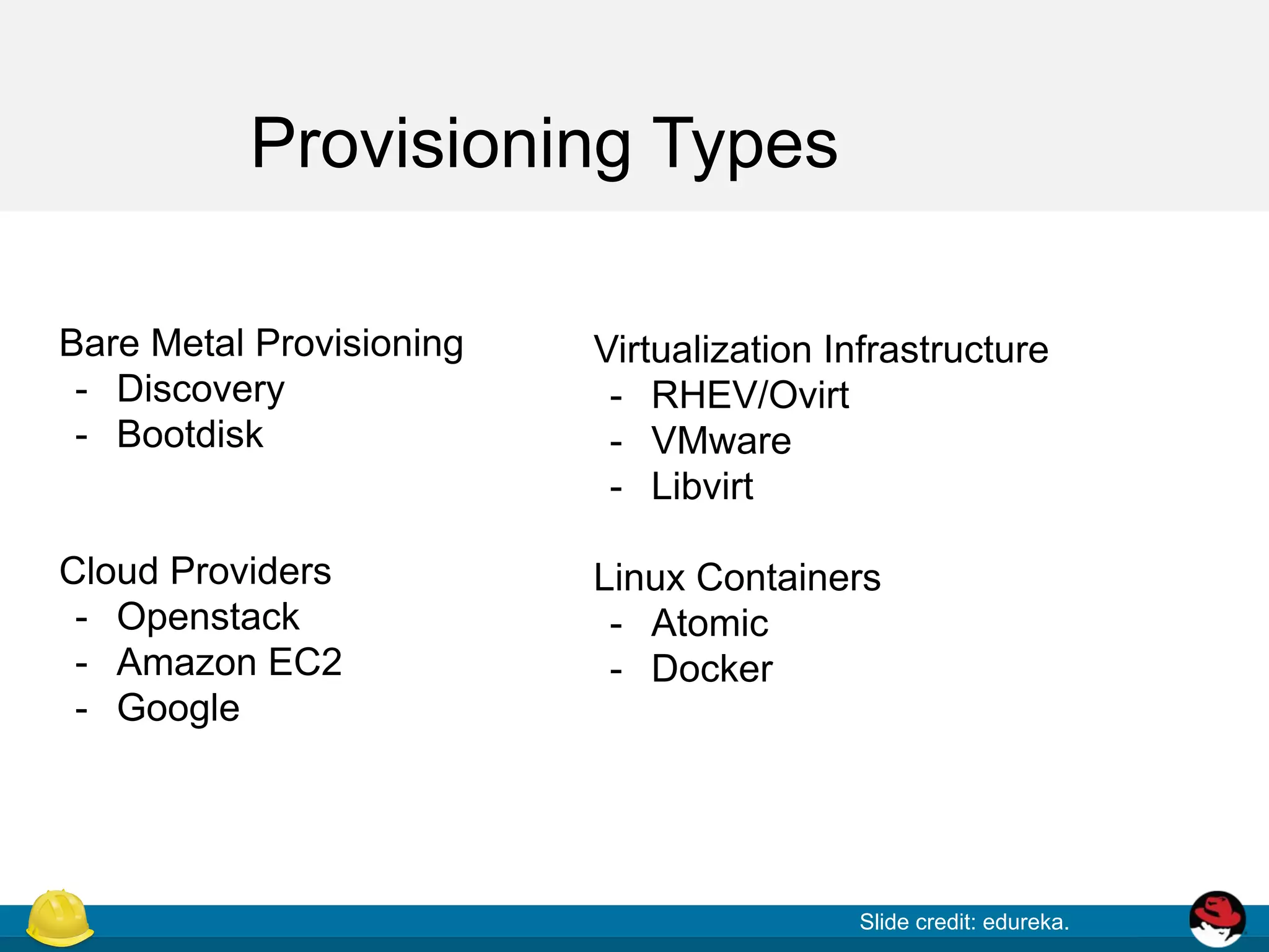
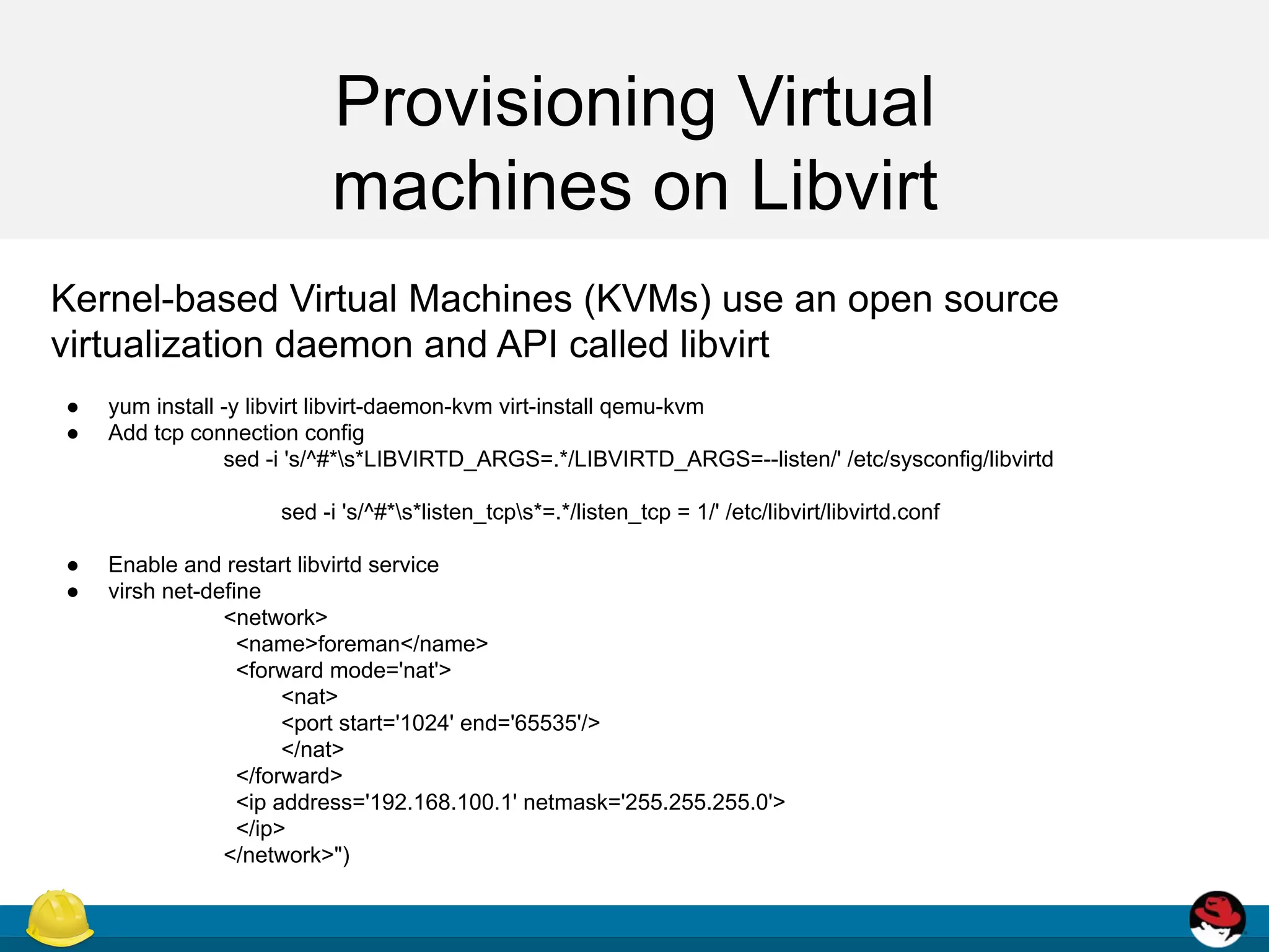
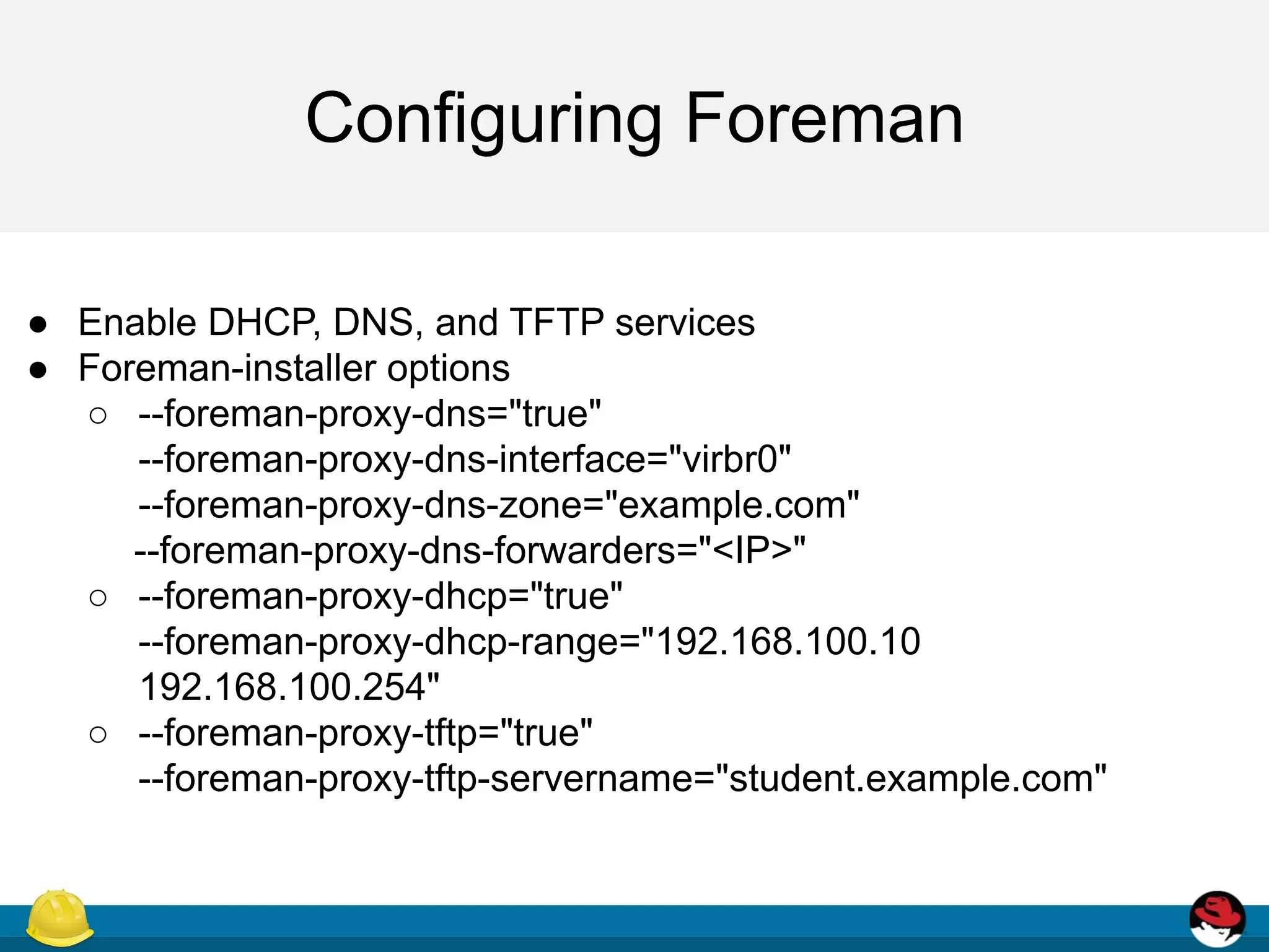
