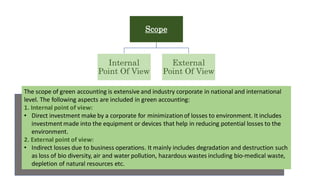
Green accounting aims to incorporate both economic and environmental information into accounting. It identifies, measures, and allocates environmental costs into business decisions and communicates this information to stakeholders. The scope of green accounting is extensive, including direct corporate environmental investments and indirect external losses from business operations like pollution and resource depletion. The objectives of green accounting are to assess environmental costs and benefits, track changes in environmental assets and protection expenditures. It helps businesses reduce environmental costs and make more informed decisions.