Embed presentation


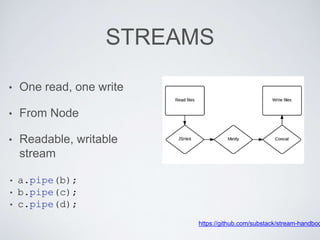

![• gulp.src(globs,[options])
Takes files and start emitting them, returns readable stream.
• gulp.dest(path, [options])
Save files to file system.
https://github.com/gulpjs/gulp/blob/master/docs/API.md](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gulp-150605082103-lva1-app6891/85/Getting-Started-with-Gulp-5-320.jpg)
![• gulp.task(name[, deps], fn)
Define a task, can be used as dependency, must have a return
• gulp.watch(glob[, opts], tasks)
Watch files for changes
https://github.com/gulpjs/gulp/blob/master/docs/API.md](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gulp-150605082103-lva1-app6891/85/Getting-Started-with-Gulp-6-320.jpg)







This document provides an overview of Gulp, a streaming build system for Node.js. Gulp uses JavaScript for configuration and has a simple API with only four main commands. It is based on streams, which allow files to be piped between processes. Common tasks like concatenating, minifying, and injecting files can be accomplished through Gulp plugins. The document demonstrates how to install Gulp, create a Gulpfile, and run basic tasks to assemble a build process.




![• gulp.src(globs,[options])
Takes files and start emitting them, returns readable stream.
• gulp.dest(path, [options])
Save files to file system.
https://github.com/gulpjs/gulp/blob/master/docs/API.md](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gulp-150605082103-lva1-app6891/85/Getting-Started-with-Gulp-5-320.jpg)
![• gulp.task(name[, deps], fn)
Define a task, can be used as dependency, must have a return
• gulp.watch(glob[, opts], tasks)
Watch files for changes
https://github.com/gulpjs/gulp/blob/master/docs/API.md](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gulp-150605082103-lva1-app6891/85/Getting-Started-with-Gulp-6-320.jpg)