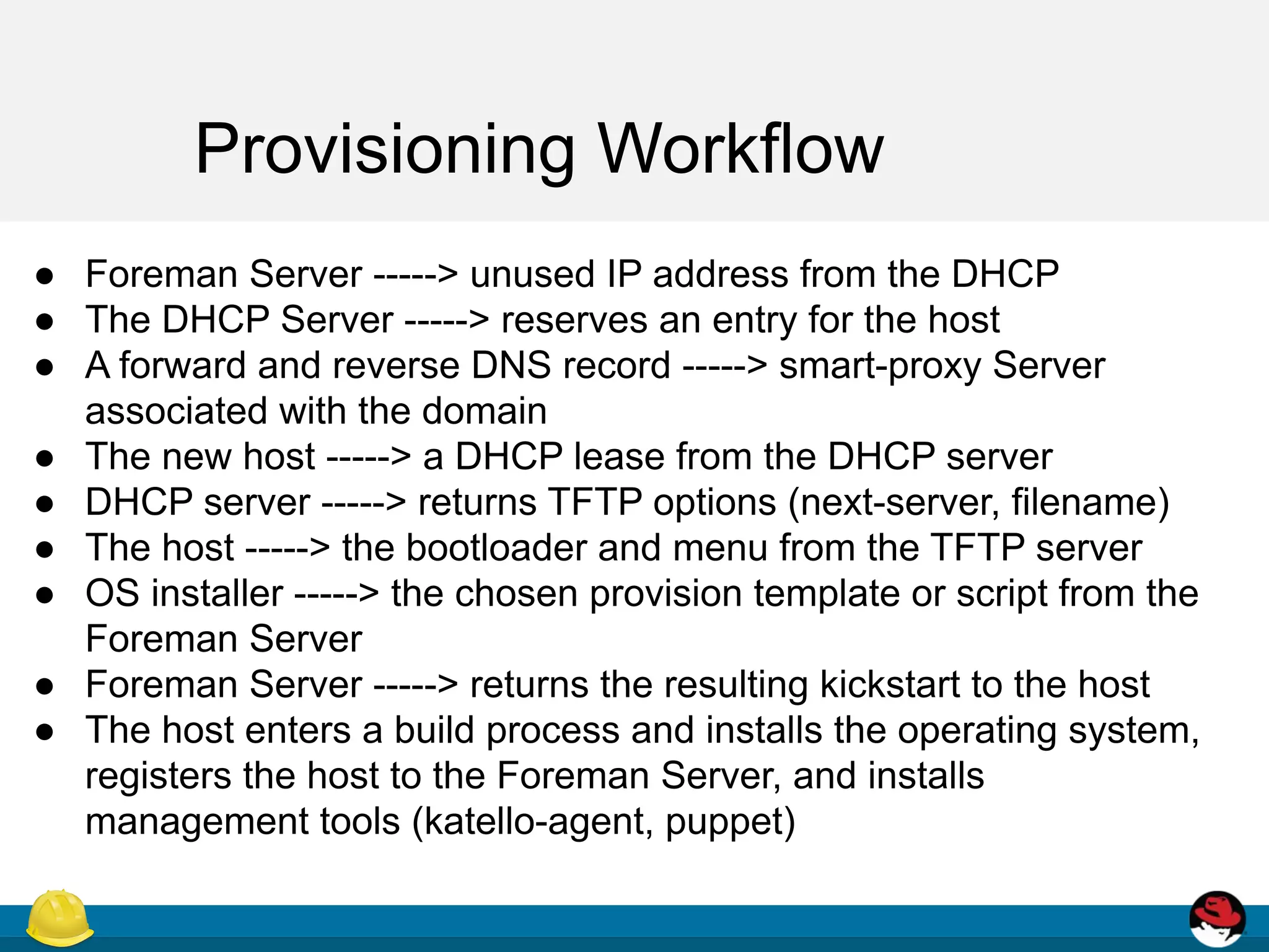
This document discusses provisioning virtual machines using Foreman and Libvirt. It provides an overview of provisioning types and the provisioning workflow. It then describes how to install and configure Libvirt and Foreman to provision VMs on Libvirt, including enabling necessary services, defining a network, and configuring host creation requirements.