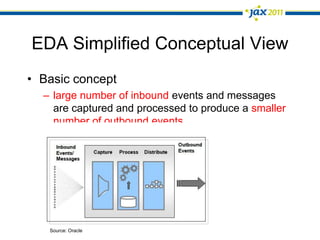
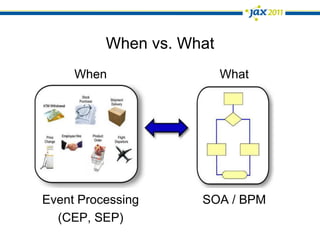
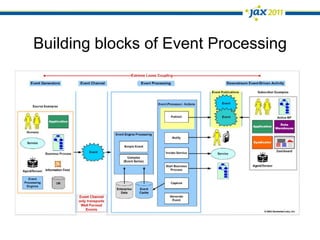
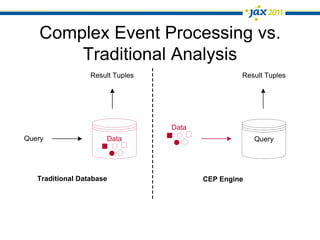
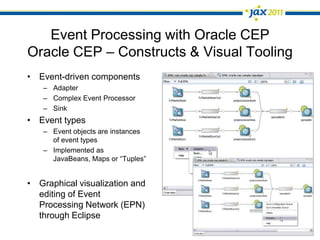
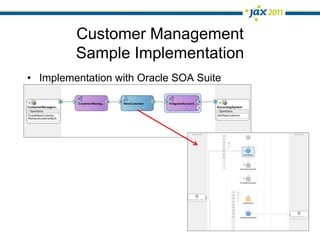
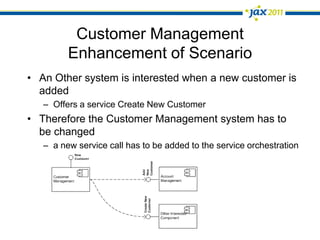
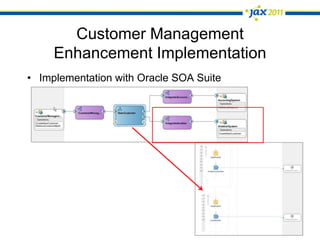
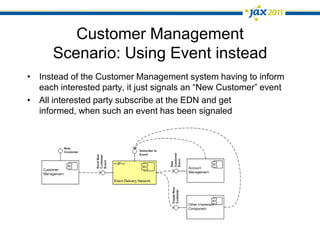
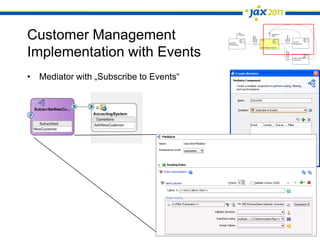
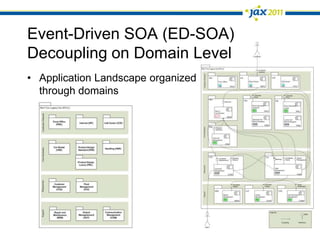
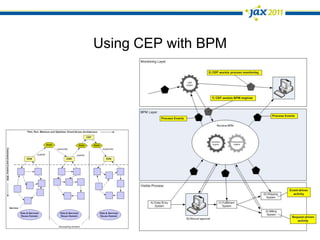
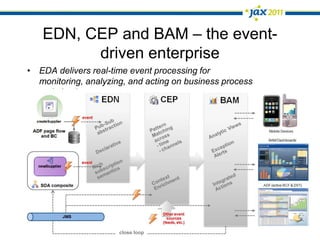
The document discusses Event-Driven Service-Oriented Architecture (ED-SOA) and its integration with business process management (BPM). It outlines the types of events, event processing, and the role of an Event Delivery Network (EDN) in decoupling services. The key takeaway is that ED-SOA enhances agility and flexibility in software systems by allowing services to react to events without strong dependencies.