The document is a presentation on using Git and GitHub, covering concepts such as repositories, staging, committing, and branching. It includes basic commands for setting up and managing Git repositories, as well as a demonstration of creating a pull request and collaborating on open source projects. Additionally, it mentions resources like Hacktoberfest and the GitHub Student Pack.












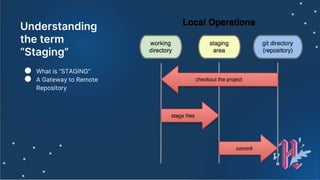



![Basic Git Commands
● ls
● cd
● git init
● git remote add origin [gitLink] (remote repo)
● git remote -v (remote repo)
● git add . (Staging)
● git commit -m "First commit“
● git push origin master
● git log --pretty=oneline](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hacktoberfestslides-201018075812/85/Hacktoberfest-slides-20-320.jpg)
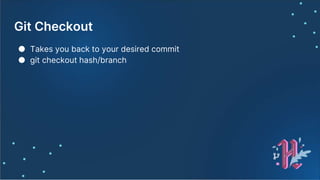


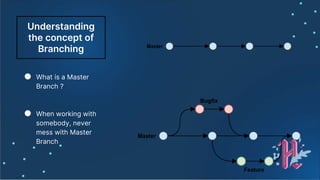
![Graph
● git log --pretty=format:'%h %ad | %s%d [%an]' --
graph --date=short --all](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hacktoberfestslides-201018075812/85/Hacktoberfest-slides-27-320.jpg)