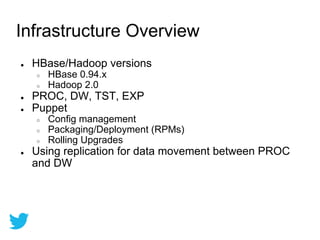
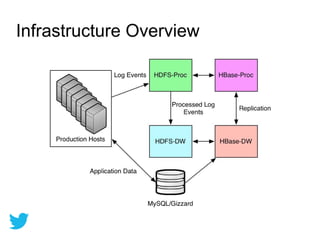
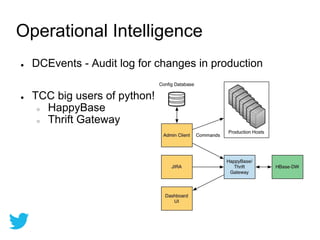
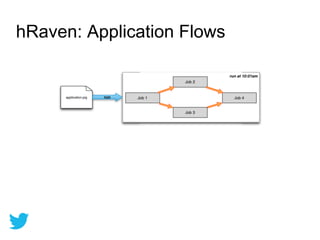
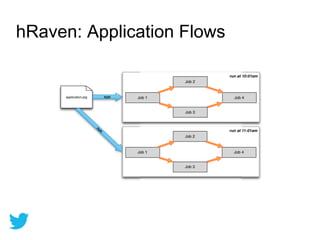
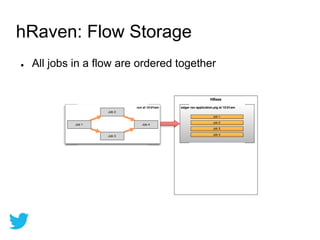
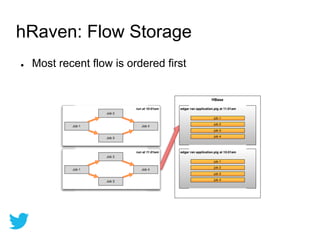
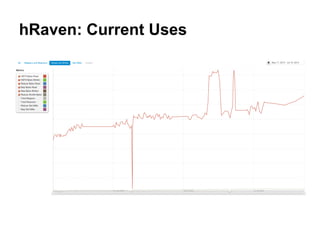
Twitter uses HBase for mutable batch processing data storage and operational intelligence. They run HBase 0.94 on Hadoop 2.0 across multiple clusters managed by Puppet. HBase stores operational audit logs and supports Python apps. hRaven stores and analyzes MapReduce job metrics to optimize Pig reducers, plan cluster capacity, and troubleshoot problems. It tracks 12.6M jobs across flows, clusters, users and versions.