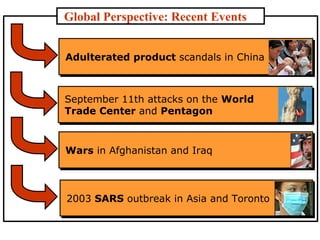
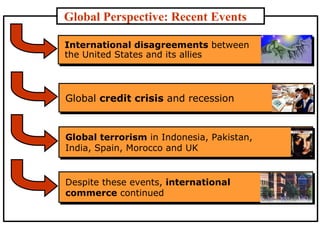
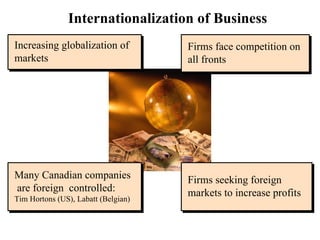
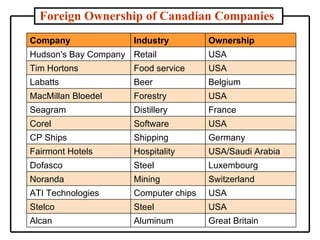
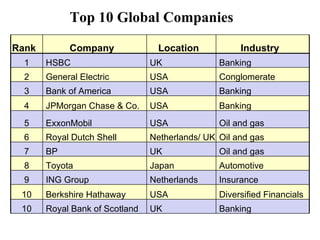
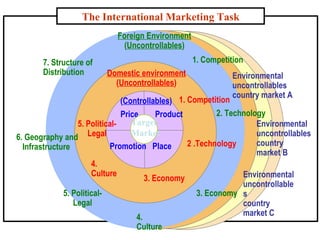
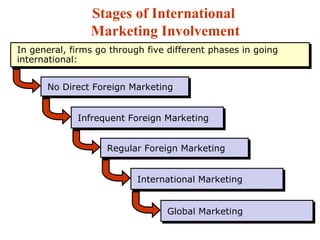
The document discusses the history and modern development of globalization. It begins around 3000 BC with trade links between early civilizations, and continued through periods like the Islamic Golden Age. After World War 2, political planning broke down borders to increase trade and interdependence. Globalization since then has integrated national economies through increased trade, investment, technology sharing, and global institutions like the WTO. Both benefits and criticisms of economic globalization are mentioned.