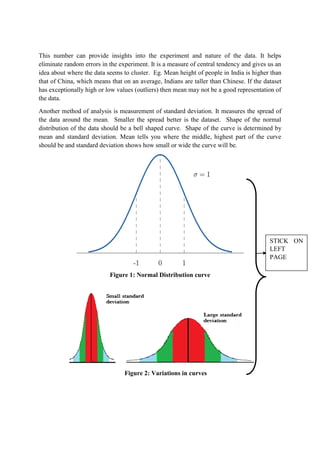
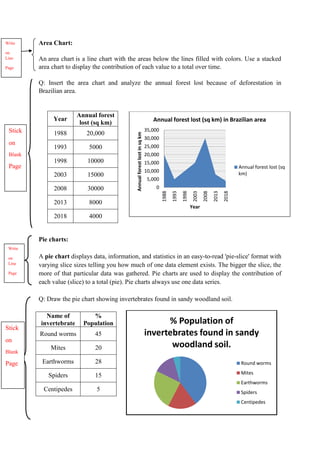
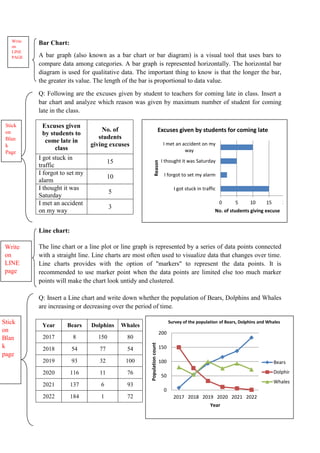
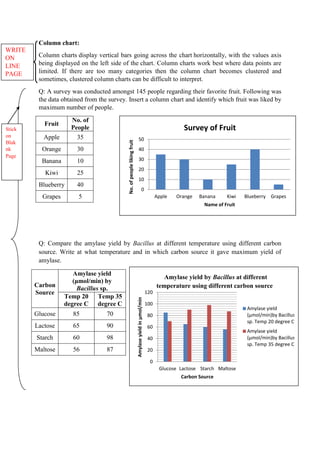
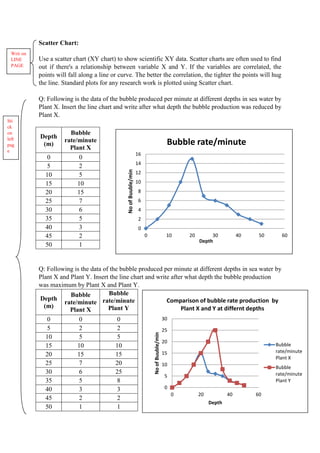
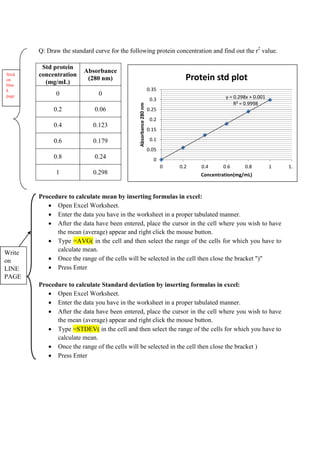
The document discusses graphical representation of data using statistical tools. It describes different types of graphs like bar charts, pie charts, scatter plots, and line charts. It explains how to select the appropriate graph based on the type of data and analyze the data. It also discusses limitations of graphs and statistical analysis methods like calculating mean and standard deviation to analyze data in a robust way.