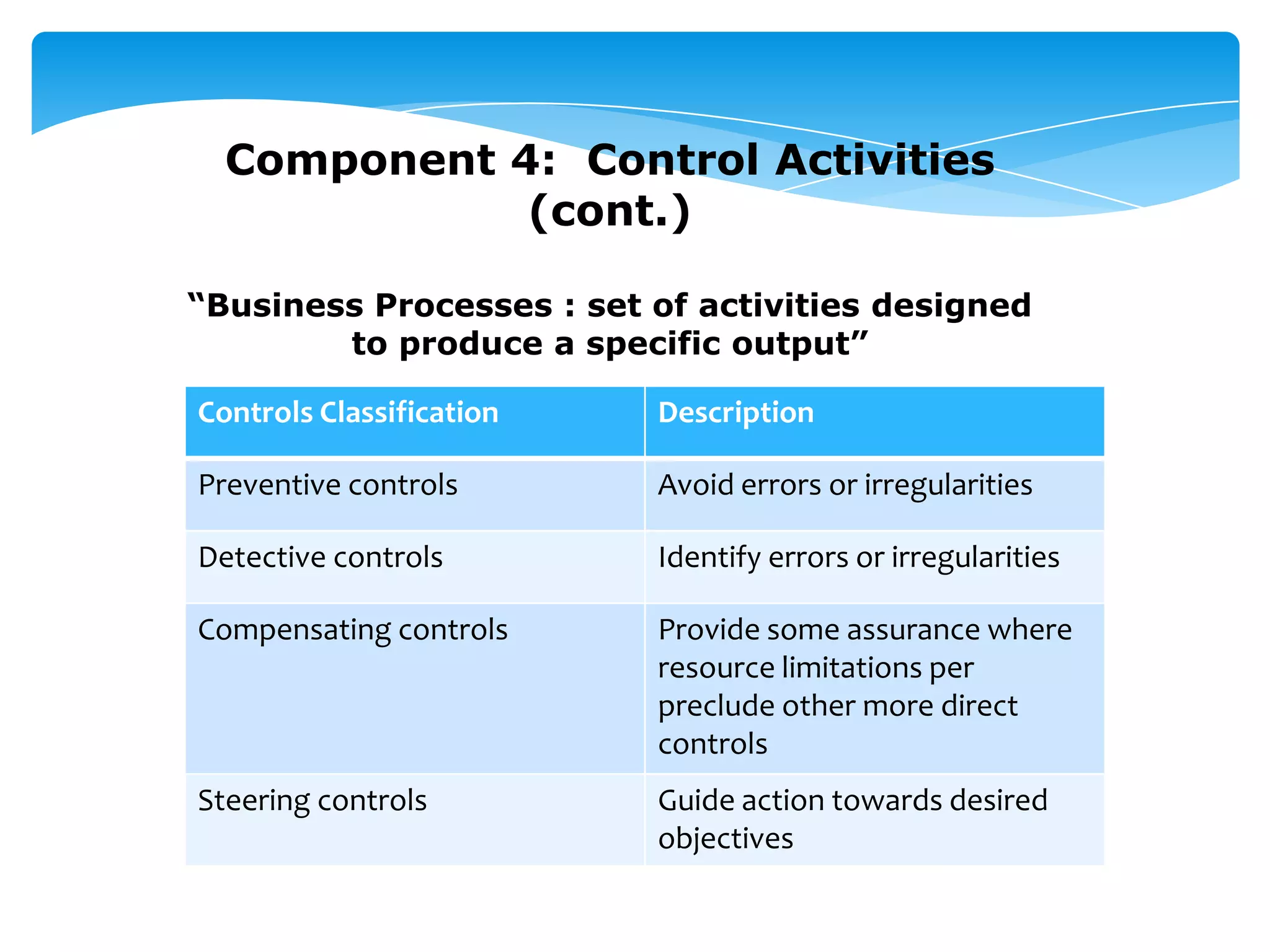
This document outlines an audit team training session focused on understanding internal controls, their components, and their significance in financial reporting. It emphasizes the need for effective internal controls and provides a framework for identifying risks and implementing control activities. The training aims to equip audit team members with the knowledge to prepare system notes and assess internal controls effectively.