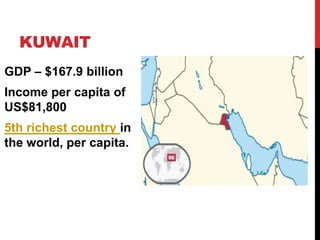
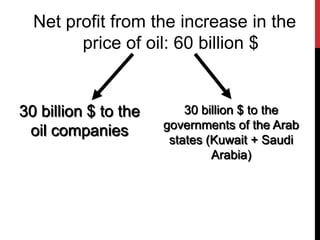
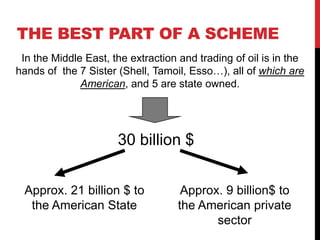
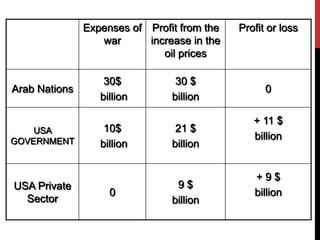
The Gulf War (January-February 1991) was a conflict initiated by a coalition of 34 nations led by the United States in response to Iraq's invasion of Kuwait, spurred by economic tensions over oil production. The war resulted in significant economic implications, including a dramatic rise in oil prices from $18 to $60 per barrel, generating immense profits primarily for Arab governments and multinational oil companies. The intervention was officially justified on humanitarian grounds and regional stability, although controversies surrounding economic motivations and the impacts on global oil markets persisted.