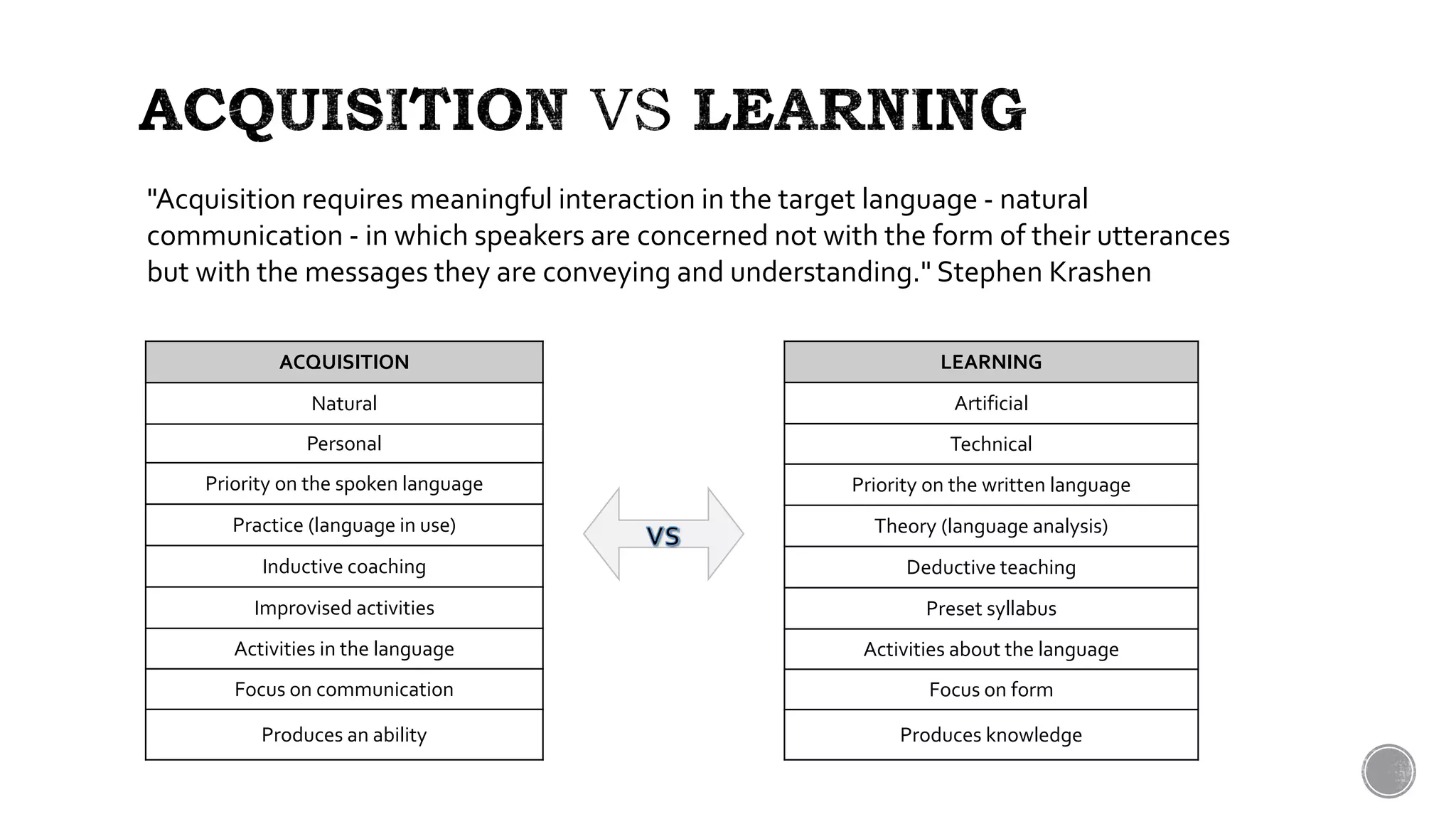
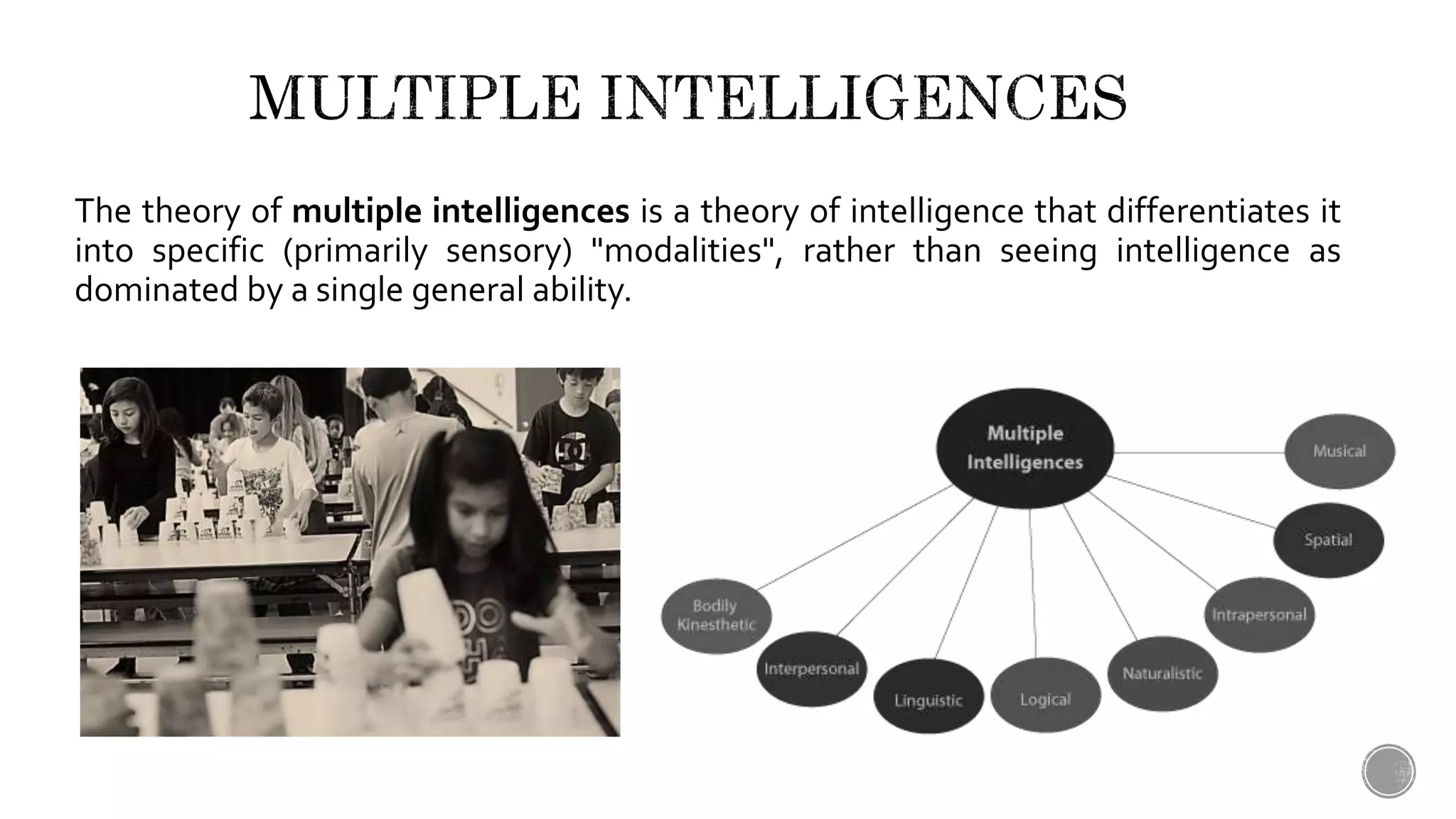
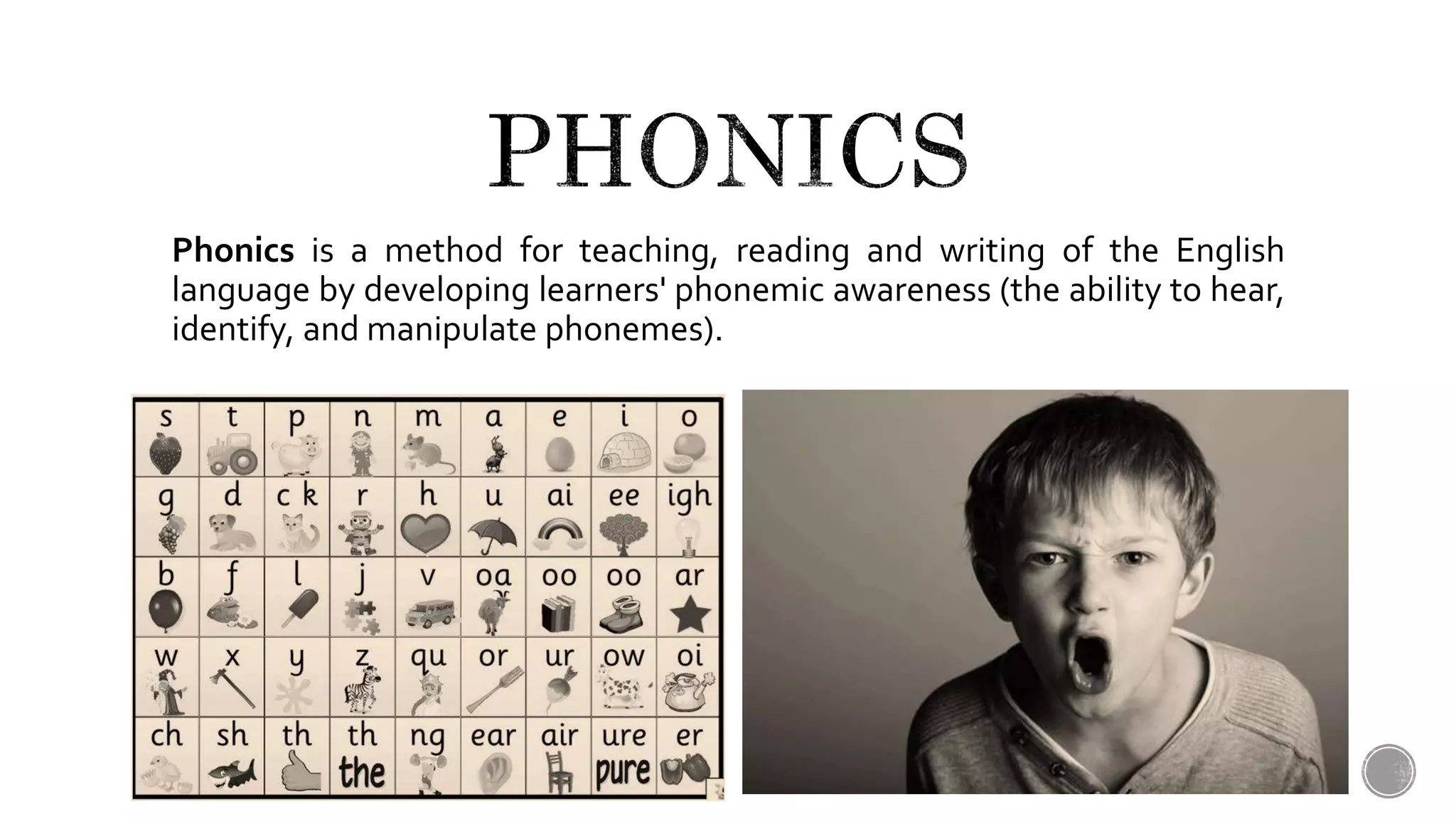
This document provides definitions and explanations of key terms related to language acquisition and teaching approaches. It discusses the differences between acquisition and learning, defining acquisition as a natural process focused on communication and learning as more artificial and focused on language forms. It also defines other important concepts like the critical period hypothesis, digital literacy, English as a foreign/second language, the language acquisition device, mother tongue and target language, multiple intelligences, phonics, the silent period, total physical response teaching, and the zone of proximal development.