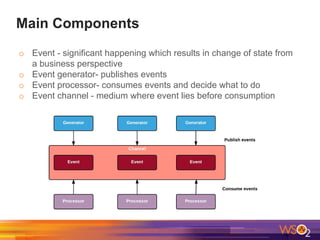
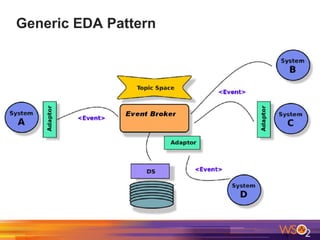
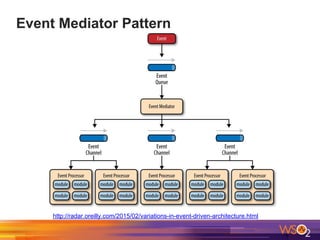
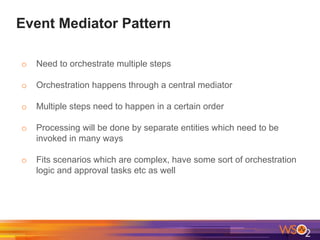
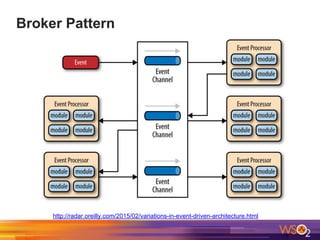
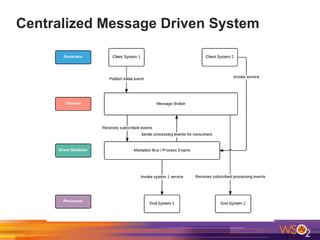
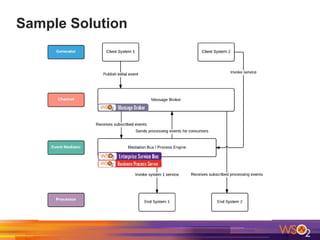
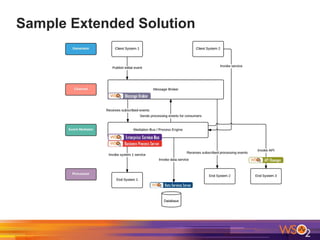
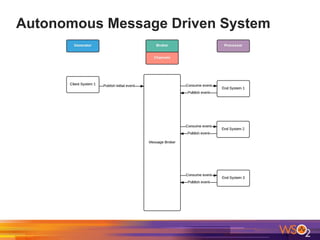
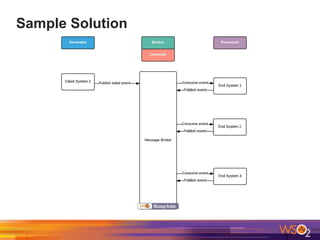
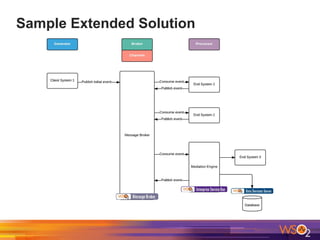
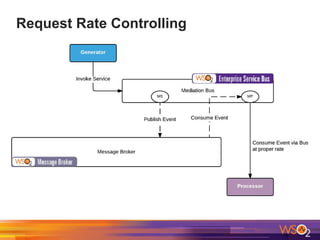
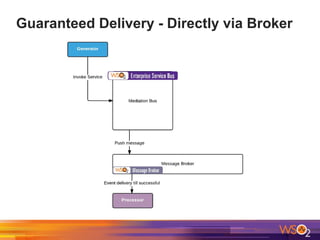
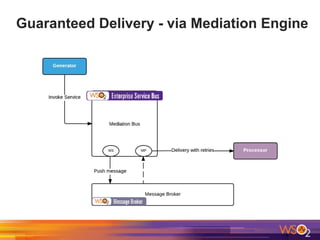
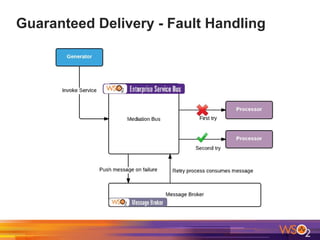
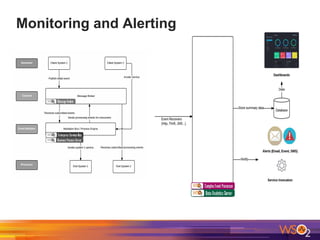
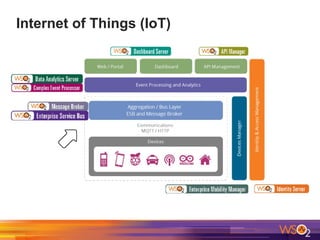
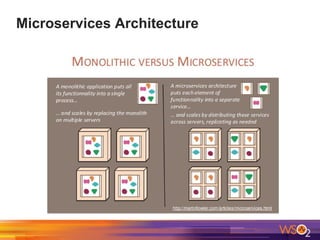
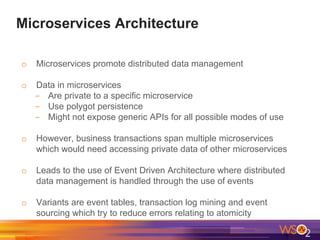
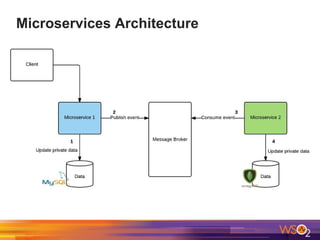
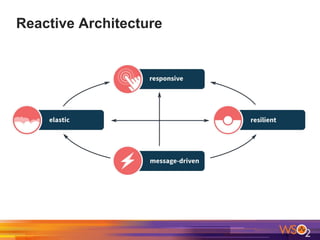
The document discusses building event-driven systems and the evolution from synchronous request-response architecture to event-driven architecture (EDA), emphasizing the significance of events in enterprise systems. It outlines key components, principles, and patterns of EDA, including the event mediator and broker patterns, which are essential for orchestrating processes and distributing message flow. Additionally, the document links EDA to trends like the Internet of Things and microservices architecture, highlighting the need for reactive design to enhance system scalability and adaptability.