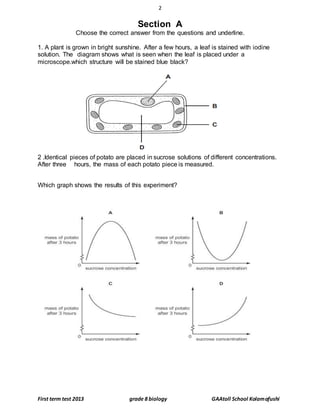
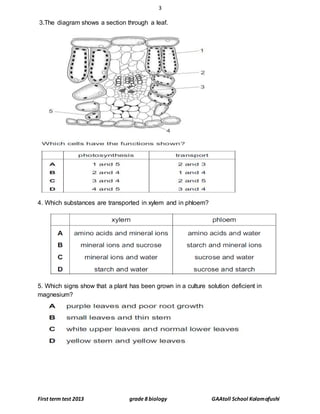
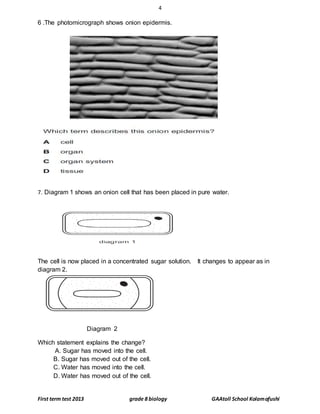
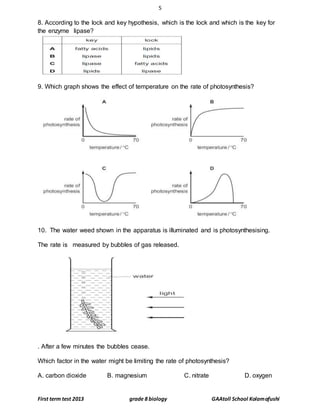
This document contains a biology test for grade 8 students with multiple choice and short answer questions. It tests knowledge of plant and animal cell structure and function, transport processes, photosynthesis, and enzyme action. The test has three sections - multiple choice questions, short answer definitions and explanations, and longer answer questions involving diagrams. Overall, the test examines key concepts in middle school biology.


![11
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
30. .The diagram shows a cell.
Which numbers show the parts named?
Section B
Answer the following questions.
1.which are the types of carbohydrates?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
2.which are the adptations of red blood cell?
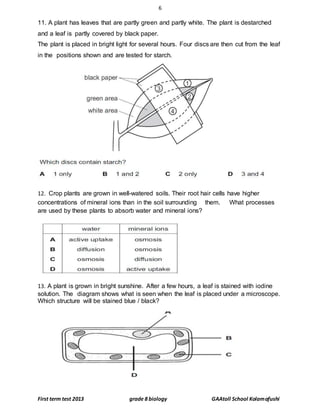
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
3.Define diffusion with example.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
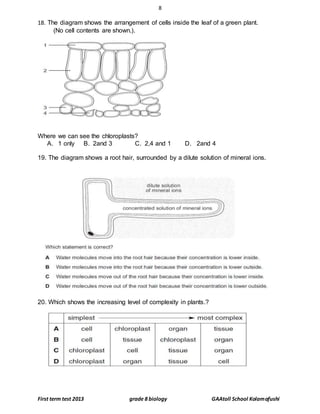
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-11-320.jpg)
