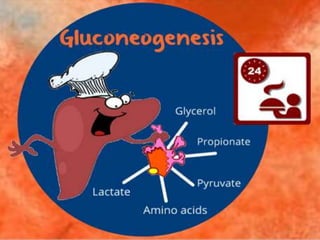
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic process primarily occurring in the liver and kidneys, converting non-carbohydrate substrates into glucose 6-phosphate and ultimately free glucose or glycogen. This pathway consists of several enzymatic reactions that bypass three irreversible steps of glycolysis using specific enzymes, including pyruvate carboxylase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. It plays a crucial role in maintaining blood glucose levels, particularly during fasting, as its failure can lead to severe neurological complications.