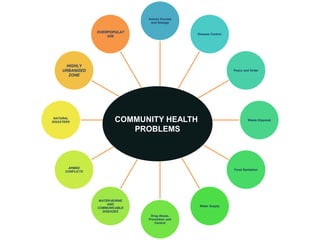
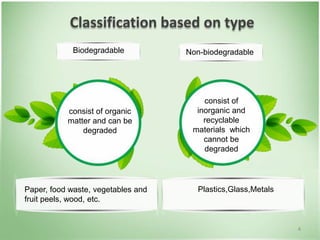
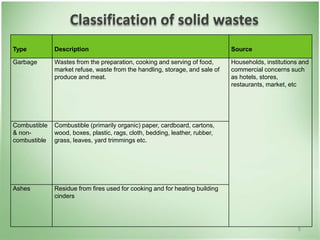
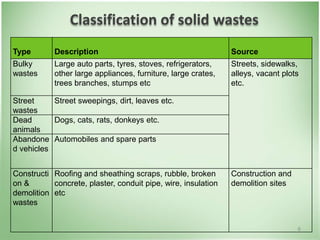
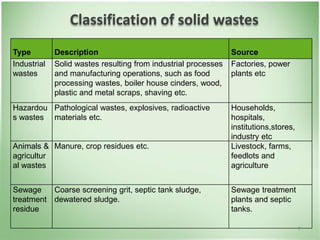
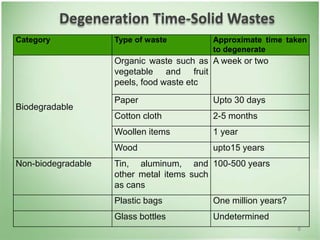
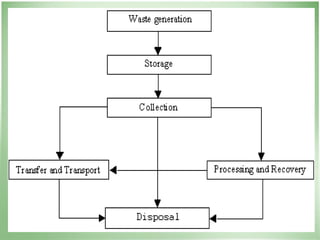
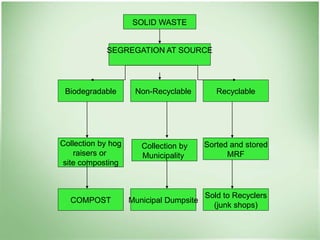
This document discusses community health problems and solid waste management. It begins by listing common community health problems such as human excreta and sewage, disease control, waste disposal, food sanitation, water supply, and drug abuse. It then classifies solid wastes based on whether they are biodegradable or non-biodegradable. Various types of solid wastes are defined and their sources listed. The document concludes by discussing segregating solid waste at its source into biodegradable, non-recyclable, and recyclable categories for appropriate disposal.