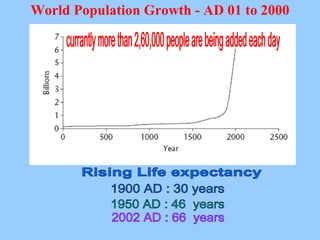
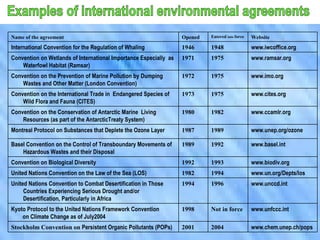
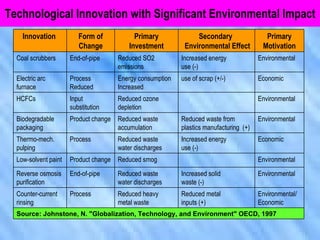
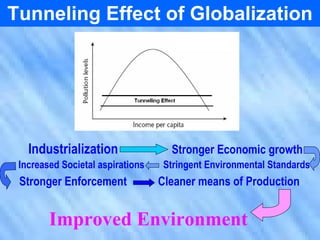
The document discusses the complex relationship between globalization and environmental issues, emphasizing that ecological processes transcend national borders. It highlights various environmental challenges like deforestation, pollution, and biodiversity loss, while stressing the necessity for sustainable development that meets present needs without compromising future generations. The text outlines significant international agreements aimed at addressing these concerns and warns against the uneven environmental burdens placed on developing nations by developed countries.