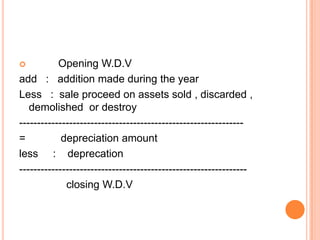
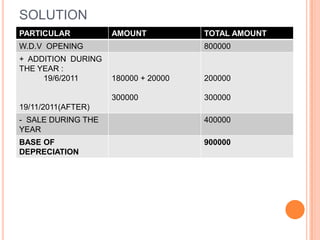
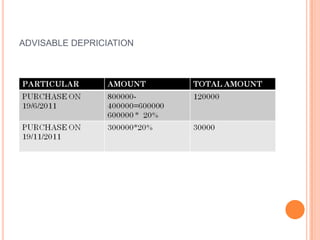
This presentation discusses the taxation of profits and gains from business or profession under the Indian Income Tax Act. It covers the basis of charging such income, what constitutes a business, basic principles for arriving at business income, methods of accounting, concepts of block of assets and depreciation, examples of deductible and non-deductible expenses, and how to calculate taxable business/profession income. The key topics covered include profits and other payments considered business income, the definition of business, principles of determining taxable profits, and rules around depreciation of assets used in business.

![BASIS OF CHARGE [SECTION 28]
profits and gains of any business or profession
any compensation or other payments due to or received by any person
specified in section 28(ii)
income derived by a trade, professional or similar association from specific
services performed for its members
the value of any benefit or perquisite, whether convertible into money or
not, arising from business or the exercise of profession
any profit on transfer of the Duty Entitlement Pass Book Scheme
any profit on transfer of duty free replenishment certificate
export incentive available to exporters
any interest, salary, bonus, commission or remuneration received by a
partner from firm
any sum received for not carrying out any activity in relation to any
business or not to share any know how , patent, copyright, trademark , etc.
profit and gains of managing agency and
income from speculative transactions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group6-120215020921-phpapp02/85/Group-6-2-320.jpg)
![BUSINESS [SECTION 2(13)]
It includes any trade, commerce, manufacture or
any adventure or concern in nature of
trade, commerce or manufacture
A person who purchases goods with a view to sell them as
profit is trade
Whereas if such transactions are repeated on a large scale
it is called commerce
Manufacture is a process which results in alteration or
change in goods which are subjected to such manufacture.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group6-120215020921-phpapp02/85/Group-6-3-320.jpg)