![12
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
4. Define osmosis.
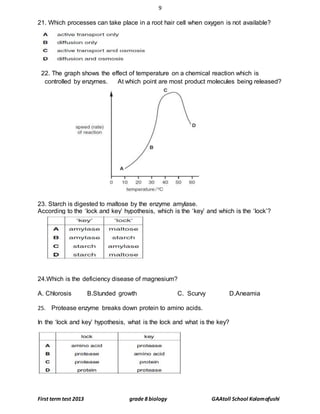
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
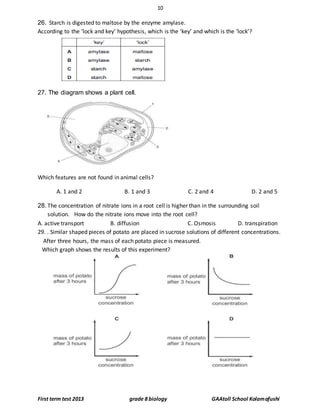
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [2 ]
5. Define active transport with example.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
6. Name different types of cells in your body.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
7.Explain the difference between cell wall and cell membrane?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
8.Which are the major and minor elements?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-12-320.jpg)
![13
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
9. Which are the raw materials of photosynthesis?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
SECTION C
1,Fig. 1.1 shows, in order, four stages in which an enzyme-controlled chemical reaction may
Occur.
Fig 1.1
(a) Identify M, N, O and P.
M .........................................................................
N ..........................................................................
O ..........................................................................
P .......................................................................... [4]
(b) By referring to Fig. 1.1, explain why only a small amount of enzyme is needed to
catalyse a reaction involving many molecules.
....................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) (i) Explain how a rise in temperature may increase the rate of an enzyme-controlled
reaction.
........................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................[ 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-13-320.jpg)
![14
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
(ii) At high temperatures, enzymes are denatured and can no longer act as catalysts.
By using the letters M and N from Fig. 2.1, suggest what happens when an enzyme is
denatured.
..........................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................................[.2]
[Total:10]
2. Fig. 2.1 shows a section through a leaf with only some of the cells drawn.
Fig 2.1
(a) On Fig. 2.1, draw and label in their correct positions:
(i) a palisade mesophyll cell; (ii) a spongy mesophyll cell;
(iii) a pair of guard cells; (iv) a cuticle. [4]
(b) On Fig. 3.1, label and name the tissue bringing water into the leaf.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
(c) Explain how plants are absorbing carbondioxide and water.
.........................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................. …….[3]
(d) Suggest one reason why epidermal cells are important to a leaf.
.........................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................ ………………[1]
[Total:10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-14-320.jpg)
![15
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
3. Fig. 3.1 shows a cell from an organism.
Fig 3.1
(a) (i) In which type of living organism are cells similar to the one shown in Fig. 3.1
normally found?
...............................................................................................................................1]
(ii) State two reasons for your choice of living organism in (i).
1. ...............................................................................................................................
2. ...........................................................................................................................[2
Fig. 3.2(a) shows the same cell after it had been placed in solution A for ten minutes.
The cell was then transferred to solution B and Fig. 3.2(b) shows how it appeared after
a further ten minutes.
3.2(a) 3.2(b)
(b) Explain what has occurred to cause the cell to appear as it does in Fig. 3.2(a).
.........................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-15-320.jpg)
![16
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
(c) Compared with the water potential of the cell, what can be deduced about solutions
Aand B?
solution A .........................................................................................................................
solution B .....................................................................................................................[2]
(d) What will be found in region C in Fig. 1.2(b) at the end of the experiment?
...................................................................................................................................[1]
Explain your answer.
.........................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................[2]
[Total:10]
4.Fig. 4.1 shows the cell membrane of an animal and a plant cell.
Fig 4.1
(a) On Fig. 4.1, draw and label
(i) one other structural feature that is found in both cells,
(ii) two features found in a plant cell but not in an animal cell. [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-16-320.jpg)
![17
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
b) Write down the difference between plant cell and animal cell?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[5]
[Total:10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-17-320.jpg)
![18
First term test 2013 grade 8 biology GAAtoll School Kolamafushi
5. Define a cell? Write down the different type of cells of plants and animals?
List down the importance of chlorophyll and root hair cell to plants?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade8biologyfirstterm2013-copy-150128090927-conversion-gate01/85/Grade-8-biology-first-term-2013-copy-18-320.jpg)