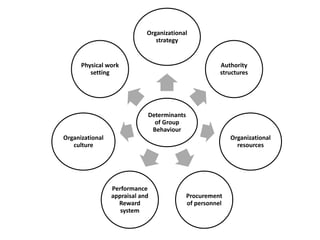
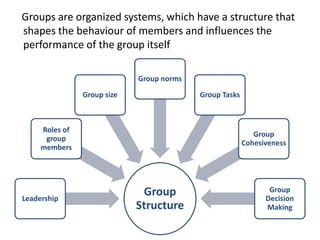
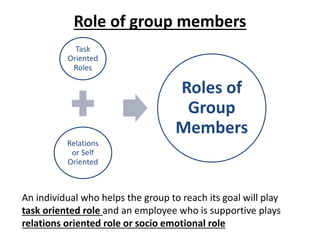
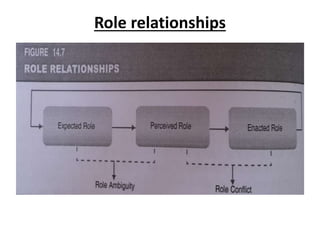
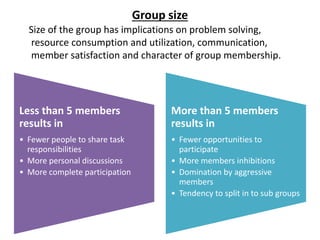
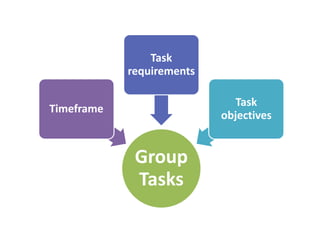
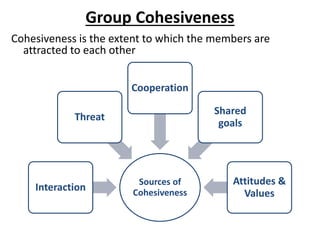
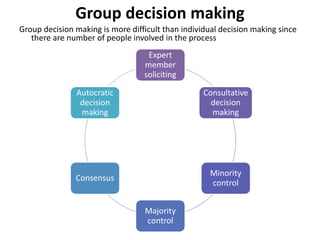
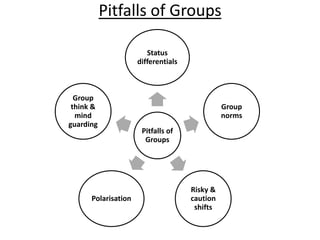
Group dynamics include determinants of group behavior, roles of group members, group structure, and decision making processes. Key determinants include organizational strategy, authority structures, and culture. Groups have task-oriented and relations-oriented roles. Group structure is shaped by leadership, roles, size, norms, tasks, and cohesiveness. Effective group decision making balances input from experts and consensus, while avoiding problems like social loafing, groupthink, and risky shifts in judgment.