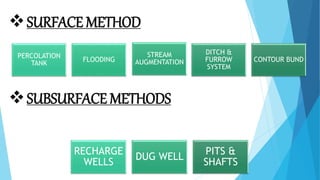
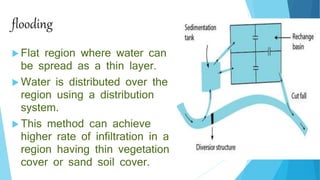
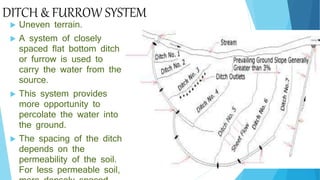
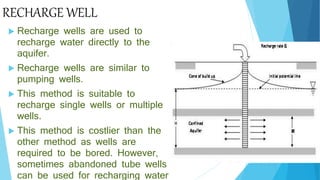
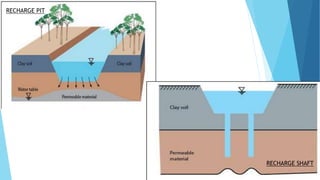
The document outlines groundwater improvement techniques, emphasizing the importance of artificial recharge to enhance groundwater storage and quality. It details various methods such as surface and subsurface techniques, including percolation tanks and recharge wells, along with indirect methods like induced recharge and aquifer modification. The advantages of these techniques include improved groundwater yield, conservation of surface water, and enhanced water quality through natural filtration.