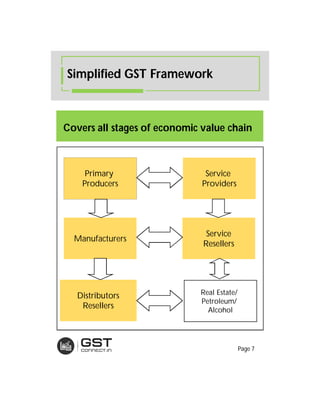
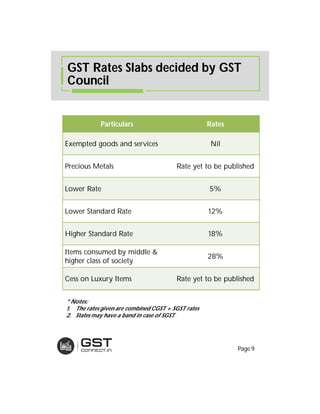
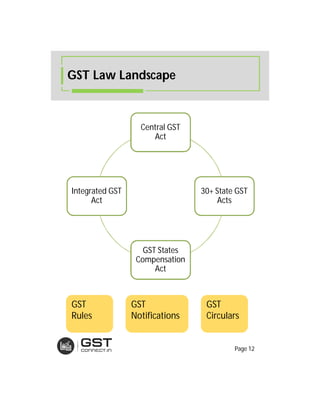
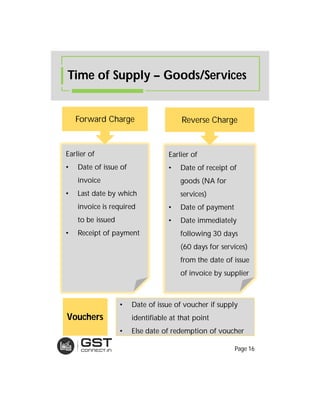
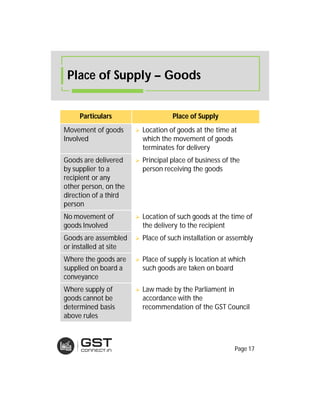
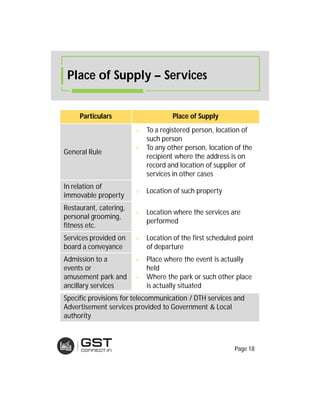
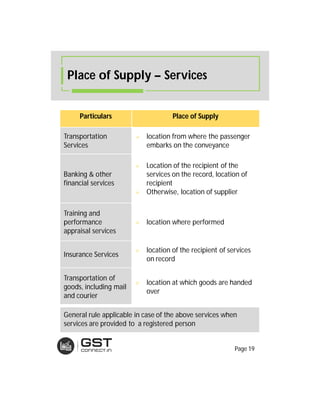
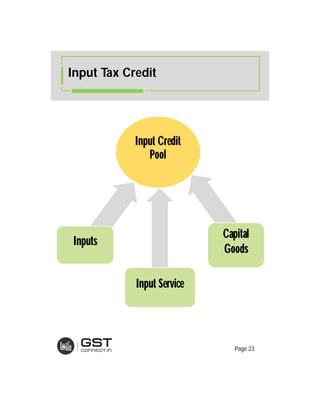
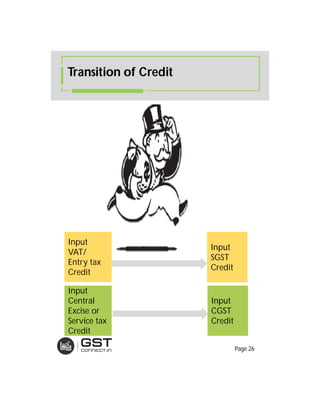
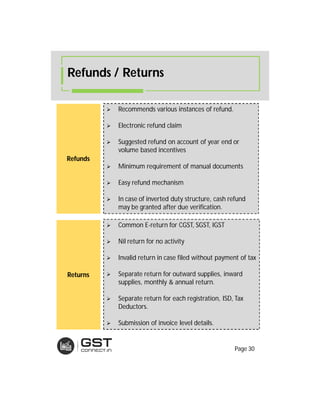
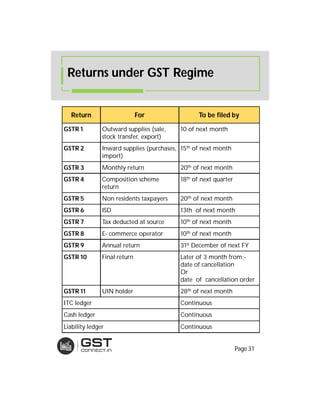
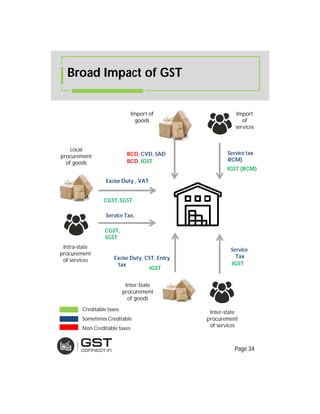
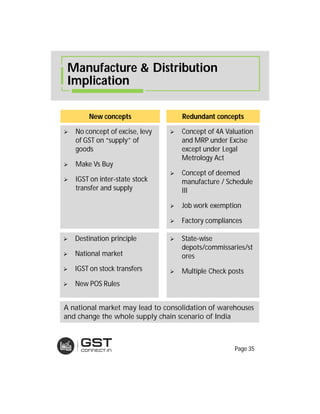
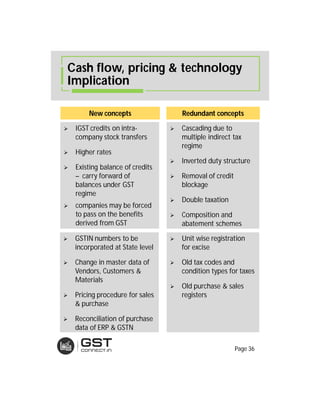
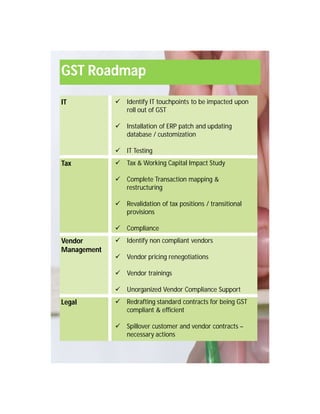
The document provides an overview of the key features and provisions of the proposed Indian Goods and Services Tax (GST) model law, including details about the tax structure, rates, implementation timeline, and rules around chargeability, time and place of supply, and transition. It is intended to help readers understand and digest the key aspects of the new indirect tax regime in a simplified manner.