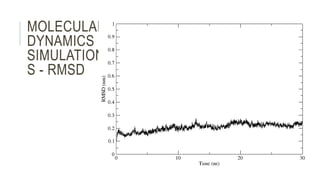
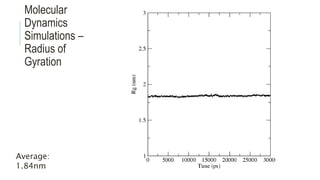
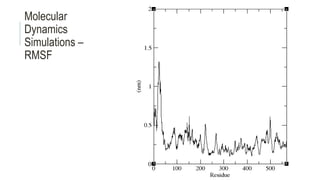
This document provides an overview of molecular dynamics simulations using GROMACS. It discusses the key components and steps involved, including preparing the protein, solvating the system, adding ions, energy minimization, and multiple equilibration steps. Data analysis techniques are also described, such as calculating the root mean square deviation (RMSD) to evaluate stability, radius of gyration to evaluate compactness, and root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) to evaluate per residue flexibility. The overall goal is to bring the molecule to a natural, dynamic state using computational modeling to mimic real-life physical forces.